Topic 1: First Up Consulting
Case study
This is a case study. Case studies are not timed separately. You can use as much exam time as you would like to complete each case. However, there may be additional case studies and sections on this exam. You must manage your time to ensure that you are able to complete all questions included on this exam in the time provided.
To answer the questions included in a case study, you will need to reference information that is provided in the case study. Case studies might contain exhibits and other resources that provide more information about the scenario that is described in the case study. Each question is independent of the other questions in this case study. At the end of this case study, a review screen will appear. This screen allows you to review your answers and to make changes before you move to the next section of the exam. After you begin a new section, you cannot return to this section.
To start the case study
To display the first question in this case study, click the Next button. Use the buttons in the left pane to explore the content of the case study before you answer the questions. Clicking these buttons displays information such as business requirements, existing environment, and problem statements. If the case study has an All Information tab, note that the information displayed is identical to the information displayed on the subsequent tabs. When you are ready to answer a question, click the Question button to return to the question.
Background
First Up Consulting recruits information technology (IT) workers for temporary or
permanent positions at client companies. The company operates offices in multiple countries/regions.
First Up has both full-time and part-time employees. The company has a team or worker support agents that respond to inquiries from current and prospective workers. Some of the worker support agents are multilingual.
The company does not have a standardized tool used for reporting purposes. The organization engages you to implement a new Power Platform solution. Workers are managed by a dedicated team that includes one primary recruiter and a contract assistant. Many client companies live in areas that do not allow for mobile data connections.
Current environment:
Existing systems and processes
First Up uses an on-premises system to manage current and historical patient data including medications and medical visits. The company plans to reference historical data in the existing system. The records held in these systems will not be migrated to the new solution except for medication information.
Employee authentication with the existing system is provided by an on-premises
Active Directory instance that is linked to Azure Active Directory. An appointment record is created for each visit with a worker. The record includes
worker contact information, preferred language, the date and time of the
appointment, and other relevant data. This information is reviewed by the worker’s primary recruiter.
First Up has no current capabilities for forecasting future worker needs based on the data held.
Client company visits
Before First Up signs a contract to place workers at a client company, a member of the audit team visits the company and interviews company management. Audit members use different types of devices including Android and iOS devices. First Up has no plans to require the use of a single type of device. Audit team members currently record information about workers on paper forms. Team members enter information from paper forms into the
system when they return to the office.
First Up audits client companies at least once each year but may schedule additional visits based on feedback from workers that they place at a client company.
Requirements
General
There is no standardized communication tool across the company, and this causes communication issues between different teams. First up employees must be able to contact each other by using a secure system to ask and answer questions about medical cases. Workers must be able to communicate in near real-time with worker support agents
.
Client company visits
Audit team records must be locked after they have been reviewed by a First Up
manager. No further edits to the record can be carried out. This must be
implemented using standard available system functionality. Audit teams must be able to enter records of their visits to the companies where they have or may place workers. Audit teams must be able to update any necessary records with the latest information. The solution must support tracking of security clearance information for a worker including the date, status, and certifying agency.
When a worker makes an appointment, the appointments must appear in the
timeline for the worker’s contact record.
Job history information
The solution must provide a worker appointment booking system that can access worker historical job placement data. The solution must allow employees to associate a primary recruiter with each worker. The solution must also allow multiple secondary recruiters to be associated with each worker.
Every worker assessment performed must be validated and countersigned by the primary recruiter for a worker.
Job posting data from previous work engagements must be accessible by the
Power Platform solution to ensure that new job postings are accurate.
First Up staff members must be able to view and update worker records. They
must be able to see current and historical job placement data on the same form in the new solution.
Worker access
The solution must support workers that speak different languages. The solution
must provide automatic translation capabilities.
The solution must support near real-time communications between workers and
recruiters.
Workers must be able to view their records online. Workers must be able to enter
any additional information that is required by or may be helpful to recruiters.
The solution must provide workers a way to search for general information about
available positions.
Workers must be able to request copies of their records by using a chatbot.
Workers must be able to provide information to a recruiter as needed.
Data platform
Audit teams must have the ability to view worker information on their mobile
devices.
Audit teams must be able to record data during visits to locations where workers
are placed.
The solution must support the ability for a corporate governance auditing team to
periodically audit the organization’s records, policies, and procedures.
Reporting and analytics
The reporting and analytics team must be able to create reports that include data
from all facilities and all workers.
Management reports must present an overview of the entire organization. Other
reports may be limited to specific offices.
You must create dashboards that show the status across all groups of workers.
The dashboards must be embedded into the Power Platform apps. Updates to
data must be displayed in near real time.
Security
Authentication for all user types must be managed by a single platform. IT teams
must use PowerShell to apply security permissions for users.
