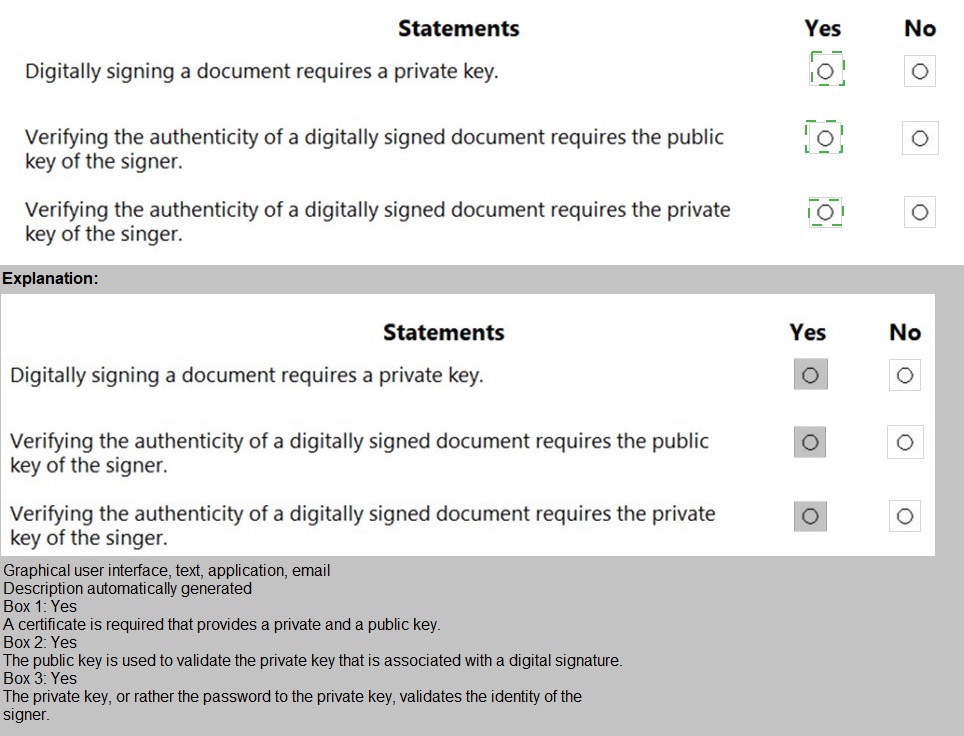
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point
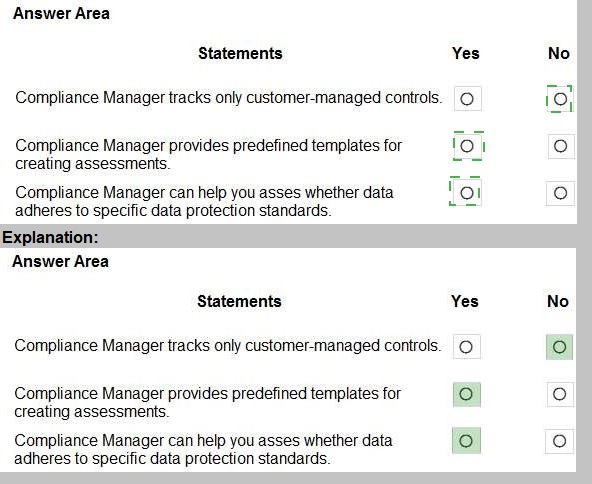
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point
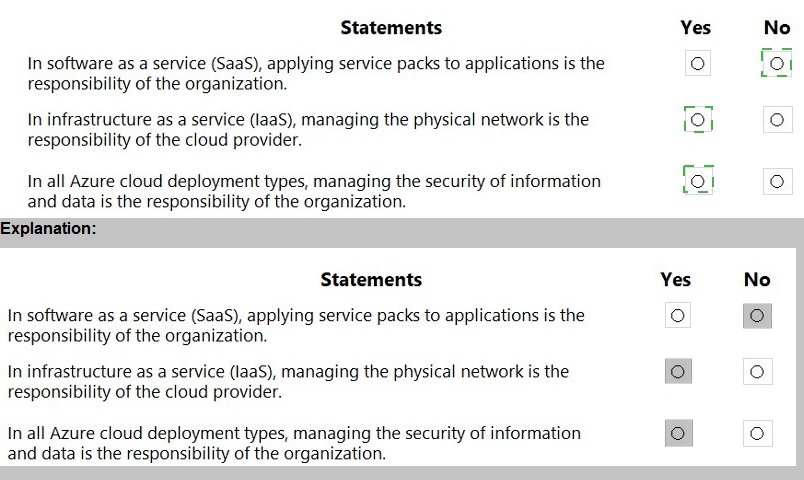
Which Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) feature can you use to provide just-in-time (JIT) access to manage Azure resources?
