Topic 2: Misc. Questions
You are a Dynamics 365 administrator for a veterinarian clinic.
On the client appointment form, there is a dropdown field for clients to select their type of pet If a client selects the option Other, the veterinarian wants a text field to appear so that additional details can be added.
You need to create a dynamically visible field.
What should you configure?
A. filed visibility on the form
B. business process flow
C. workflow
D. business rule
Explanation:
This requirement is a classic example of dynamic form behavior based on user input within a single form. A field's visibility must change immediately when the "Pet Type" dropdown is set to "Other," without navigating away from the form or running a background process. This is a client-side logic requirement.
Correct Option:
D. Business rule
A Business Rule is the correct tool to configure client-side logic on a Dynamics 365 form. You can create a business rule that uses the "Pet Type" field as a condition. When the condition is met (e.g., Pet Type Equals "Other"), you can define an action to "Show" the additional text field. You can also add a corresponding action to "Hide" the field when "Other" is not selected. This provides an immediate, dynamic user experience.
Incorrect Options:
A. Field visibility on the form
This is a static property set in the form designer. It determines whether a field is always visible, hidden, or optional on the form layout by default. It cannot be changed dynamically based on the value of another field during runtime.
B. Business process flow
A Business Process Flow (BPF) guides users through a series of stages and steps for a record. It controls navigation and data entry progression, but it does not control the dynamic visibility of individual fields on a form based on another field's value.
C. Workflow
A workflow is a server-side automation that runs asynchronously, often on a record event (like save) or on a schedule. It cannot manipulate the user interface in real-time to show or hide a field while the user is filling out the form. It is designed for backend data updates and notifications, not for dynamic form interactivity.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on Business Rules states they are used to "apply business logic without writing code" and can perform actions such as "Show, hide, enable, or disable fields" and "Set field values" based on conditions, all of which execute on the client side as the user interacts with the form.
You manage the Dynamics 365 environment for a company.
You need to ensure that there are no leads for a customer before you create a new opportunity for the customer.
How can you use duplicate detection rules to achieve this goal? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.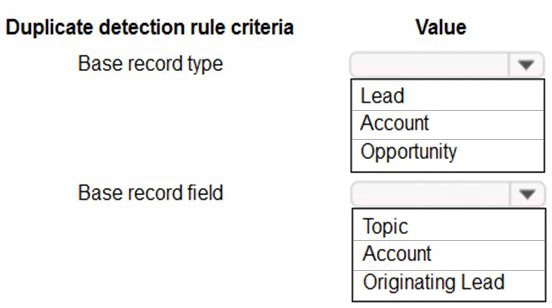
Explanation:
This scenario requires configuring a duplicate detection rule to prevent the creation of a new Opportunity if a Lead for the same customer already exists. The rule must compare the new Opportunity against existing Leads based on a common customer identifier.
Correct Options:
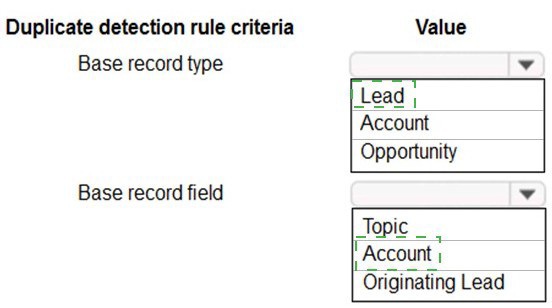
1. Base record type: Opportunity
The Base record is the record you are creating or updating that will be checked for duplicates. The goal is to check before creating a new Opportunity, so the base record type must be Opportunity.
2. Base record field: Originating Lead
This is the critical link. In Dynamics 365, when a Lead is qualified, it can create an Account, Contact, and an Opportunity. The new Opportunity created from a qualified Lead will have its "Originating Lead" field populated with a lookup to that original Lead record. Therefore, a duplicate rule checking if a new Opportunity's Originating Lead matches any existing Lead would find duplicates only for Opportunities created from that specific qualified Lead process. However, this logic is incomplete for the stated goal.