Worker records must only be viewed by the recruiting office that the worker visits.
Worker still records must be archived after ten years and are then removed from the main system. Worker information must not be deleted from the system while
skill and job placement history records for the worker exist in the system.
User security roles must be customized to ensure that users are able to interact
only with the specific data in which they need access.
Workers must be able to sign into a portal by using their own email address.
Workers must be required to use a secure method of authentication to be able to
view their data.
Alerts regarding the number of recruited and placed at client companies must be
updated as background processes.
Issues
The organization reports the following issues:
Recruiters report that they cannot see historical job placement data for workers.
API usage reports show that the number of API calls made exceeds limits. This
causes delays saving data.
Users cannot view Power BI reports within the Power Platform apps.
Some security clearance information for workers not visible from within the Power
Platform solution.
Audit teams report that they cannot view or edit worker data when the device on
which they access the solution does not have network connectivity.
The testing ream reports that one of the canvas apps is not working as expected.
An error message displays as specific pages load.
You need to investigate the canvas app functionality issues.
Which two tools can you use? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. App checker
B. Errors function
C. Solution checker
D. Power Platform admin center
Explanation:
When investigating functionality issues in a canvas app, you need tools that can analyze the app's logic, connections, and structure for problems. The App Checker and Solution Checker are built-in diagnostic tools designed for this purpose. They scan for known issues, performance problems, and non-best practices that could cause unexpected behavior, providing detailed reports to guide troubleshooting.
Correct Option:
A. App checker:
This is a tool within Power Apps Studio. It scans the specific canvas app you are editing for issues like invalid formulas, connectivity problems, or performance anti-patterns. It provides a detailed list of errors and warnings directly in the development environment, making it the first line of defense for app-specific functionality issues.
C. Solution checker:
This tool runs a broader validation on the entire solution that contains your app. It uses a set of rules to check for problems across all solution components (apps, flows, custom connectors, etc.) and their dependencies. It is crucial for identifying issues that may arise from interactions between components before deployment.
Incorrect Option:
B. Errors function:
This is a Power Fx function used within an app's formula to capture and display error information at runtime (e.g., Errors(DataSource)). It is a reactive debugging aid for end-users or creators, not a proactive investigative or diagnostic tool for analyzing the app's overall functionality.
D. Power Platform admin center:
This is the administrative portal for managing environments, policies, user licenses, and analytics. While it can show high-level error analytics and deployment histories, it does not contain a dedicated tool to deeply investigate the internal functionality or logic issues of a specific canvas app.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "How to use App Checker" and "Use solution checker to validate your solutions" outlines the purpose of these tools for diagnosing issues in apps and solutions.
You need to recommend a solution for handling data entry requirements for the mobile
audit teams.
What are two possible ways to achieve the goal? Each correct answer presents a complete
solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. Canvas app within Power Apps Player
B. Canvas app within a browser
C. Dynamics 365 Field Service
D. Dynamics 365 App for Outlook
Explanation:
The core requirement is a mobile-friendly data entry solution for audit teams. The fundamental need is a canvas app, as it provides a flexible, custom interface optimized for mobile devices. The decision point is how to deliver and run that app. Both installing it via the Power Apps mobile app (Player) and accessing it through a mobile browser are valid, native methods for running a canvas app on a mobile device.
Correct Option:
A. Canvas app within Power Apps Player:
This involves publishing the canvas app and having users install the Power Apps mobile application (the "Player") on their iOS or Android devices. This provides a native mobile experience, supports offline capability, and allows access to device features like the camera, GPS, and barcode scanner, which are often critical for audit work.
B. Canvas app within a browser:
The canvas app can be accessed directly via a URL on the mobile device's web browser (like Chrome or Edge). This is a "zero-install" approach, ideal for quick access or on shared devices. Modern canvas apps are responsive and render effectively in mobile browsers, providing full functionality without a separate app installation.
Incorrect Option:
C. Dynamics 365 Field Service:
This is a specific, licensed application designed for managing service jobs, scheduling, inventory, and technicians. While it involves mobile workers, it is a pre-built solution for field service operations, not a general-purpose tool for building a custom data entry app for an unspecified audit process. It is over-prescriptive for the stated goal.
D. Dynamics 365 App for Outlook:
This is an Outlook integration add-in that allows users to view and interact with Dynamics 365 records (like accounts or contacts) directly within their Outlook desktop or web client. It is designed for productivity within email, not for mobile field data collection by audit teams.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "Power Apps Mobile" and "Run canvas apps in a web browser" details these as the primary methods for running apps. The "Power Apps Mobile" app is frequently referred to as the "player" in older documentation.
