You plan to implement a security strategy and place multiple layers of defense throughout a network infrastructure. Which security methodology does this represent?
A. threat modeling
B. identity as the security perimeter
C. defense in depth
D. the shared responsibility model
Explanation:
Defense in depth is a security strategy that employs a series of layered, redundant defensive mechanisms to protect valuable data and information. If one layer fails, another layer steps up to prevent an attack. Placing multiple layers of defense throughout a network infrastructure is the very definition of this approach. These layers can include:
Physical security
Perimeter security (firewalls)
Network security (segmentation)
Endpoint security
Application security
Data security (encryption)
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. threat modeling:
This is a structured process for identifying, quantifying, and addressing the security risks associated with an application or system. It's a planning and analysis exercise, not the implementation of layered defenses.
B. identity as the security perimeter:
This is a modern security concept that argues the primary security boundary is no longer the physical network but the user and device identity. While identity controls are a critical layer in a defense-in-depth strategy, this term describes a specific philosophy, not the overarching methodology of multiple layers throughout the infrastructure.
D. the shared responsibility model:
This model clarifies the security responsibilities between a cloud provider (like Microsoft) and the cloud customer. It defines who is responsible for securing what, but it is not the methodology for how to implement those security controls (which is defense in depth).
Reference:
Microsoft Learn:
What is defense in depth? - "Defense in depth is a strategy that employs a series of mechanisms to slow the advance of an attack aimed at acquiring unauthorized access to information." The article goes on to describe the multiple layers used in this approach.
Which feature provides the extended detection and response (XDR) capability of Azure Sentinel?
A. integration with the Microsoft 365 compliance center
B. support for threat hunting
C. integration with Microsoft 365 Defender
D. support for Azure Monitor Workbooks
Explanation:
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is a platform approach that unifies security data from multiple sources (like endpoints, email, identity, and applications) into a single system to improve threat detection, investigation, and response.
Azure Sentinel's integration with Microsoft 365 Defender is what provides its core XDR capability. Microsoft 365 Defender is itself an XDR solution that consolidates signals from Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, Microsoft Defender for Office 365, Microsoft Defender for Identity, and Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps. By connecting this unified XDR platform to the broader SIEM (Azure Sentinel), you extend the visibility and correlation across your entire digital estate, including non-Microsoft data sources.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. integration with the Microsoft 365 compliance center:
This integration is for compliance and data governance management, not for cross-domain security detection and response (XDR).
B. support for threat hunting:
While threat hunting is a critical capability of Azure Sentinel, it is a function that benefits from XDR data but is not the feature that provides the XDR capability itself. Hunting can be done on any data in the SIEM.
D. support for Azure Monitor Workbooks:
Workbooks are tools for data visualization and dashboarding. They are used to present data, including security data, but they do not provide the underlying XDR capability of ingesting and correlating unified signals from multiple security domains.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn:
Microsoft 365 Defender integration with Microsoft Sentinel - "Microsoft 365 Defender integration with Microsoft Sentinel... provides a more consolidated and streamlined experience for Secure XDR (Extended Detection and Response) and SIEM... This integration allows you to... ingest advanced hunting events from M365D into your Microsoft Sentinel workspace."
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select
No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
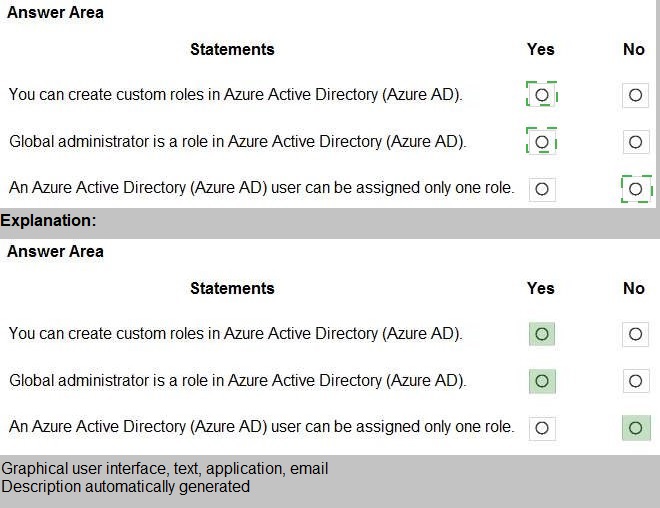
Which Microsoft 365 compliance feature can you use to encrypt content automatically based on specific conditions?