A. conditional access policies
B. Azure AD Identity Protection
C. Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
D. Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
Explanation:
Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is the service specifically designed to provide Just-In-Time (JIT) administrative access to Azure resources and other privileged roles. Its core principle is to enforce the concept of "least privilege" by ensuring that users are only assigned elevated permissions when they need them, for a limited time, and often with approval requirements.
Key features of PIM that enable JIT access:
Eligible Assignments:
Instead of making a user a permanent Global Administrator, you make them eligible for the role. They must then activate the role when they need to perform a task.
Time-Bound Activation:
When a user activates an eligible role, it is only active for a pre-configured duration (e.g., 2 hours). After this time, the permissions are automatically revoked.
Approval Workflows:
You can require that a designated approver must grant permission before a user can activate their privileged role.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. Conditional Access Policies:
This is a tool that uses signals (like user, device, location) to enforce access controls on applications. For example, it can block access from an untrusted network or require Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). While it can complement PIM by adding another layer of security (e.g., requiring MFA upon role activation), it does not, by itself, provide the JIT provisioning and de-provisioning of administrative roles.
B. Azure AD Identity Protection:
This is a tool for detecting and remediating identity-based risks, such as leaked credentials or impossible travel. It helps protect all users from compromise but is not used to grant temporary, privileged access to resources.
D. Authentication Method Policies:
These policies define the methods available for users to authenticate, such as enabling FIDO2 security keys, the Microsoft Authenticator app, or SMS-based verification. They configure how a user signs in, not what privileged access they get or for how long.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: What is Azure AD Privileged Identity Management? - "Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is a service in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) that enables you to manage, control, and monitor access to important resources in your organization... Just-in-time privileged access to Azure AD and Azure resources.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.
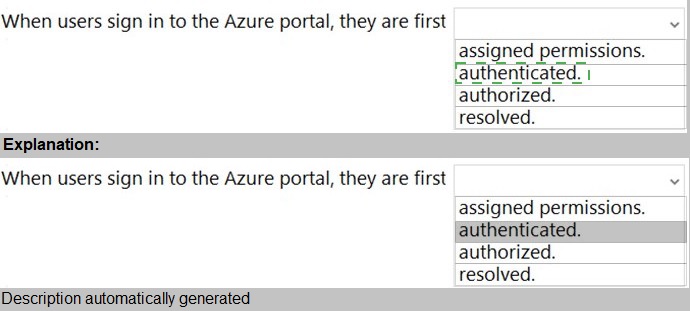
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence
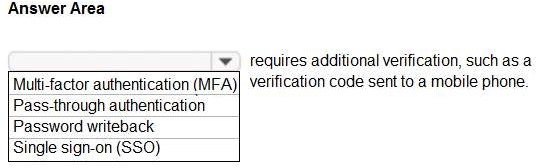

Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence

Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence

For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
In the shared responsibility model for an Azure deployment, what is Microsoft solely responsible for managing?
A. the management of mobile devices
B. the permissions for the user data stored in Azure
C. the creation and management of user accounts
D. the management of the physical hardware
Explanation:
The shared responsibility model is a core concept in cloud computing. It clarifies that security is a joint effort between the cloud provider (Microsoft) and the customer. Microsoft is always responsible for the security of the cloud, meaning the underlying infrastructure. The customer is always responsible for security in the cloud, which refers to anything they put on that infrastructure.
For any Azure service (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), Microsoft is solely responsible for:
The physical data centers
The physical network infrastructure
The physical servers and host hardware
This is a non-negotiable, fixed responsibility that does not change based on the type of deployment.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. the management of mobile devices:
This is a customer responsibility. Managing and securing devices that access corporate data (Mobile Device Management) is handled by the customer, often using services like Microsoft Intune.