Important Correction:
The provided answer area seems flawed for the exact goal. The rule described would only catch duplicates for Opportunities created from an already qualified Lead. To ensure "no leads for a customer before creating a new opportunity," you need a rule that compares a customer identifier (like Account field on both records).
Correct Logic (if fields allowed matching):
Base Record Type: Opportunity
Matching Record Type: Lead
Comparison Fields:
The Account field on the Opportunity should be compared to the Company Name (or Parent Account) field on the Lead, assuming they refer to the same customer entity.
Given the limited options in your image, Opportunity is correct for the base type. For the field, Account might be the closest, as both Leads and Opportunities have an associated Account/company, but a direct match isn't standard. The Originating Lead field is not appropriate because a new Opportunity created manually for an existing Lead would have this field blank, so the rule would not fire. This highlights a limitation of the provided fields for the exact goal.
Final Answer Based on Available Options & Goal Intent:
Base record type: Opportunity
Base record field: Account (This is the most logical, as it represents the common customer. The rule would need a corresponding match on the Lead's Company Name, but that's not selectable here, implying the UI might handle this mapping.)
You need to design the FAQ solution to handle unknown responses.
Which component should you use? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point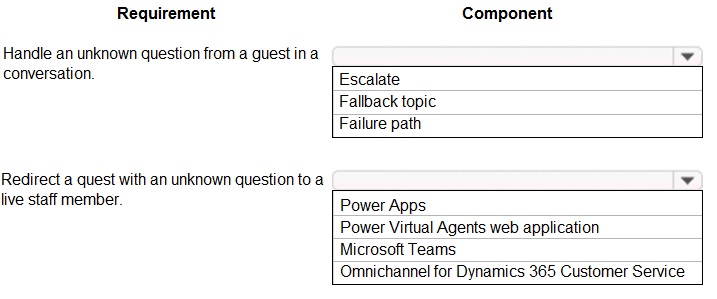
Explanation:
This question involves designing the error-handling logic for a Power Virtual Agents (PVA) FAQ chatbot. When a guest asks a question the bot cannot answer (an "unknown question"), the solution must have a defined conversational path to manage this scenario and then transfer the guest to a human agent for further assistance.
Correct Options:
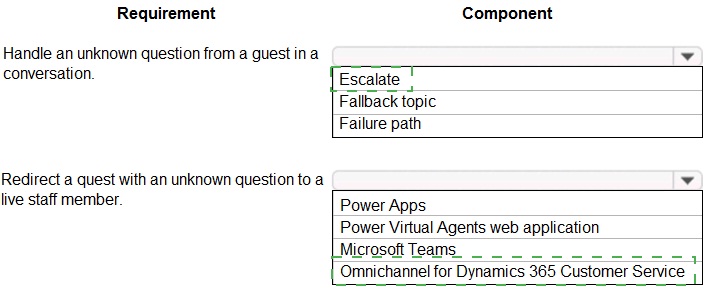
1. Fallback topic
The Fallback topic is the core PVA component designed specifically to handle unknown questions. It is an automatically created system topic that triggers when user input does not match any other topic's trigger phrases. This is where you define the bot's response for unhandled queries, making it the correct choice for the first requirement.
2. Omnichannel for Dynamics 365 Customer Service
To escalate the conversation and redirect a guest to a live staff member, you must integrate the PVA bot with Omnichannel for Customer Service. This add-on service provides live chat, agent routing, and seamless hand-off capabilities. Within the Fallback topic, you would add a "Transfer to agent" node, which is powered by the Omnichannel integration.
Incorrect Options for "Requirement":
Escalate:
While this describes the desired action, it is not a specific, configurable component within PVA. "Escalate" is the outcome achieved by using the "Transfer to agent" node, which requires Omnichannel.