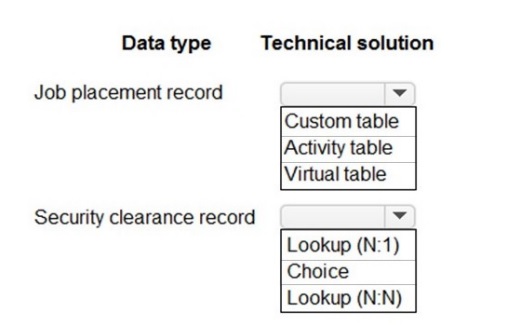
You need to design tables for the solution.
What should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation:
The design must use standard Dataverse capabilities to model business data with proper relationships. Core business records are stored in custom tables, while certain specialized functionalities are best served by built-in table types. Relationships are chosen based on cardinality: a standard lookup for a single parent record (N:1) or a many-to-many junction (N:N) for complex affiliations.
Correct Matching:
Job placement record: A core, custom business entity.
Table Type: Custom Table
Explanation:
A "Job placement record" is a unique business entity central to the solution's operations. It requires its own custom table with tailored columns to store all relevant data (e.g., placement date, candidate, position).
Relationship Type: Lookup (N:1)
Explanation:
A job placement would typically relate to one candidate and one job opening. These are classic "many placements can link to one candidate" relationships, best modeled with a Lookup (N:1) field.
Security clearance record: A record tied to an individual and their status.
Table Type: Custom Table (or potentially part of a related table, but standalone is common)
Explanation:
Security clearance is distinct data with its own lifecycle (issue date, level, expiry). It merits a custom table to manage it properly, which can then be linked to a Candidate or Contact table.
Relationship Type: Lookup (N:1) or Choice
Explanation:
The level of clearance (e.g., Confidential, Secret) is best stored as a Choice column (dropdown). The link to a person would be a Lookup (N:1) to a Contact table (one person can have one primary clearance record).
Technical solution: A method of integrating external data.
Table Type: Virtual Table
Explanation:
The term "Technical solution" in this context often refers to accessing data from an external system (like an HR database). A Virtual Table (also known as a Virtual Entity) is the correct Dataverse feature for representing external data without physically storing it in Dataverse.
Relationship Type: Lookup (N:1)
Explanation:
A virtual table can be the target of a standard Lookup (N:1) relationship, allowing a custom table (like Job Placement) to reference a record from the external system.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
Activity Table:
Used for tasks, emails, phone calls, or appointments. Job placements and security clearances are not activities but core data records.
Lookup (N:N):
Used for many-to-many relationships, like linking multiple skills to multiple candidates. The described relationships (placement to candidate/job) are typically many-to-one.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "Table types" and "Create and edit relationships" details the use cases for Custom tables, Virtual tables, and the different relationship types (N:1, N:N).
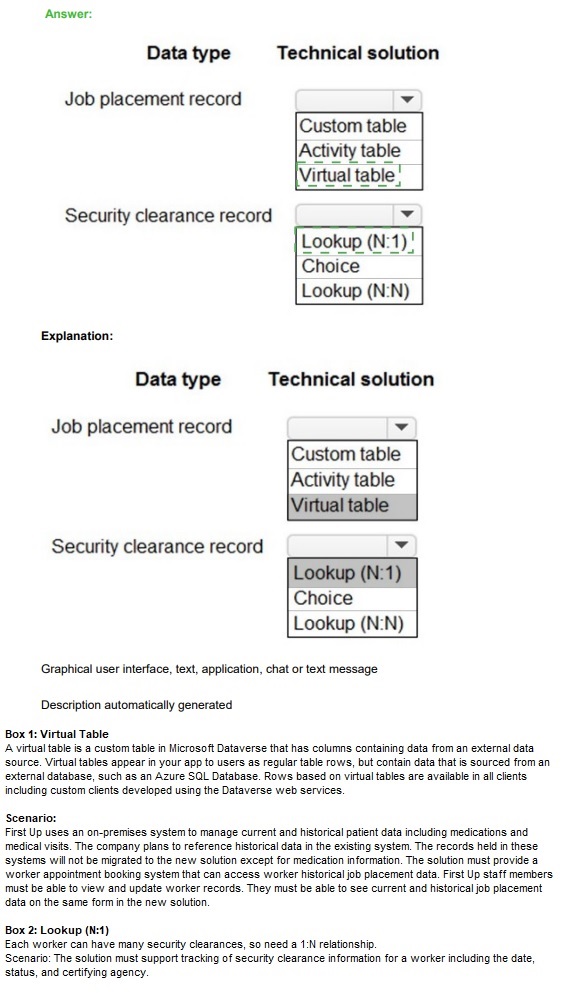
You need to recommend methods for assigning security to each group of users.
