Topic 1: Alpine SKi House Case Study
Background
Alpine SKi House is a boutique mountain resort that offers year-round spa and outdoor
activities such as snow sports, hiking, mountain biking, and more. The resort has been
family owned and operated for more than 50 years. The company has been able to remain
profitable while not needing to adopt new technologies.
General
Booking at the resort have decreased. The company has decided to focus on creating a
tailored, first-class experience for guest. The company also plans to target corporate
meetings and events.
The company recently purchased a chatbot named FAQbot from AppSoure. The chatbot
uses the resort’s existing FAQS
Communication
* Communication between staff members is primarily conducted through email and SMS
text messages.
* Conversations between staff members and guest often lost.
* Conference calls are used for all group meeting
Event Registration
* Corporate customers can reserve a meeting room at the resort to host meetings. The
meetings will include lunch and choice of either an inside-spa experience or a seasonally
appropriate outdoor activity.
* Event registration is conducted three weeks prior to start of the event. It is assumed that
all event attendees will attend the meeting
Check-in process
* Guests wait in lines to check in and obtain name badges. At this time, guests can specify
any dietary restrictions and select their activity preference. This can result in long wait
times and crowding at the front desk.
* For health and compliance reasons, guests must answer a series of questions with a yes
or no answer during check-in. The front desk will ask and record these answers for the
resort's records.
Marketing
At the check-in counter, the guests can drop their business cards into a bowl for a chance
to win an all-inclusive weekend stay at the resort. The resort uses the business card
information to send announcements about promotions and upcoming events.
Resort policies and event inquiries
* A guest can call or send an email to the event coordinator at the resort to get information
about hotel policies, snow conditions, or to pre-select their after-meeting event;
* Guests can also go to the website to view the extensive list of frequently asked questions
(FAQ) compiled over the years. Many of the answers to the FAQ's are out of date.
General
Alpine Ski House does not employ technical staff and does not have the budget to hire an
external firm to develop solutions. There are two team members who are proficient at
Microsoft Excel formulas. Any solution created must use the capabilities of current team
members.
All solutions must be simple to use, easy to maintain, and represent the brand of the resort.
You must implement the following solutions:
* a centrally managed communication solution
* a customer service solution
* a resort portal
* a chat solution
* a check-in solution
Communication
* Communication between team members must be centrally managed and unified in
Microsoft Teams.
* When the company confirms an event they, must provide a list of guest's names and
email addresses.
* You must send guests a welcome email that includes a unique registration number for
authentication with the resort's portal.
* Guests must receive a separate email to verify proof of ownership for their registration.
Event attendance
* Guests must create an account and sign into a resort portal to confirm their attendance to
an event and pre-select an after-meeting event
* Prior to the event, guests must be able to identify any personal dietary restrictions.
Check-in processes
* Check-in processes must be self-service. Each screen must ask for specific data from the
guest. The check-in solution will use some data that is stored in Microsoft Excel.
* The check-in solution must continue to function if there are internet issues. If the selfservice
kiosks are not available, staff must be able to use the check-in solution from within
their communication solution.
* The check-in solution must have a screen where the guest will select either yes or no to
health and wellness questions.
* Guests must physically interact with each answer before proceeding to the next screen.
Guests must be able to confirm any dietary restrictions they may have entered from the
portal or add new ones at this time.
* Data must be entered in each screen before users move on to the next screen.
Marketing
* To eliminate the handling of business cards, the check-in solution must be able to
translate the contents of the business cards into Alpine Ski House's marketing system.
* The solution must not require any effort or manual entry from the guest to prevent any
mistyped information and to make it more appealing to the guest to participate.
Hotel policies and event inquiries
The portal must allow the guest to ask questions about hotel policies, event information,
weather reports, and current weather condition at the resort.
Chat solution
The chat solution must specifically address the following key words. No additional key
words will be added until a later implementation phase:
* Snow reports
* Weather conditions
* Start time
* End time
* Event date
* Outdoor activities
* Indoor activities
* Most popular
The chat solution must be available always and not require staff to answer all of the
questions. If a question does require a staff member's attention, the solution must
determine which staff member is best to assist the customer with the question.
The information in the FAQ on the legacy website must be used in the chat solution but
retyping all the data from the website should not be required. If quests ask about topics that
are not listed in the FAQ, the chat solution must identify the issue and escalate to a staff
member.
Team members must be able to ask their own questions through a centrally managed
communication solution instead of using the guest portal. Team members must be able to
access the same FAQ across multiple solutions.