Failure path:
This is a generic term, not a named feature in PVA. The specific, built-in component for handling conversation failures due to unrecognized input is the Fallback topic.
Incorrect Options for "Redirect...":
Power Apps, Power Virtual Agents web application, Microsoft Teams:
These are all channels or interfaces where the bot can be deployed or accessed. They are not the service that provides live agent routing and escalation capabilities. Omnichannel is the dedicated service for managing and transferring conversations to human agents within the Dynamics 365 Customer Service framework.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on configuring bot hand-off explicitly states that to transfer a conversation to a live agent, you must add Omnichannel for Customer Service to your environment and then use the "Transfer to agent" node in a topic (like the Fallback topic). The Fallback topic is described as the place to handle messages that don't match other topics.
The business team provides the following list of features that they would like you to implement:
• Group by or sort columns in the current view.
• Configure a business rule to show an error message.
• Edit values in calculated fields.
• Edit the Address composite field.
• Use the editable grid on mobile phones.
Which actions can you perform? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point

Explanation:
This question tests knowledge of standard capabilities versus limitations within model-driven app forms and grids in Dynamics 365. Some actions are user interface features, while others are restricted by system design (like editing calculated fields) or require specific configurations.
Correct Options (Actions You CAN Perform):
Group by or sort columns in the current view.
This is a standard user interface feature available in model-driven app views (grids). Users can click column headers to sort or use the "Group By" option to organize records.
Configure a business rule to show an error message.
Business Rules are a configurable feature that allows administrators to apply client-side logic, including validating data and showing error messages to users on a form when conditions are met.
Edit the Address composite field.
The Address field is a special composite field that contains multiple components (Street, City, State, etc.). Users can click into this field on a form to edit its constituent parts. It is designed to be editable.
Use the editable grid on mobile phones.
The editable grid control is supported in the Power Apps mobile app, allowing users to edit records directly from a view on their mobile device.
Incorrect Option (Action You CANNOT Perform):
Edit values in calculated fields.
Calculated fields are read-only by design. Their values are automatically determined by a formula defined by an administrator, referencing other fields in the system. Users cannot manually edit the value of a calculated field on a form or in a grid.
Summary of Selections:
You should select all options except "Edit values in calculated fields."
You have a canvas app that allows users to view, select and purchase products. The app uses a Gallery control to display products and checkboxes that allow users to select products.
When users select items from the product catalog, they move to a different screen to complete a purchase.
Users must be able to clear all product selections when they click the button.
You need to configure the button.
What should you do?
A. Use the Reset (Control) formula and pass the gallery control as a parameter to the Reset formula.
B. Use the Reload(control) formula and pass the gallery control as parameter to the Reload formula.
C. Use the ForAall( ) function to iterate through each item of the Gallery and clear user selections.
D. Set the OnCheck value to populate a collection and the OnUncheck value to remove the item from the collection. Clear the collection when the user selects the button.
Explanation:
This question focuses on resetting the selection state of a Gallery control in a Power Apps canvas app. The requirement is to clear all user selections (presumably checkboxes) when a button is clicked, without reloading data from the source. The solution must efficiently reset the UI controls to their default, unselected state.
Correct Option:
A. Use the Reset(Control) formula and pass the gallery control as a parameter to the Reset formula.
The Reset(Control) function is specifically designed to revert a control to its default property values. When you pass a Gallery control as the parameter, Reset(Gallery1) will reset all controls within that gallery template (including the checkboxes) to their default state (e.g., Default property of a checkbox is false). This is the most efficient and direct method to clear all selections at once.
Incorrect Options:
B. Use the Reload(control) formula and pass the gallery control as parameter to the Reload formula.
There is no Reload(Control) function in Power Apps. You might reload the data source with Refresh(), but that does not reset the selection state of controls within the gallery. It would re-query the data, which is unnecessary and inefficient for simply clearing selections.