What should you recommend? To answer, drag the appropriate methods to the correct groups of users. Each method may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation:
Security in the Power Platform is assigned by associating Dataverse security roles with specific principals. The correct method depends on whether the principal is a specific user, a team, or a non-human service principal. Teams are the primary mechanism for grouping users and bulk-assigning roles.
Correct Matching:
Outcome Application User: This is an individual, functional user account.
Recommended Method: Power Platform Local Business Owner Team
Explanation:
While a specific user account, the most manageable and recommended practice is to add individual application users (like service accounts) to a dedicated Team (e.g., "App User Team") and assign the security role to that team. This simplifies management and follows the principle of least privilege via team-based role assignment.
Group of users (Full-time employees): This is a large, defined group of internal users.
Recommended Method: Power Platform Local Business Owner Team
Explanation:
For a defined group like all full-time employees, the correct approach is to create an Azure AD security group, synchronize it to Dataverse as a Team (Owner team type), and assign the required security role to this team. All members then inherit the permissions.
Name Active Directory (AD) Guest Access (Agent AD Security Group Team, Corporate auditing team): This describes external users (guests) grouped in an AD security group.
Recommended Method: Power Platform Local Business Owner Team
Explanation:
This scenario explicitly describes an "Active Directory Security Group Team." For external guest users, you create an Azure AD security group containing the guest users, sync it to Dataverse as a Team, and assign roles to that team. This is the standard method for managing external collaborator access.
Why "Automation" is Incorrect:
Automation:
This is not a standard security assignment method for user groups. "Automation" typically refers to a Service Principal used for server-to-server authentication (e.g., for an Azure Function). It is assigned a security role directly, not used to manage groups of human users. It does not apply to the listed human user groups.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "Security roles and privileges" and "Use teams to organize users" establishes that Teams (especially Owner teams synced from Azure AD groups) are the primary mechanism for grouping users and assigning security roles in bulk. The "Manage security, users, and teams" learning path covers this as a core concept.
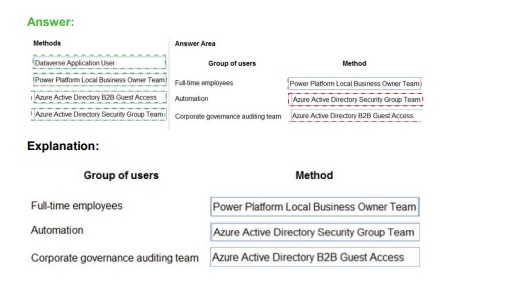
You need to recommend methods to resolve the organization’s issues.
What should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
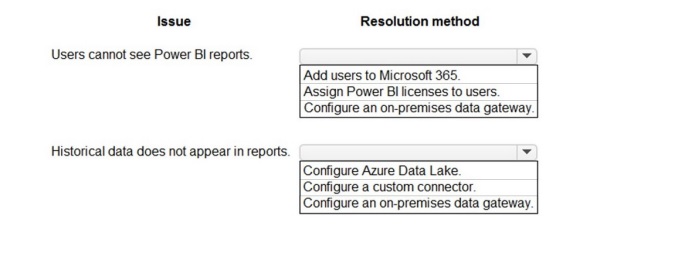
 Explanation:
Explanation:
The resolution must address the root cause. Visibility issues are typically related to user identity, licensing, or data access permissions. Missing historical data often points to a connectivity problem between Power BI and the on-premises data source where that history is stored.
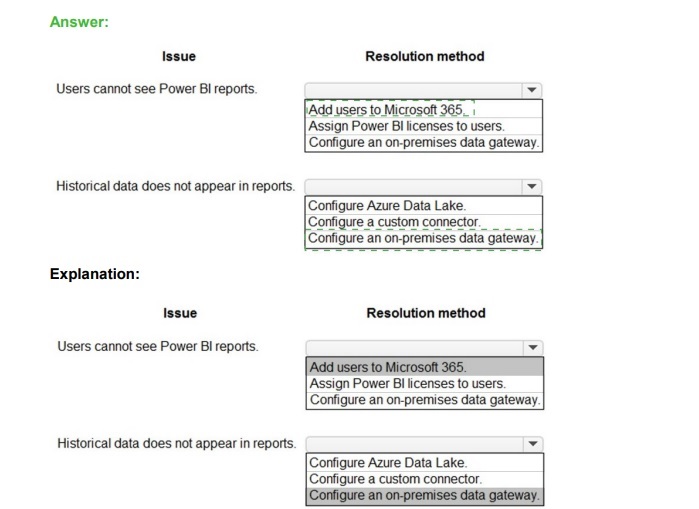
Correct Matching:
Issue: Users cannot see Power BI reports.