Issue
Guest1 inquires about snow conditions several times each day of their stay.
You need to add controls to the check-in solution for the health and wellness questions.
Which form control should you use?
A. Drop down
B. Check box
C. Text input
Explanation:
This question relates to designing a user-friendly interface for health and wellness data entry within the Power Apps check-in solution. The key requirement is to efficiently capture simple, binary responses (e.g., Yes/No questions like "Have you exercised today?"). The control must be intuitive, fast to use, and minimize data entry errors for straightforward affirmative/negative answers.
Correct Option:
B. Check box
A checkbox is the standard UI control for capturing a simple Boolean (true/false or yes/no) value. For health and wellness questions like "Do you have any allergies?" or "Are you feeling well today?", a checkbox provides the clearest, most efficient interaction. The user can quickly tap to select or deselect, which aligns perfectly with the need for a fast check-in process.
Incorrect Options:
A. Drop down
A dropdown list is used when presenting a list of options from which the user must select one. For a simple yes/no question, a dropdown is overly complex, requires more user taps to open the menu, and is less intuitive than a direct checkbox. It introduces unnecessary steps for a binary choice.
C. Text input
A text input field is designed for free-form text entry. For standardized yes/no wellness questions, a text box is inefficient, prone to inconsistent data entry (e.g., "Y," "Yes," "yes"), and requires validation logic. It significantly increases user effort and the potential for data quality issues.
Reference:
This aligns with standard UX principles and Power Apps best practices for form design, where the control type must match the data type and intended user interaction. Microsoft Learn documentation on Power Apps controls recommends using the Checkbox control for Boolean data fields.
You need to design the resort portal to meet the business requirements. Which data source should you use?
A. Microsoft Excel
B. Azure SQL Database
C. SQL Server
D. Common Data Service
Explanation:
This question tests the understanding of core data architecture in Power Apps solutions. A "resort portal" implies a production business application requiring robust data management, relationships, security, logic, and integration with other Power Platform components (like Power Automate). The chosen data source must natively support these enterprise needs within the platform.
Correct Option:
D. Common Data Service (Dataverse)
Dataverse is the native, low-code data platform for Power Apps. It is explicitly designed for building business applications like a resort portal. It provides built-in features critical for business requirements: a flexible, table-based relational database, robust role-based security, predefined business logic capabilities (business rules, workflows), rich data types, and seamless integration with all Power Platform tools. It is the foundation for scalable, manageable solutions.
Incorrect Options:
A. Microsoft Excel
While Excel can be a data source, it is a poor choice for a business application like a portal. It lacks true relational capabilities, concurrent user access is problematic, security is very basic (file-level), and it cannot support complex business logic or automation natively. It is suitable for prototyping or very simple, single-user lists, not for a production portal.
B. Azure SQL Database & C. SQL Server
These are powerful, professional relational databases. However, for a Power Apps solution built to leverage the Power Platform's low-code strengths, they are connectors, not the native, integrated platform. Using them requires more custom development for security, logic, and integration. While viable for specific high-performance needs, they are not the primary recommended data source for meeting comprehensive business requirements within the Power Platform context.
Reference:
The PL-200 exam focuses on using the Power Platform's core services. Microsoft Learn content consistently positions Dataverse (formerly Common Data Service) as the recommended, integrated data service for building scalable business applications with Power Apps, precisely to meet complex business requirements without managing infrastructure.
You need to embedded the check-in solution into the communication solution. To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
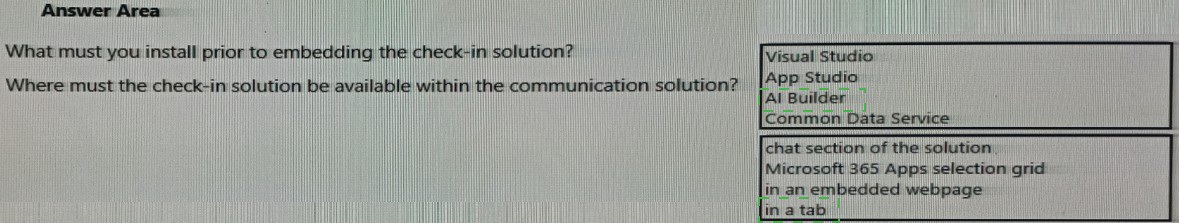
Explanation:
This question deals with embedding a Power Apps canvas app (the "check-in solution") into Microsoft Teams (the "communication solution"). To accomplish this, you must first install the appropriate Power Platform extension within Teams to enable app development and management, and then deploy the app to a specific location where users can access it.