A. Content Search
B. sensitivity labels
C. retention policies
D. eDiscovery
Explanation:
Sensitivity labels in Microsoft 365 are designed to classify and protect sensitive content. A key protection capability is encryption. You can configure a sensitivity label to automatically apply encryption with specific permissions when the label is applied to a document or email.
Conditions for automatic encryption:
You can set rules so that encryption is applied based on conditions you define. For example, you can create a label that automatically encrypts any document containing a credit card number.
User-applied encryption:
Even without automatic conditions, when a user manually applies a sensitivity label that includes encryption settings, the content is encrypted.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. Content Search:
This is a tool within the Purview compliance portal for finding content across Microsoft 365 locations (like Exchange, SharePoint, OneDrive). It is used for discovery and investigation, not for applying protection like encryption.
C. Retention policies:
These policies are used to decide how long to retain content, and whether to delete it after a period. Their purpose is records management and information governance, not encryption. They control the lifecycle of content but do not encrypt it.
D. eDiscovery:
This is a legal workflow tool used to identify, hold, and export content for use as evidence in legal cases. It is a process for finding and preserving information, not for protecting it with encryption.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Apply encryption using sensitivity labels - "You can configure sensitivity labels to apply encryption to email and documents. This encryption protects the content in transit and at rest, and the content remains encrypted in Outlook... as well as in other apps and services." The ability to use "auto-labeling" policies to apply these labels (and their encryption) based on conditions is a core feature.
Which three authentication methods can be used by Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)? Each correct answer presents a complete solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. text message (SMS)
B. Microsoft Authenticator app
C. email verification
D. phone call
E. security question
Explanation:
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a critical security feature within Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory) that requires users to provide two or more forms of verification to access resources. MFA reduces the risk of unauthorized access due to compromised credentials by combining multiple authentication factors such as something you know (password), something you have (mobile device), and something you are (biometric verification).
Microsoft supports several verification options for Azure MFA to ensure users can authenticate securely and conveniently.
1. Text message (SMS) – Correct (Option A)
Azure MFA supports authentication via text messages (SMS) sent to a user’s registered phone number. When a user attempts to sign in, Azure sends a one-time verification code (OTP) via SMS. The user must enter this code correctly to complete authentication. This method is widely used for simplicity and accessibility because it does not require a smartphone or internet access, only a device capable of receiving text messages.
However, while SMS-based MFA provides a second layer of defense, it is less secure than app-based or phone call authentication because SMS messages can be intercepted or redirected through SIM-swapping attacks. Nonetheless, it remains an officially supported and valid method within Azure MFA.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn – Azure AD MFA verification methods
2. Microsoft Authenticator App – Correct (Option B)
The Microsoft Authenticator app is the most secure and recommended method for MFA. It provides two main verification mechanisms:
Push notifications that the user approves with a simple tap.
Time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) generated by the app even without an internet connection.
The Authenticator app leverages strong cryptography and device registration to ensure high assurance. It also supports number matching and location context for additional security, minimizing phishing risks. Because of its strong security posture and ease of use, Microsoft promotes this method as the primary MFA option for enterprise environments.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn – How it works: Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication
3. Phone call – Correct (Option D)
Azure MFA also allows authentication through an automated phone call to the user’s registered number. The system prompts the user to answer the call and press a key to confirm their identity. This method is effective when mobile data or internet connectivity is limited, making it a useful backup to the Microsoft Authenticator app.