Resolution: Assign Power BI licenses to users.
Explanation:
A user must have an appropriate Power BI license (Free, Pro, or PPU) assigned to their account to consume published Power BI content (dashboards, apps). Adding them to Microsoft 365 alone is insufficient without the specific service license. This is the most direct resolution for this access issue.
Issue: Historical data does not appear in reports.
Resolution: Configure an on-premises data gateway.
Explanation:
If reports are built from on-premises data sources (like SQL Server), historical data resides there. For Power BI cloud service to refresh and access this on-premises data, a secure connection via the On-premises Data Gateway must be configured and the dataset's refresh settings must use it.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect for These Issues:
Add users to Microsoft 365:
This is a prerequisite for having an identity but does not grant Power BI service access. A user must also be assigned a Power BI license.
Configure Azure Data Lake:
This is a data storage solution. It is not a resolution for missing historical data unless the explicit problem was the lack of a data lake to store that history, which is not stated.
Configure a custom connector:
This is for connecting to proprietary or niche APIs/data sources. It does not resolve a generic issue of missing historical data from a standard source like a database.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "Power BI licensing" and "What is an on-premises data gateway?" directly addresses these scenarios. Licensing is required for user access, and the gateway is the bridge for cloud services to access on-premises data for refresh.
You need to recommend solutions for the organization’s technical challenges.
What should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
 Explanation:
Explanation:
The solution must map the business requirement to the appropriate Microsoft cloud service. Self-service applications require an automation tool and an identity solution for external users. Planning routes is a core function of field service management.
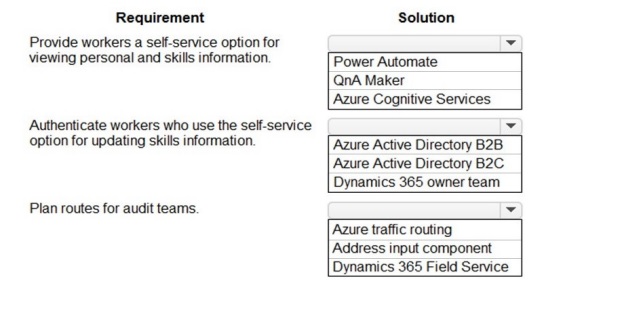
Correct Matching:
Requirement: Provide workers a self-service option for viewing personal and skills information.
Solution from Group 1: Power Automate
Explanation:
A self-service portal can be built with Power Apps. Power Automate is used to create the backend workflows that trigger when a worker submits information (e.g., a skills update request), automating approval processes, notifications, and data updates between systems without manual intervention.
Requirement: Authenticate workers who use the self-service option for updating skills information.
Solution from Group 2: Azure Active Directory B2C
Explanation:
"Workers" likely includes a large, external user base (not just employees). Azure AD B2C is a customer identity and access management solution designed specifically for authenticating external users (like workers, customers, or partners) in self-service applications, providing secure sign-up, sign-in, and profile management.
Requirement: Plan routes for audit teams.
Solution from Group 3: Dynamics 365 Field Service
Explanation:
Dynamics 365 Field Service includes sophisticated scheduling and route planning & optimization capabilities. It is designed to efficiently schedule resources (like audit teams) to locations (audit sites), optimize travel routes, and manage the entire field service lifecycle, making it the ideal fit for this business need.
Why Other Key Options Are Incorrect:
Group 2 - Azure AD B2B:
Best for collaborating with individual, identified users from other organizations (like specific partner employees). B2C is better for a large, scalable population of unidentified external users (workers) who need to self-register.
Group 3 - Address input component / Azure traffic routing:
An address component is just a UI control for entering an address. Azure traffic routing manages network traffic, not physical logistics. Neither provides the business logic for planning and optimizing audit team schedules and travel routes.
Group 1 - QnA Maker / Cognitive Services:
These are for building conversational AI (chatbots) and adding AI capabilities like vision or language understanding, not for creating the core automation logic of a self-service application.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "Power Automate overview," "What is Azure AD B2C?", and "Dynamics 365 Field Service overview" defines the primary use cases for these services: automation, external identity management, and field workforce management, respectively.
You need to recommend technology for accessing historical job placement data. What should you recommend?
A. Power Virtual Agents chatbots
B. Virtual tables
C. Power Bl
D. Power Automate flows
Explanation:
Accessing "historical job placement data" implies the data exists in an external system or legacy database, not natively within Dataverse. The core requirement is to make this external data viewable and usable within the Power Apps or Dynamics 365 context without complex, custom integration code for every interaction.