Correct Options:
1. App Studio
App Studio is a Microsoft Teams app that is part of the Power Platform. It must be installed in Teams to manage, configure, and embed custom applications like Power Apps. It is the tool used to package the Power App (check-in solution) as a Teams app, define its tabs, and make it available within the Teams environment. It is the essential prerequisite for this embedding process.
2. Microsoft 365 Apps selection grid in an embedded webpage in a tab
This describes the Teams personal app experience. After using App Studio to package it, the Power App is installed as a personal app for users. It appears in the Teams app bar (the selection grid) and can be opened in its own dedicated tab. Embedding the app "in a tab" means users will interact with it within a Teams tab interface.
Incorrect Options for "What must you install...":
Visual Studio: A professional IDE for traditional code development, not required for low-code Power Platform solutions within Teams.
AI Builder: An AI service for adding models to apps, not a prerequisite for embedding an app into Teams.
Common Data Service (Dataverse): The underlying data platform. While the app likely uses it, it is not something you "install" into Teams for the embedding process; it's a cloud service.
Incorrect Options for "Where must the check-in solution be available...":
Chat section of the solution: This refers to embedding an app within a Teams chat or channel tab, which is context-specific to that conversation. The scenario's need for a general "check-in solution" implies it should be a standalone, always-available personal app for users, not confined to a specific chat.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on "Add a Power Apps app to Microsoft Teams" outlines the process of using App Studio to create an app package and deploy it as a personal app (available from the app bar) or a tab.
You need to design the resort portal's email registration process.
Which solutions should you use? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point
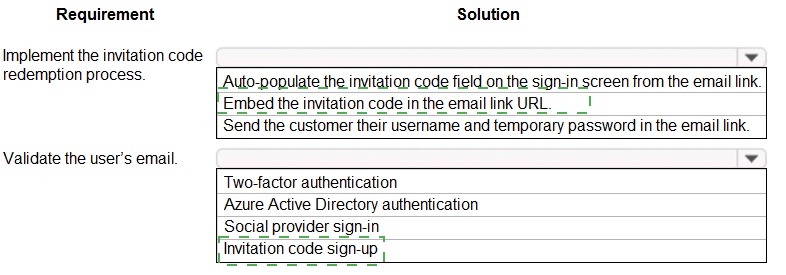
Explanation:
This question focuses on designing a secure, user-friendly email invitation and sign-up process for an external customer portal. The solution must allow invited users to redeem a code and validate their email address without managing complex passwords upfront, aligning with common "invite-only" registration patterns.
Correct Options:
1. Embed the invitation code in the email link URL.
This is the most seamless method for implementing code redemption. The unique invitation code is included as a query parameter in the link (e.g., https://portal.com/signup?code=ABC123). When the user clicks the link, the target application (the Power App) can read this code from the URL and automatically apply it to the sign-up process, eliminating manual entry and reducing errors.
2. Invitation code sign-up
This is the core identity provider configuration required for this scenario. Power Apps portals can be configured to use an "Invitation Code" as a local identity provider. This allows you to generate unique, one-time-use codes sent via email. Users redeem the code to create their account, which inherently validates the email address belongs to the intended recipient.
Incorrect Options for "Solution":
Auto-populate the invitation code field on the sign-in screen from the email link:
This is incorrect terminology. The goal is to redeem the code during the sign-up or account creation process, not to auto-populate a field on the sign-in (log-in) screen. The sign-in screen is for existing users.
Send the customer their username and temporary password in the email link:
This is an insecure and outdated practice. Sending credentials directly in a URL or email body is a security risk. The invitation code pattern is preferred as it requires the user to set their own password upon first redemption.
Incorrect Options for "Requirement":
Two-factor authentication, Azure Active Directory authentication, Social provider sign-in:
These are all valid authentication methods, but they do not directly fulfill the specific requirement for an invitation code redemption process. AAD authentication and social sign-in are for users with existing Microsoft or social (e.g., Google, Facebook) accounts. Two-factor authentication adds a security layer after the primary sign-in method is established.
Reference:
This solution is based on the Invitation Code local identity provider for Power Apps portals. Microsoft Learn documentation details how to configure this provider to send invitation emails with redemption links, enabling a secure, closed user registration model.
You need to design and create the solution for gathering contact information from guests for marketing purposes.