While convenient, it is less secure compared to app-based verification because it relies on telephony networks, which can be targeted for social engineering or call interception. Despite that, it remains a fully supported MFA method in Microsoft Entra ID.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn – Azure AD MFA verification methods
4. Email verification – Incorrect (Option C)
Email verification is not supported as an Azure MFA method. Email is only used for password resets or communication, not for multi-factor authentication. The reason is that email relies on username and password, which does not qualify as a “second factor.” Using email would not provide additional assurance because it depends on the same credentials MFA is designed to protect.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn – Authentication methods in Microsoft Entra ID
5. Security question – Incorrect (Option E)
Security questions are also not supported by Azure MFA. They are considered a weak authentication method because answers can often be guessed or obtained through social engineering or public information. Microsoft does not include this method in Azure MFA since it fails to meet modern security standards. Security questions might appear in legacy systems but not in Microsoft Entra MFA.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn – Microsoft Entra authentication methods
Summary
Azure MFA strengthens identity protection by enforcing multiple verification options. The valid methods — SMS (A), Microsoft Authenticator app (B), and Phone call (D) — provide flexible, layered authentication to secure access to Azure and Microsoft 365 resources. Methods like email and security questions are not supported because they do not meet MFA’s security standards.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select
No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
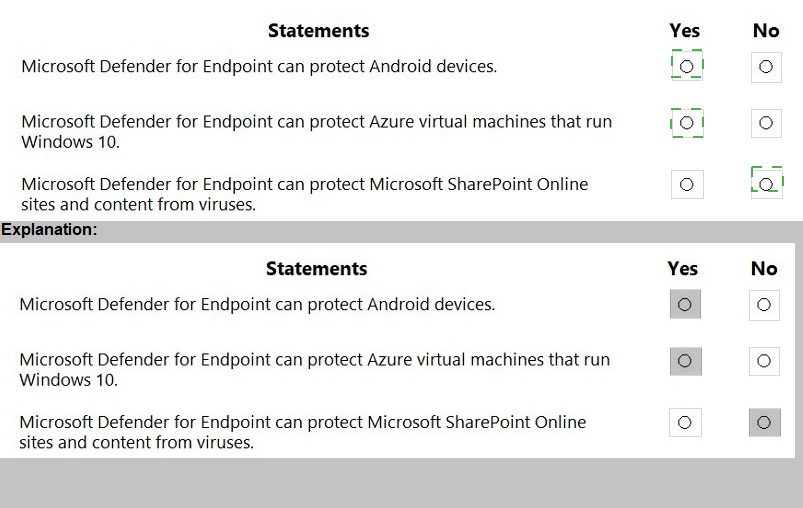
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select
No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point
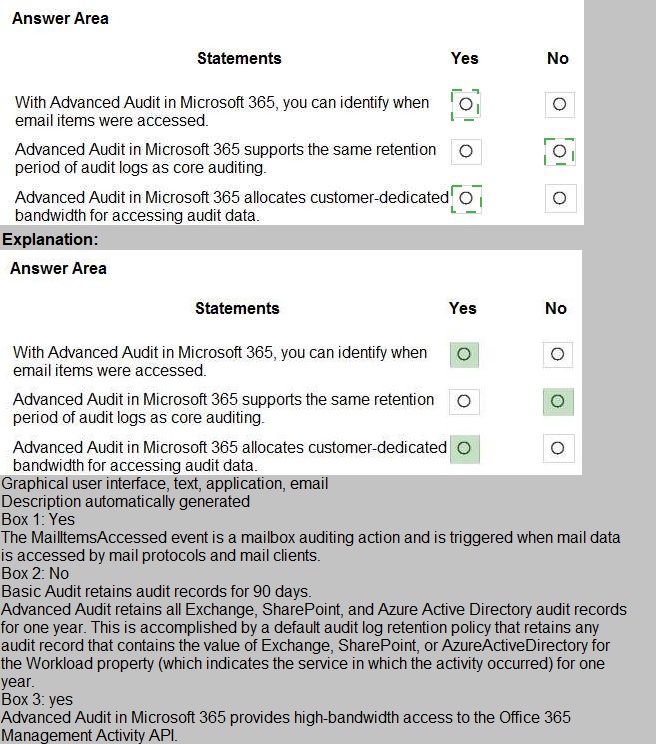
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select
No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
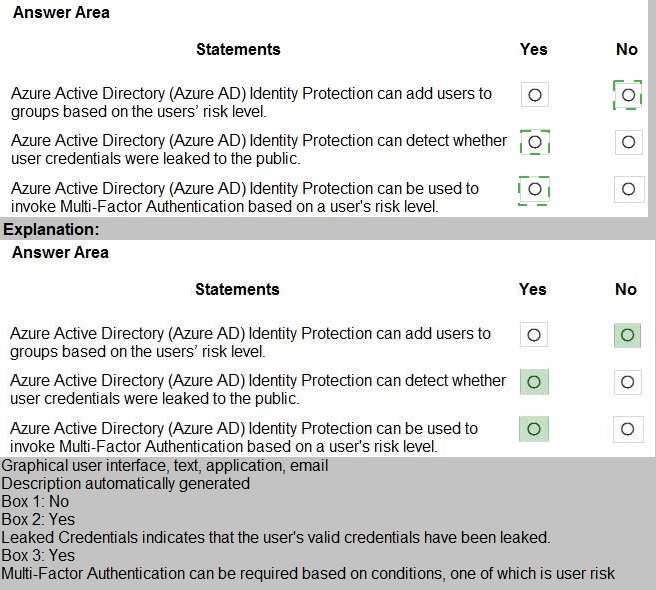
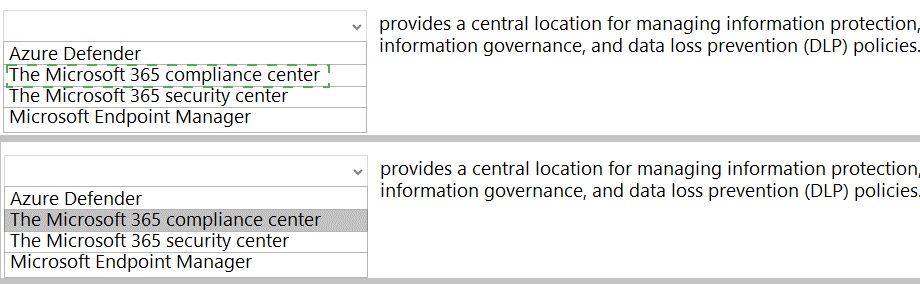
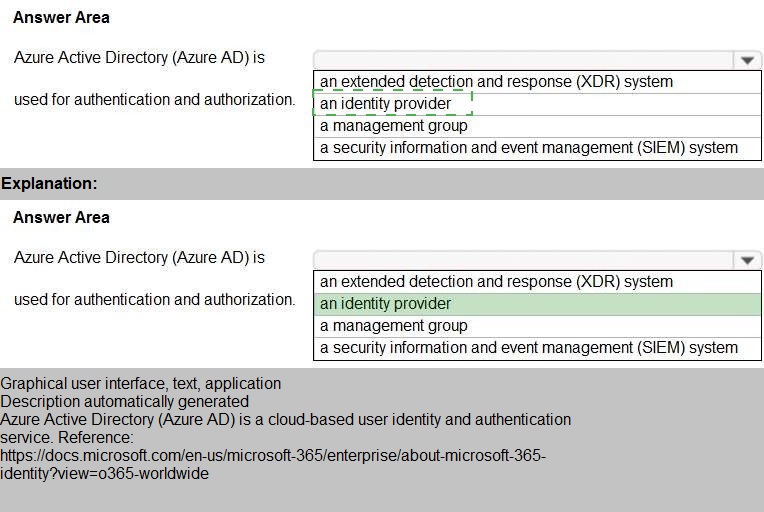
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence
What do you use to provide real-time integration between Azure Sentinel and another security source?
A.
Azure AD Connect
B.
a Log Analytics workspace
C.
Azure Information Protection
D.
a connector
a connector
Explanation:
To on-board Azure Sentinel, you first need to connect to your security sources. Azure
Sentinel comes with a number of connectors for Microsoft solutions, including Microsoft
365 Defender solutions, and Microsoft 365 sources, including Office 365, Azure AD,
Microsoft Defender for Identity, and Microsoft Cloud App Security, etc.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sentinel/overview
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence
| Page 2 out of 8 Pages |
| Previous |