C. Use the ForAll( ) function to iterate through each item of the Gallery and clear user selections.
While technically possible (e.g., using ForAll to set a custom variable for each item), this is an overly complex and less efficient workaround. It requires managing a separate collection or variable for selection state and writing more complex logic. The Reset() function is the built-in, one-step solution for this exact purpose.
D. Set the OnCheck value to populate a collection and the OnUncheck value to remove the item from the collection. Clear the collection when the user selects the button.
This describes a valid alternative architecture for managing selections using a collection. However, the question asks how to configure the button given the existing app setup (which uses checkboxes bound to the gallery). If selections are already managed by the checkbox controls' native Selected property (the typical pattern), clearing a separate collection would not reset the visual state of the checkboxes. The Reset() function directly addresses the visual control state.
Reference:
Power Apps documentation for the Reset function states it "Resets a control to its default value." Using Reset on a Gallery or Form control is the standard method for clearing user input.
You are creating a Power Virtual Agents chatbot that uses multiple topics.
Each user interaction can reference more than one topic.
You need to be able to capture a value in an initial topic and use it in subsequent topics.
Which type of variable should you create?
A. Bot
B. Topic
C. Context
Explanation:
This scenario requires sharing a user-provided value across multiple, independent topics within the same chatbot conversation. The variable's scope must persist throughout the entire user-bot interaction, not be confined to a single topic or a specific branch of logic.
Correct Option:
A. Bot
A Bot variable (also known as a Global variable) has a scope that spans the entire conversation across all topics. Once you create a Bot variable (e.g., Bot.CustomerName) and set its value in one topic, that value can be read, updated, and used by conditions or messages in any other topic triggered later in the same conversation. This is ideal for capturing user details like name, case number, or product interest for reuse.
Incorrect Options:
B. Topic
A Topic variable is scoped only to the specific topic where it is created. Its value is lost once the conversation exits that topic. It cannot be accessed by other topics, making it unsuitable for sharing information across the conversation as required.
C. Context
Context variables are used within a specific node path inside a single topic. They are typically created by certain nodes (like "Call an action" from a Power Automate flow) to pass outputs to the next node in the same topic. Their scope is even more limited than a Topic variable and does not persist outside their immediate node sequence or to other topics.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on variables in Power Virtual Agents clearly defines the scopes: Bot variables "can be accessed by any topic, at any point in the conversation." This makes them the correct choice for sharing information between topics.
On a Contact record, a user creates a Note record that contains the word running.
One week later, the user reports that they cannot find the Contact record associated with the Note record.
You need to find the Note record.
Solution: Use Categorized Search to search for the word run.
Does the solution meet the goal?
A. Yes
B. No
Explanation:
The goal is to find a specific Note record (an annotation) when the user only remembers a keyword ("running") from its content and the associated Contact is lost. The proposed solution is to use Categorized Search for a partial word.
Correct Option:
B. No
The solution does not meet the goal.
Why it Fails:
Categorized Search is used for finding records of a specific entity type (like Contacts, Accounts, or Notes) based on fields configured for searching in that entity's quick find view. The core issue is that Notes (annotations) are not included in the default Categorized Search. They are not a searchable entity in the global, categorized search experience.
Partial Word Issue:
Even if Notes were searchable, searching for "run" may not find "running" depending on the search configuration. Quick Find searches typically do not perform stemming or wildcard substring matching by default; they often look for the exact word or the beginning of the word. A search for "run" might miss "running."
The Correct Approach:
To find a Note by its text content, you should use Advanced Find. In Advanced Find, you can:
Set the "Look for:" field to "Notes".
Add a condition where the "Description" field "contains" the word "running".
Execute the query. This will return the Note record, which will have a Regarding field linking to the associated Contact record.
Reference:
Microsoft's documentation on search capabilities differentiates between Categorized Search (for common primary entities) and Advanced Find (for complex queries across all entities, including Notes). Notes are not part of the default global search scopes.
You manage the Dynamics 365 Customer Service environment for an organization.