What should you use? To answer, select the appropriate options In the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point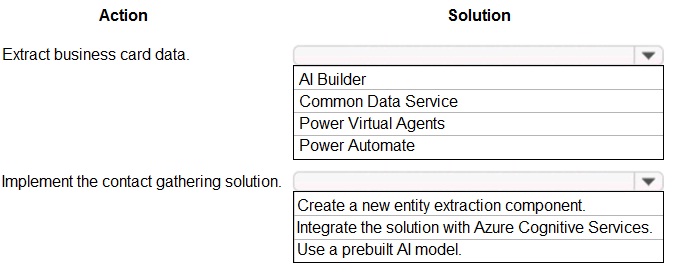
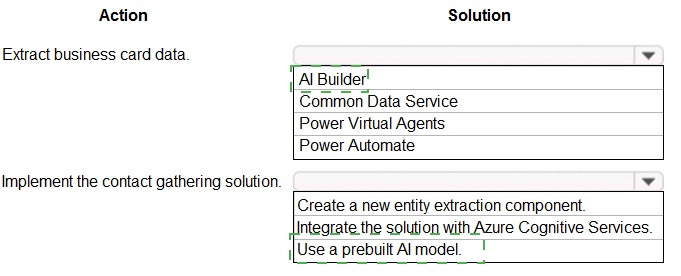
Explanation:
This question involves automating the extraction of structured data (like name, company, phone, email) from unstructured business card images. The solution must leverage low-code AI capabilities and integrate the extracted data into a database for marketing purposes.
Correct Options:
1. AI Builder
AI Builder is the core low-code AI service within the Power Platform. It provides prebuilt and custom models to analyze and extract information from images and documents. For business cards, you would use the prebuilt business card reader model, which is designed specifically for this task without requiring any model training.
2. Use a prebuilt AI model
This is the specific action to take within AI Builder. The prebuilt business card model is trained by Microsoft to recognize common fields on business cards. Selecting this option means you configure the AI Builder action to use this model, which is the fastest, most accurate, and most efficient way to implement the requirement without development.
Incorrect Options for "Action":
Common Data Service (Dataverse):
This is the target destination for the output of the extracted data (storing the contact records). However, it is not the tool used to perform the data extraction from the business card.
Power Virtual Agents:
This is for building chatbots, not for processing images or documents to extract data.
Power Automate:
While Power Automate is essential as the orchestration tool to create a flow that triggers the AI Builder model and saves the data to Dataverse, it is not the primary component that performs the extraction itself. The question asks for the core solution for the "extract" action.
Incorrect Options for "Solution":
Create a new entity extraction component:
This implies building a custom AI model, which is unnecessary and inefficient when a high-quality, purpose-built prebuilt model already exists. It requires time for training and may be less accurate.
Integrate the solution with Azure Cognitive Services:
While technically possible, this is a pro-code approach using Azure's Form Recognizer service. The PL-200 exam focuses on low-code Power Platform solutions, where AI Builder is the intended, simplified wrapper for these Cognitive Services capabilities.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on AI Builder's prebuilt models explicitly lists the Business Card Reader model for extracting contact information from business card images, which can be used directly in Power Apps or Power Automate.
You need to create the FAQ solution content.
What should you do first?
A. Al Builder
B. Suggest fs
C. Automate
D. Trigger phrases
Explanation:
This question focuses on the initial step when building a Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) solution, specifically within the context of a Power Virtual Agents chatbot. The first step is to determine the core knowledge base that the bot will use to answer customer questions before configuring conversational triggers or automations.
Correct Option:
A. AI Builder
For a Power Virtual Agents FAQ solution, the primary component is a knowledge base. This is created using AI Builder's Q&A capability, which allows you to import an existing FAQ document or website. AI Builder processes this content to build a knowledge base that the bot's Topics can use to automatically find and generate answers to user questions. It is the foundational step of ingesting and structuring the FAQ content.
Incorrect Options:
B. Suggest FAQs
"Suggest FAQs" is likely a feature within Power Virtual Agents that analyzes existing chat transcripts to propose new topics or questions. This is an optimization step performed after the bot is deployed and has interaction data. It is not the first step when initially creating the FAQ content from scratch.
C. Automate
"Automate" typically refers to Power Automate flows. While you can use Power Automate to enhance a bot (e.g., to create a ticket if the FAQ answer doesn't resolve the issue), it is an integration or extension step that comes after the core bot and its knowledge base (FAQ content) have been created.