Correct Option:
B. Virtual tables
A Virtual Table (Virtual Entity) is a Dataverse table type that represents data stored in an external system (like an old SQL Server database). It allows you to surface the external historical data within Dataverse, making it appear as a native table. Users and apps can then interact with this data (view, filter, relate) in a familiar way without needing to know the underlying data source or manage data migration/duplication.
Incorrect Option:
A. Power Virtual Agents chatbots:
This is a service for building conversational AI chatbots. While a chatbot could be programmed to fetch and display data from an external API, it is not a direct data access or integration technology. It is an interface layer built on top of other data access methods.
C. Power BI:
This is a business analytics and visualization tool. It is excellent for reporting on historical data through dashboards, but it is not designed for transactional access, data entry, or integrating external records directly into the business process apps (like a Canvas or Model-driven app) as "table" data.
D. Power Automate flows:
This is an automation and integration service. A flow could be triggered to fetch historical data on-demand via an API and return it. However, this provides a point-in-time, procedural data fetch, not a persistent, relational data model that can be browsed, related to other tables, or used seamlessly within app forms and views like a native table.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "Virtual tables (Virtual Entities)" states their primary use case is to integrate data from external sources into Dataverse, making it available within the Common Data Service without data duplication, which fits the historical data access requirement precisely.
You need to recommend a reporting solution for the organization.
Which two options should you recommend? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. AI Builder
B. SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS)
C. Dynamics 365
D. Power BI
Explanation:
The PL-600 exam focuses on implementing solutions with the Power Platform and Dynamics 365. When recommending a reporting solution in this context, the goal is to provide tools for creating, viewing, and sharing analytical insights from business data, especially data within Dataverse or Dynamics 365. The solutions should be cloud-oriented, integrated, and support self-service analytics.
Correct Option:
D. Power BI
Power BI is Microsoft's flagship cloud-based business analytics service. It is natively integrated with the Power Platform and Dynamics 365. It enables the creation of interactive dashboards and reports from Dataverse and other data sources. It is the primary, modern tool recommended for self-service and enterprise reporting within the Microsoft ecosystem.
C. Dynamics 365
Dynamics 365 applications (like Sales, Customer Service) contain embedded, out-of-the-box reports and dashboards. These are built-in analytics that provide immediate insights into operational data (e.g., sales pipelines, service cases) without requiring a separate reporting project. This is a complete, ready-to-use reporting solution for users within the Dynamics 365 apps.
Incorrect Option / Why B is not the best primary recommendation:
A. AI Builder:
This is a tool for adding artificial intelligence models (like form processing, object detection, prediction) into apps and flows. It is not a reporting or data visualization tool. Its purpose is automation and insight extraction, not creating traditional reports.
B. SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS):
While SSRS is a robust, on-premises paginated reporting tool, it is not the primary cloud-focused solution emphasized in the Power Platform. SSRS requires significant infrastructure and development effort. For a PL-600 exam question asking for a general recommendation for an organization using Power Platform/Dynamics 365, the modern answers are Power BI and the built-in Dynamics 365 analytics. SSRS would only be recommended in very specific legacy or regulatory paginated report scenarios, which the question does not mention.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "Power BI" and "Analytics in Dynamics 365" establishes these as the core reporting and analytics solutions. The PL-600 exam guide focuses on Power Platform analytics, which centers on Power BI and embedded Dynamics 365 insights.
You need to ensure that the solution meets the data security and compliance requirements.
What should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation:
Relationship behaviors in Dataverse control what happens to related child records when a parent record's owner changes (Assign) or when a parent record is deleted (Delete). The correct setting depends on business rules and compliance needs, such as preserving audit history.
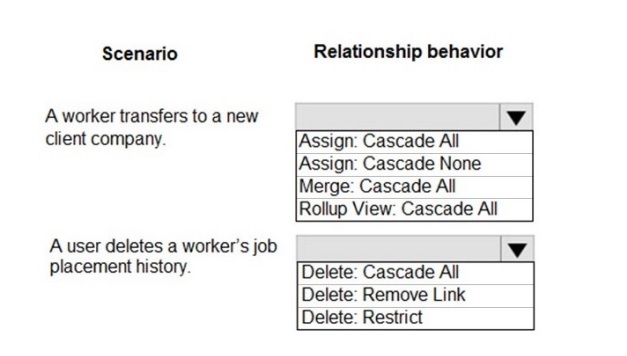
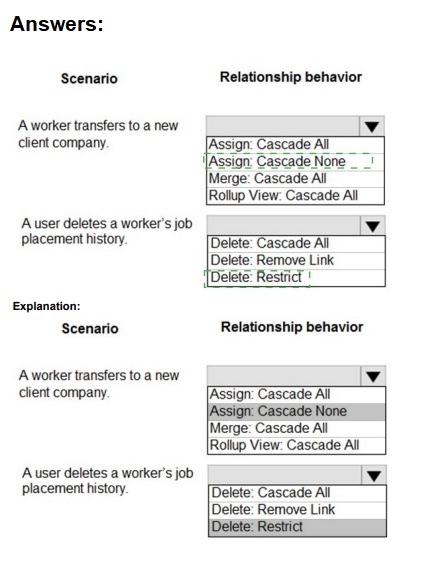
Correct Matching:
Scenario: A worker transfers to a new client company.