Microsoft SharePoint will not be deployed in the environment for a year.
You need to integrate Microsoft Office 365 solutions with the Dynamics 365 instance to help the sales team with internal collaboration efforts.
Which three solutions can you currently implement? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. Microsoft OneDrive for Business
B. Microsoft Yammer
C. Microsoft OneNote
D. Microsoft Skype for Business
E. Microsoft Exchange Online
Explanation:
The requirement is to integrate Office 365 solutions with Dynamics 365 for sales team collaboration without using SharePoint (which is unavailable). The integration must leverage services that work directly with Dynamics 365 and do not require SharePoint as a backend or document storage location.
Correct Options:
B. Microsoft Yammer
Yammer can be integrated with Dynamics 365 to enable social collaboration. Users can post and discuss Dynamics 365 records (like Opportunities) within Yammer groups directly from the record, fostering team communication without SharePoint.
D. Microsoft Skype for Business (or now, Microsoft Teams)
Skype for Business (and its successor, Microsoft Teams) can be integrated. This enables presence indicators, click-to-call, and instant messaging directly from within Dynamics 365 records, facilitating real-time communication among team members.
E. Microsoft Exchange Online
Exchange Online is the backbone for email integration. Dynamics 365 can be configured to use Exchange Online for email tracking, synchronizing appointments/contacts, and enabling the "Email" activity directly within Dynamics, all without SharePoint dependency.
Incorrect Options:
A. Microsoft OneDrive for Business
OneDrive for Business integration requires SharePoint Online. The OneDrive for Business integration in Dynamics 365 (to attach files from OneDrive to records) uses the underlying SharePoint infrastructure and APIs. Since SharePoint is not deployed, this integration cannot be implemented.
C. Microsoft OneNote
While OneNote can be integrated with Dynamics 365, it typically does so via SharePoint. The standard integration for embedding OneNote notebooks within Dynamics 365 records (like Accounts) creates and stores the notebook in a SharePoint document library associated with the record. Without SharePoint, this standard integration path is blocked.
Reference:
Microsoft documentation for integrating Office 365 with Dynamics 365 specifies dependencies. For example, the "OneDrive for Business" integration guide states it requires a SharePoint Online environment. Similarly, embedding OneNote notebooks is part of the SharePoint document management integration. Yammer, Skype/Teams presence, and Exchange Online (via Server-Side Sync or Exchange folder tracking) are independent integrations.
You configure an alert in Power Bl.
You need to alert users when the value of a tile exceeds a threshold. To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation:
This question is about configuring alert notifications in Power BI. The first part asks where to set up the alert so it triggers an automation process (like sending an email or a Teams message). The second part concerns the visibility of who can see and manage those configured alerts.
Correct Options:
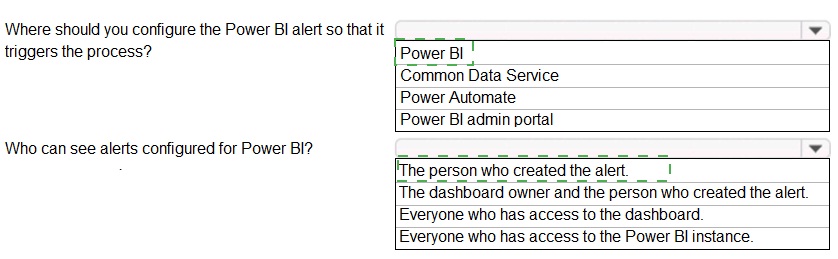
1. Where should you configure the Power BI alert so that it triggers the process?
Power BI
Alerts are a native feature of the Power BI service. You configure them directly on a dashboard tile within the Power BI portal. However, to trigger an external process (like a flow), you need to connect this Power BI alert to Power Automate. Therefore, while the alert is created in Power BI, the "trigger the process" action is set up in Power Automate. Given the options, Power BI is the primary location where the alert itself is configured, and it's the starting point. The more complete answer for triggering a process would be Power BI → Power Automate, but from the list, Power BI is the foundational step.