D. Trigger phrases
Trigger phrases are the user utterances that activate a specific Topic in a Power Virtual Agents chatbot. Defining these is a crucial part of building a Topic. However, for an FAQ solution powered by a knowledge base, the system can automatically generate trigger phrases from the imported content. Therefore, the priority is first to create that knowledge base using AI Builder.
Reference:
The standard workflow for creating an FAQ bot in Power Virtual Agents, as documented in Microsoft Learn, starts with creating a Topic and then adding a "Call an action" node that uses the "Get answers from QnA Maker" prebuilt action, which relies on an AI Builder Q&A knowledge base. The initial action is creating that knowledge source.
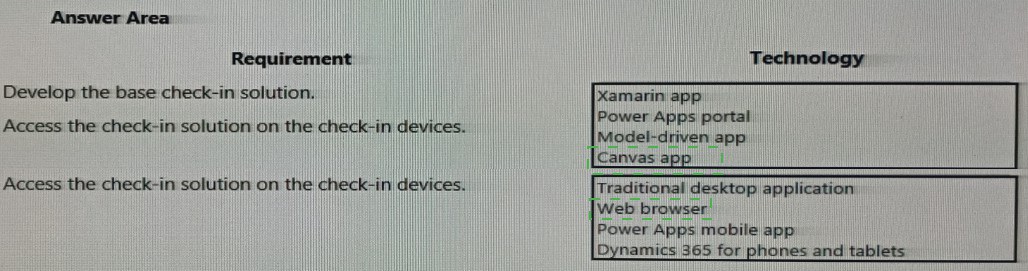
You need to design the guest check-in solution. Which technologies should you use? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point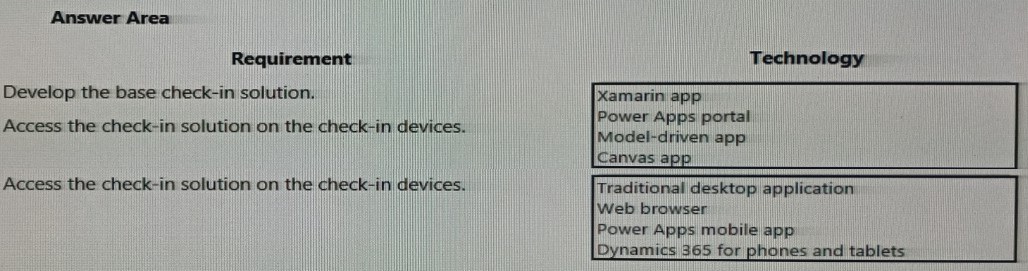
Explanation:
This question involves selecting the correct Power Platform technology to build a device-based check-in application for guests. The solution must be a dedicated application accessible on specific check-in devices (likely kiosks or tablets). The design prioritizes a custom, touch-optimized interface deployed to mobile devices over a broad, anonymous web portal or a complex backend system.
Correct Options:
1. Canvas app
A canvas app is the correct choice for developing the base solution. It allows you to design a highly customized, pixel-perfect user interface tailored specifically for the check-in process. You can optimize the layout for touch on a tablet or kiosk, connect to necessary data sources (like Dataverse), and build the exact user journey required for guest check-in.
2. Power Apps mobile app
This is the correct method for accessing the check-in solution on the devices. The canvas app is published and then opened on the tablet or kiosk device by installing the Power Apps mobile app (from an app store). Within this mobile app, users or kiosk attendants sign in and run the specific check-in canvas app. It is the standard player for running canvas apps on mobile devices.
Incorrect Options for "Requirement":
Xamarin app: This is a pro-code, cross-platform mobile development framework. It is not a low-code Power Platform solution and would require significant custom development, contradicting the PL-200's focus on Power Apps.
Power Apps portal: Portals are designed for external, anonymous, or authenticated users via a web browser (e.g., customer self-service sites). A check-in device typically requires a dedicated, full-screen application interface, not a public-facing website.
Model-driven app: Model-driven apps are best for complex data management and business process apps that are centered around Dataverse tables and forms. They offer less UI flexibility than a canvas app and are not typically the best fit for a simple, customized touch-screen check-in interface.
Incorrect Options for "Technology":
Traditional desktop application / Web browser:
These are generic access methods, not specific Power Platform technologies. While a canvas app can run in a browser, the requirement for dedicated "check-in devices" strongly implies a managed, app-based experience best delivered via the Power Apps mobile app.