Behavior: Assign: Cascade All
Explanation:
This is an ownership reassignment (Assign) scenario. When the worker (parent/user record) is reassigned to a new business unit or owner ("new client company"), Cascade All ensures all their related child records (like active job placements, tasks) are also reassigned to the same new owner/team. This maintains data access integrity under the new context.
Scenario: A user deletes a worker’s job placement history.
Behavior: Delete: Restrict
Explanation:
For compliance, historical records should not be easily deleted. Delete: Restrict prevents a user from deleting the worker (parent) record if any related job placement history (child) records exist. This enforces data integrity and compliance by forcing the user to address or archive the history first, preventing accidental or unauthorized loss of audit trails.
Why Other Key Options Are Incorrect:
For Scenario 1 (Assign):
Assign:
Cascade None would leave the child records (placements) with the original owner, causing orphaned records and access issues for the new team managing the worker.
Merge and Rollup View behaviors are not triggered by a simple ownership reassignment.
For Scenario 2 (Delete):
Delete:
Cascade All would automatically delete all related job placement history when the worker is deleted, which violates the compliance requirement to preserve history.
Delete:
Remove Link would set the lookup field on the child records to blank (null), severing the relationship but keeping the child records. This is less secure than Restrict for compliance, as it still allows the parent deletion and creates unlinked, ambiguous historical data.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "Configure relationship behavior" defines these specific behaviors: Cascade All for Assign propagates ownership changes, and Restrict for Delete prevents deletion when related records exist, which is a standard pattern for enforcing referential integrity and audit compliance.
You need to recommend solutions to meet the organization’s communication needs.
What should you recommend? To answer, drag the appropriate technologies to the correct groups of users. Each technology may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

 Explanation:
Explanation:
The choice depends on whether the communication need is for internal collaboration or external, self-service interaction. Internal staff benefit from a unified hub for chat, meetings, and calls. External users need a secure, branded web portal for information and limited interaction.
Correct Matching:
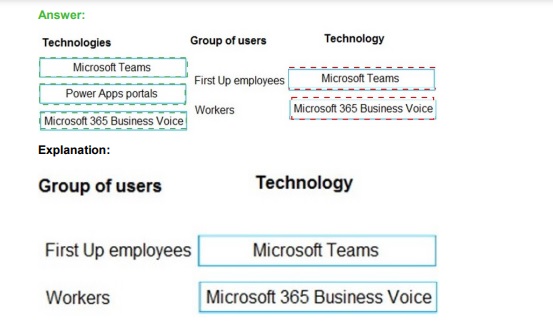
Group: First Up employees (Internal Staff)
Recommended Technology: Microsoft Teams
Explanation:
Microsoft Teams is the primary internal collaboration and communication hub for organizations. It integrates chat, meetings, calling (potentially powered by Business Voice), file sharing, and app integration. It is the definitive solution for day-to-day communication and collaboration needs among internal employees.
Group: Workers (External/Contract Workers)
Recommended Technology: Power Apps portals
Explanation:
Power Apps portals create external-facing, secure websites that allow users outside the organization (like contractors, field workers, or partners) to interact with business data. Workers can use it to view schedules, submit timesheets, access policies, or communicate via a secure, branded interface without needing internal system access or a Teams license.
Why the Other Technology is Not the Best Direct Match:
Microsoft 365 Business Voice:
This is a cloud-based phone system add-on for Microsoft 365. It provides calling plans, a business phone number, and call routing/management. While it can enhance the calling capabilities within Microsoft Teams, it is not a standalone communication "solution" to drag to a user group. It is an enabling technology for the phone features within Teams. Therefore, it is not the primary tool to recommend directly for a group's general communication needs in this drag-and-drop format.
Reference:
Microsoft product documentation defines Microsoft Teams as the "hub for teamwork" for internal users. Power Apps portals are described as for creating "external-facing websites" for B2B or B2C scenarios, making them ideal for external worker engagement. Business Voice is marketed as "a calling plan for Microsoft Teams."
You need to recommend the appropriate messaging channel solutions for the organization.