2. Who can see alerts configured for Power BI?
The person who created the alert.
Power BI alerts are personal and private. Only the user who creates an alert on a dashboard tile can see, manage, and receive notifications for that specific alert. Dashboard owners or other users with access to the dashboard do not see alerts created by others.
Incorrect Options for the first question:
Common Data Service:
This is a data platform, not a tool for configuring Power BI alerts.
Power Automate:
Power Automate is where you would build the process triggered by the alert (using the "When a Power BI tile alert is triggered" connector), but the alert configuration itself is done in the Power BI service.
Power BI admin portal:
This is for tenant-level administration, not for setting up individual data alerts on tiles.
Incorrect Options for the second question:
The dashboard owner and the person who created the alert: Alerts are not shared with the dashboard owner.
Everyone who has access to the dashboard / Power BI instance: Alerts are not visible to other users; they are a personal feature.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn documentation on data alerts in Power BI states: "Data alerts are a personal feature. You can create an alert on a tile, and you'll be the only one who sees it... You create and manage data alerts on dashboards in the Power BI service." For automation, you connect Power BI alerts to Power Automate flows.
You are creating a canvas app.
A user will click a button on each screen of a Power Apps app to proceed to the next screen. You need to implement an action that selects the next screen that the user sees.
Which event should you handle?
A. OnLoad
B. OnCheck
C. ScreenTransition
D. OnSelect
Explanation:
This question is about implementing navigation in a canvas app. The requirement is that a user clicks a button to proceed to the next screen. The action of selecting the next screen must be triggered by the user's interaction with that button.
Correct Option:
D. OnSelect
The OnSelect property of a Button control is the correct event to handle for navigation. You write a formula (e.g., Navigate(NextScreen, ScreenTransition.Cover)) in the button's OnSelect property. When the user clicks (selects) the button, this formula executes and transitions the user to the specified next screen. This is the standard, event-driven method for handling user-initiated navigation.
Incorrect Options:
A. OnLoad
The OnLoad property belongs to a Screen, not a button. It triggers when the screen loads (becomes visible). It is used to initialize data or set variables when a user arrives on a screen, not to handle a button click to leave the screen. It is the wrong event for user-initiated navigation.
B. OnCheck
The OnCheck property is specific to Toggle or Checkbox controls. It triggers when the control's state changes to "checked" (or true). It is not a property of a standard button and is not used for navigation.
C. ScreenTransition
ScreenTransition is not an event; it is an enumeration (a set of fixed values) used as a parameter within the Navigate() function. You use it to specify the visual transition effect (e.g., ScreenTransition.Cover or ScreenTransition.Fade). You cannot "handle" it as an event.
Reference:
Power Apps documentation for the Navigate function and button properties instructs developers to place the Navigate() formula in a control's OnSelect property to change screens. The OnSelect event is the primary handler for button clicks.
A company plans to implement AI Builder to add intelligence to several business processes.
Each business process uses different sources and produces different outputs.
You need to determine which AI Builder model types to use.
Which model types should you use? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Explanation:
This question involves selecting the correct AI Builder model type based on the source data and the specific data extraction requirement. AI Builder offers different prebuilt and custom models, each optimized for a particular task and input format.
Correct Options:
1. Recognition requirement: Identify a person’s age in a paragraph when written using the pattern "twenty years old".
Model type: Entity extraction
This requirement is about extracting a specific piece of structured data (an age) from unstructured text (a paragraph). The Entity Extraction model type (specifically, the prebuilt "Age" entity or a custom entity trained to recognize age phrases) is designed to identify and categorize key information within sentences or documents. It analyzes text for patterns and contexts, making it ideal for finding phrases like "twenty years old."