Dynamics 365 for phones and tablets:
This is the mobile app specifically for running model-driven apps on mobile devices. Since the base solution is a canvas app, the correct player is the generic Power Apps mobile app.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on app types states that canvas apps are used to create "custom, tailored experiences with a design-first approach," making them ideal for task-specific apps like kiosks or check-in stations, which are then run via the Power Apps mobile player.
The sales manager receives a list of leads from a partner company monthly. The field names that are provided do not match the fields in Dynamics 365. A data map does not exist. You need to import the leads without changing the data from the partner company.
What should you do?
A. Create a data map in Data Management.
B. Add a template for Import Data.
C. Use Import Field Translations.
D. Create a data map on the first import by using the Import Data wizard
Explanation:
This scenario requires importing data from a source file with mismatched field names into Dynamics 365 without altering the original file. A data map is necessary to define the correspondence between the source columns and the target Dynamics 365 fields. Since no map exists, one must be created during the import process.
Correct Option:
D. Create a data map on the first import by using the Import Data wizard
The Dynamics 365 Import Data wizard provides a step-by-step interface for mapping source columns to target entity fields during an import. On the "Map Fields" step, you can manually match each incoming column from the partner's file to the corresponding field in the Leads entity. The wizard allows you to save this mapping as a new data map for future use, ensuring consistency for subsequent monthly imports without needing to redo the mapping.
Incorrect Options:
A. Create a data map in Data Management.
While you can pre-create a data map in the Data Management settings area, this is a separate, manual process that requires defining source and target attributes in a more abstract way. It is less intuitive and efficient for a one-time setup compared to creating the map interactively during the import wizard, where you can see the actual source data.
B. Add a template for Import Data.
"Templates" in this context typically refer to predefined Excel formats. This does not solve the core problem of field name mismatches. A template would require the partner to change their file format to match Dynamics 365, which contradicts the requirement not to change the data from the partner company.
C. Use Import Field Translations.
Field Translations are used to localize or translate field values (e.g., translating "Yes" to "Oui" for French users), not to map different field names or column headers from a source file to the target system. This feature does not address the structural mapping problem.
Reference:
The Dynamics 365 Customer Engagement (on-premises) documentation for importing data outlines the process where the Import Data wizard is used to create mappings. Specifically, it states that during the import process, you can review automatic mappings, change them, and save the mappings as a data map for reuse.
A company has a custom website.
You need to embed a Power Virtual Agents chatbot into the website.
What should you use?
A. Webpage URL
B. Form ID
C. Bot ID
D. IFrame
Explanation:
This question tests the technical method for embedding a Power Virtual Agents (PVA) chatbot into an existing, custom external website. The solution must allow the chat interface to be seamlessly integrated as a component within the website's pages, maintaining its functionality and security context.
Correct Option:
D. IFrame
An IFrame (Inline Frame) is the standard HTML element used to embed external web content, such as a PVA chatbot, into a webpage. Power Virtual Agents provides a direct "Embed" option in its publication settings, which generates an HTML snippet containing an tag with the correct src URL pointing to your bot. You copy this snippet and paste it into your custom website's HTML code where you want the chat widget to appear.
Incorrect Options:
A. Webpage URL
A webpage URL is simply the address of a bot published as a standalone webpage. While you can share this URL to open the bot in a new browser tab, it does not embed the bot into your existing website's interface. It provides a link to the bot, not integration within your site.
B. Form ID
A Form ID is associated with embedding Power Apps (specifically model-driven app forms) into external websites, not Power Virtual Agents chatbots. This is a different Power Platform component and is not relevant for chatbot deployment.
C. Bot ID
The Bot ID is a unique identifier (GUID) for your PVA chatbot within the Azure Bot Service. It is used for pro-code integration scenarios (e.g., using the Bot Framework SDK) or for authentication when connecting other services. It is not the direct tool or method used for the simple, low-code website embedding process.
Reference:
The Microsoft Learn documentation for Power Virtual Agents explicitly outlines the steps to embed a bot on a website under the "Embed" section. It instructs you to go to the PVA portal > Manage > Channels, add the "Website" channel, and then copy the provided iframe HTML code to paste into your site's source code.
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are creating Power Virtual Agents chatbot that captures demographic information about customers.
The chatbot must determine the group a customer belongs to based on their age. The age groups are:
0 - 17
18 - 25
26 - 35
36 - 55
55 - 100
You need to configure the chatbot to ask a question that can be used to determine the correct age group.
Solution: Create a custom Age group entity and synonyms for each individual age in the corresponding item. Use Age group for Identify in the question.
Does this meet the goal?