B. the permissions for the user data stored in Azure:
This is a customer responsibility. While Microsoft secures the infrastructure where the data resides, the customer is responsible for controlling access to that data through permissions, firewalls, and authentication settings.
C. the creation and management of user accounts:
This is a customer responsibility. Managing identities and user accounts (who has access) is done by the customer within their Azure Active Directory tenant.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Shared responsibility in the cloud - "The provider (Microsoft) is always responsible for the following: Physical hosts, Physical network, Physical datacenters. The customer is always responsible for the following: Data and information, Devices (mobile phones and PCs), User accounts and access."
Which two tasks can you implement by using data loss prevention (DLP) policies in Microsoft 365? Each correct answer presents a complete solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. Display policy tips to users who are about to violate your organization’s policies.
B. Enable disk encryption on endpoints.
C. Protect documents in Microsoft OneDrive that contain sensitive information.
D. Apply security baselines to devices.
Explanation:
Microsoft 365 Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is specifically designed to help you discover, monitor, and protect sensitive information across Microsoft 365 services like Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, OneDrive for Business, and Microsoft Teams.
A. Display policy tips to users:
This is a core feature of DLP. When a user performs an action that would violate a DLP policy (like trying to share a document containing credit card numbers externally), a policy tip can appear in apps like Outlook or OneDrive to warn the user and educate them about the policy, potentially blocking the action.
C. Protect documents in Microsoft OneDrive:
A primary function of DLP is to scan and protect data at rest in locations like OneDrive for Business. You can create policies that automatically detect sensitive information in OneDrive documents and take protective actions, such as restricting access, encrypting the content, or blocking external sharing.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. Enable disk encryption on endpoints:
While Microsoft 365 has tools for endpoint management (like Microsoft Intune), which can enable disk encryption (e.g., BitLocker), this is not a function of a Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policy. DLP focuses on classifying and protecting data based on its content, not on managing device-level security settings.
D. Apply security baselines to devices:
Applying security baselines (pre-configured groups of Windows settings that recommend security configurations) is a function of endpoint security and device management services like Microsoft Intune or the Microsoft 365 security center, not a capability of DLP policies.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Learn about data loss prevention - "A data loss prevention (DLP) policy is made up of rules that allow you to identify and monitor sensitive content across... SharePoint Online, OneDrive for Business... so that you can prevent the accidental sharing of sensitive information." The documentation specifically lists actions like "showing policy tips to users" and "blocking access to the document" as outcomes of a DLP policy.
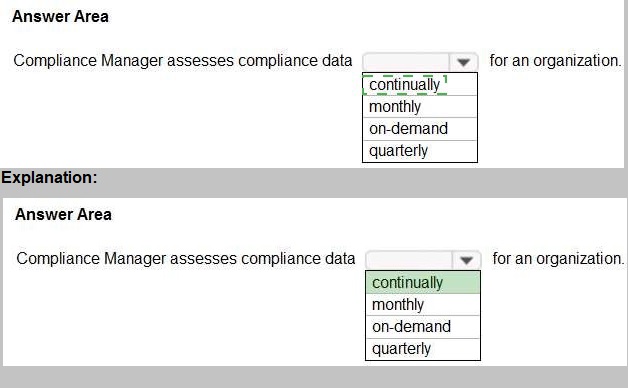
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.
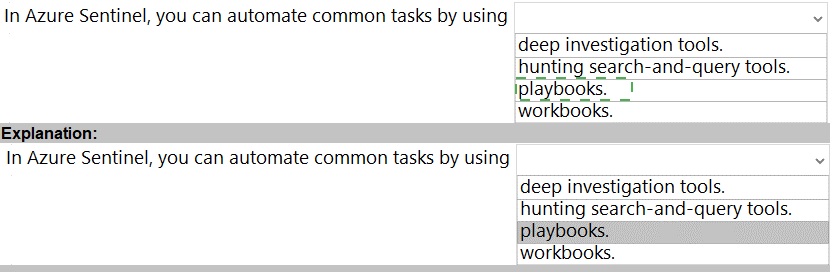
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence

| Page 1 out of 8 Pages |