2. Recognition requirement: Identify items and prices from an invoice.
Model type: Form processing
This requirement involves extracting structured data (line items, prices) from a structured or semi-structured document (an invoice). The Form Processing model type is explicitly built to analyze forms, receipts, invoices, and similar documents. You can use a prebuilt invoice model or train a custom model to recognize the specific fields (like "Description," "Quantity," "Unit Price") from scanned or digital invoice documents.
Incorrect Options for the first requirement (Age in a paragraph):
Text recognition:
This refers to Optical Character Recognition (OCR), which converts text in an image into machine-readable characters. It does not understand or extract the meaning or specific entities (like age) from the text; it merely reads the text.
Key phrase:
This model extracts the main topics or important phrases from a document (e.g., "budget," "project deadline"). It would not reliably extract a specific numerical age value from a descriptive phrase.
Incorrect Options for the second requirement (Items and prices from an invoice):
Text recognition (OCR):
Again, OCR is a prerequisite for form processing (to get the text from a scanned invoice), but by itself, it only provides raw text. It does not identify which text corresponds to an "item" or a "price" and cannot structure the data into fields.
Object detection:
This model identifies and locates objects within an image (e.g., finding a car, a chair, a dog in a photo). It is used for visual analysis, not for extracting textual data and values from documents.
Reference:
AI Builder documentation clearly categorizes its models. Entity extraction is listed for identifying specific categories of information in text. Form processing is described as the service for "extracting text, key/value pairs, and tables from documents."
You are a Dynamics 365 Customer Service help desk administrator.
Cases entered in forms require different types of data to be stored in different types of fields. You need to create forms for each of the following case types:
Explanation:
This question requires matching Dynamics 365 form types to specific business requirements for Case entry. Each form type serves a distinct purpose: Main forms are for full-featured interaction, Quick Create forms are for rapid mobile entry, Quick View forms display read-only data from related records, and Card forms are for dashboards.
Correct Matches:
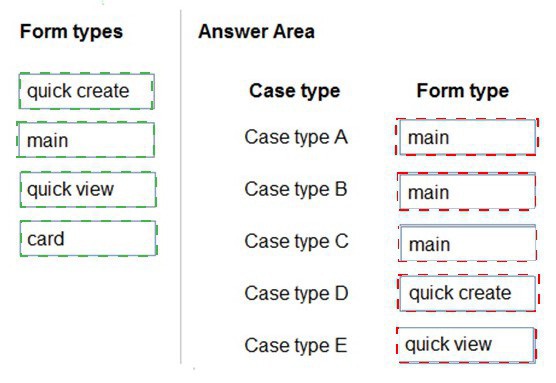
Case type A: A new case form that includes a timeline
Form type: Main
The timeline (activity wall) is a feature only available on the Main form. Main forms are the primary, full-featured forms used in the web application and support all rich components like the timeline, sub-grids, and business process flows.
Case type B: A new case form that includes a business process flow
Form type: Main
Business Process Flows (BPF) are also a feature exclusive to Main forms. They cannot be added to Quick Create or Card forms.
Case type C: A new case form that can display case data on an interactive dashboard
Form type: Card
Card forms are specifically designed for use on interactive dashboards. They display a focused subset of data in a card-like layout within a dashboard view. A main form cannot be embedded in a dashboard in this way.
Case type D: A new mobile-friendly case form that requires minimal fields for record creation
Form type: Quick Create
Quick Create forms are optimized for speed and mobile use. They contain a minimal set of fields, allow users to create records from the global "Create" button or in mobile apps without loading the full main form, perfectly meeting the "mobile-friendly" and "minimal fields" requirements.
Case type E: A new mobile-friendly case form that displays the subject, case title, and status fields from a parent case
Form type: Quick View
A Quick View form is used to display read-only information from a related (parent) record on the form of another record. Here, the requirement is to display fields from a parent case on a new case form. This is the exact function of a Quick View control, which is populated by a Quick View form schema.
| Page 2 out of 9 Pages |
| Previous |