A. Yes
B. No
Explanation:
The goal is to capture a user's specific age via a question and then use that number to determine which age group they belong to. The proposed solution incorrectly focuses on capturing the group name directly rather than the raw age number needed for the grouping logic.
Correct Option:
B. No
The solution does not meet the goal.
The Goal:
The bot needs to ask for the customer's age (a numeric value). This numeric input must then be evaluated by business logic (e.g., Conditions in a Power Automate flow or within the PVA Topic) to place it into one of the predefined ranges.
Why the Solution Fails:
Creating a custom "Age group" entity with synonyms for individual ages (e.g., "20" as a synonym for the "18-25" group item) forces the user to select a group label or utter a number that is merely a synonym for a group. This approach:
Makes the bot's question ambiguous (Is it asking for a group or a number?).
Incorrectly assumes a user will say a number that maps to the correct group synonym.
Captures the group name as the primary data, not the actual age. This loses the precise age data, making it impossible to later recalculate groups if the ranges change or to use the exact age for other purposes.
The correct approach is to ask the question using a Number entity to capture the raw age. Then, use a Condition node or call a Power Automate flow to compare the captured number against the defined ranges and assign the group.
Reference:
This aligns with Power Virtual Agents best practices for collecting and processing numeric data. Entity definitions are for extracting known terms or categories from free text, not for performing logical comparisons on numerical ranges. The task requires a conditional branch based on a variable's value.
You are a Dynamics 365 for Customer Service developer.
You must trigger a mobile notification whenever a specific hashtag is posted from Twitter.
The notification will send email to the company’s social media teams distribution list.
You need to create a connection to the Twitter service and build a solution.
Which four actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.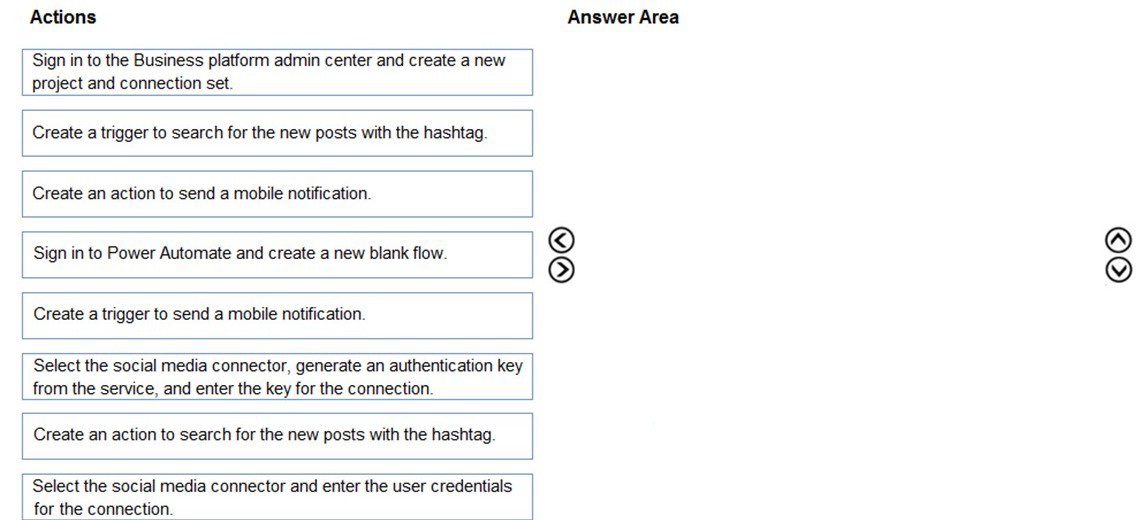
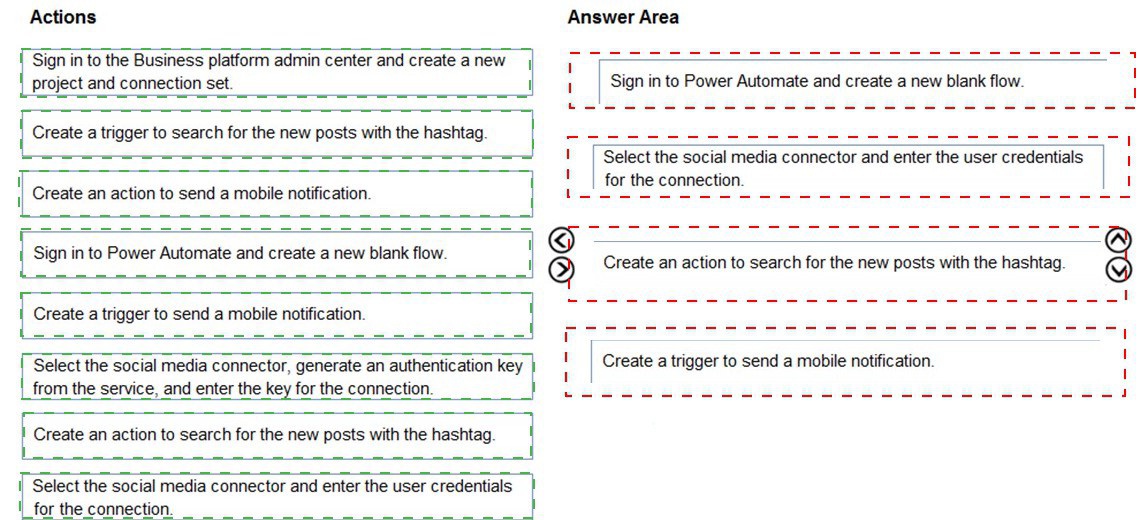
Sign in to Power Automate and create a new blank flow.