What should you recommend? To answer, drag the appropriate messaging options to the correct user types. Each messaging option may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

 Explanation:
Explanation:
The question requires selecting the correct Microsoft Power Platform or Dynamics 365 component to facilitate communication between specific user roles. In a Solution Architect context, you must distinguish between the Internal Agent interface used for managing high-volume, multi-channel conversations and the External Client interface used by end-users to initiate those conversations. Understanding the licensing and functional boundaries of Omnichannel for Customer Service versus Power Pages (formerly Portals) is critical for matching these user types to their respective messaging environments.
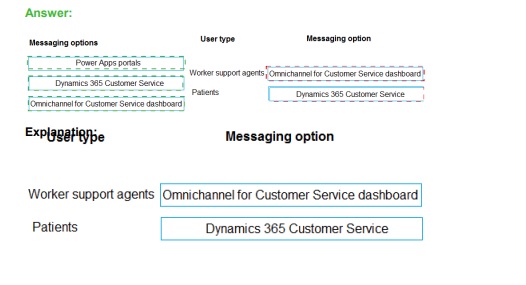
Correct Option:
Worker support agents:
Omnichannel for Customer Service dashboard Worker support agents require a specialized interface designed for handling simultaneous sessions across various channels (chat, SMS, social). The Omnichannel dashboard provides agents with a unified view, real-time notifications, and productivity tools like sentiment analysis and quick replies. It is the primary workspace for agents to engage with incoming messaging requests routed through the Power Platform ecosystem, ensuring they have the context needed to resolve issues efficiently.
Patients:
Power Apps portals Patients are external users who need a secure, accessible entry point to interact with the organization. Power Apps portals (now Power Pages) serve as the public-facing website where a chat widget can be embedded. By using the portal, patients can initiate authenticated or anonymous messaging sessions. This provides a seamless user experience where they can access self-service resources or trigger a live chat that is then routed to the internal support agents.
Incorrect Option:
Dynamics 365 Customer Service (standard interface):
While this is the overarching application, the standard Model-driven interface is primarily for case management and record entry. It lacks the specific session-management and multi-stream capabilities found in the Omnichannel dashboard. Recommending the standard interface for "messaging" specifically would result in a poor user experience for agents who need to manage live, real-time chat interactions across multiple concurrent threads.
Swapping Roles:
Assigning the Omnichannel dashboard to Patients is incorrect because it is an internal-facing, licensed application restricted to organization members. Conversely, providing agents with only a Portal interface would strip them of necessary CRM data, telemetry, and the ability to manage multiple workstreams effectively. The Portal is strictly an engagement layer for the external stakeholder, not a management tool for the support worker.
You need to propose a solution for form requirements.
What should you recommend? To answer, drag the appropriate solutions to the correct requirements. Each solution may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation:
This question tests the understanding of the standard, low-code tools available within the Power Platform (specifically, model-driven apps in Dynamics 365) for implementing form customizations. The goal is to use the simplest, most declarative tool that meets the requirement without unnecessary code.
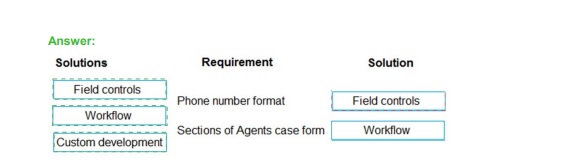
Correct Matching:
Requirement: Phone number format
Recommended Solution: Field controls
Explanation:
Enforcing a specific input format for a phone number is achieved by configuring the field control on the form. Using the built-in Text field with the Phone format selected applies automatic formatting, masking, and validation. This is a purely declarative configuration within the form designer, requiring no code or business process logic.
Requirement: Sections of Agent's case form
Recommended Solution: Field controls
Explanation:
Organizing a form into logical sections (and tabs) is a core function of the form designer. You add and configure Sections as a type of container control to group related fields together. This is a fundamental layout task performed entirely by dragging and configuring controls in the form editor.
Why the Other Solutions Are Incorrect:
Workflow:
This is a business process automation tool (Power Automate cloud flow or classic workflow). It is used to automate actions (like sending an email, updating a record) when certain conditions are met. It is not used for defining form layout (sections) or field-level UI formatting.
Custom development:
This involves writing code (e.g., JavaScript, PCF controls). It is unnecessary for both of these requirements. Formatting a phone number and adding form sections are out-of-the-box capabilities of the model-driven app form designer. Custom development is reserved for complex UI interactions or logic that cannot be achieved declaratively.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "Create and design forms" details how to use the form editor to add sections, tabs, and configure field properties (like format), which are all categorized under configuring "field controls" and form structure. This is a core skill for customizing model-driven apps without code.
| Page 1 out of 16 Pages |