(This is the foundational first step—you must be in the Power Automate service to begin building the automation.)
Select the social media connector, generate an authentication key from the service, and enter the key for the connection.
(This step establishes the authenticated connection to Twitter. For Twitter, you typically generate API keys/tokens in the Twitter Developer Portal and enter them as the "authentication key" in the Power Automate connector setup.)
Create a trigger to search for the new posts with the hashtag.
(After the connection is set, you add the trigger—the event that starts the flow. The correct trigger is from the Twitter connector, such as "When a new tweet is posted" with the search query set to your specific hashtag.)
Create an action to send a mobile notification.
(The final step is to add the action that performs the required task. Since the requirement is to send a notification to a distribution list via email, you would use an action like "Send an email (V2)" or "Send an email notification" to the team's email list. The phrasing "mobile notification" in the provided list likely refers to this email action, as email is the channel for the distribution list.)
Incorrect/Actions Not in Sequence:
"Sign in to the Business platform admin center..." is not the correct starting point; flows are built in Power Automate.
"Select the social media connector and enter the user credentials..." is less specific and less secure than using generated API keys (OAuth).
"Create a trigger to send a mobile notification" and "Create an action to search..." reverse the logical order; the trigger must be the Twitter search, and the action is the notification.
"Create an action to send a mobile notification" is correct, but only after the trigger is defined.
Final Sequence:
Sign in to Power Automate and create a new blank flow.
Select the social media connector, generate an authentication key from the service, and enter the key for the connection.
Create a trigger to search for the new posts with the hashtag.
Create an action to send a mobile notification.
You are designing a Power Virtual Agents chatbot.
You observe that the environment you plan to use does not appear as an option in the Power Virtual Agents user interface.
You need to ensure that you can create the chatbot in the environment that you want to use. What should you do?
A. Create an environment in a supported region.
B. Convert the environment to a sandbox environment.
C. Change the region for the environment.
Explanation:
The Power Virtual Agents (PVA) authoring portal only lists environments that are supported for bot creation. Support is determined by Microsoft based on the environment's region and type. If an environment does not appear, it is most likely because it is in a geographic region where PVA is not yet available or because it is an unsupported environment type (like a default environment in certain scenarios).
Correct Option:
A. Create an environment in a supported region.
Power Virtual Agents has a specific list of supported regions (e.g., United States, Europe, United Kingdom, Australia, Asia Pacific). If your target environment was created in an unsupported region, it will not appear in the PVA dropdown. The solution is to create a new environment and select a supported region (like "United States") during its creation. You can then select this new, supported environment when creating your bot.
Incorrect Options:
B. Convert the environment to a sandbox environment.
Changing the environment type (from Production to Sandbox or vice versa) does not affect its regional availability for PVA. A sandbox environment in an unsupported region will still not appear as an option. The "sandbox" type is for development and testing lifecycle management, not for enabling geographic service availability.
C. Change the region for the environment.
The region of an existing environment cannot be changed after creation. Region is a fundamental, immutable property set when the environment is provisioned. To use a different region, you must create a new environment in that desired region.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on environment considerations for Power Virtual Agents states: "Power Virtual Agents is only available in certain regions. If you don't see the environment you want to create a bot in, it might be because it's in a region where Power Virtual Agents isn't available. You need to create a new environment in a supported region."
| Page 1 out of 9 Pages |