Topic 3: Exam Pool C (NEW)
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.


Summary
This question tests your ability to identify the correct Azure service for a specific use case. The description clearly outlines a Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS) solution, where the desktop operating system itself (Windows 10 or Windows 11) is hosted in the cloud and accessed remotely by users from various locations and devices.
Correct Option
Azure Virtual Desktop:
This is the correct answer. Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) is a comprehensive desktop and app virtualization service that runs in the cloud. It allows you to deploy a scalable and flexible environment to provide users with a cloud-hosted, multi-session Windows experience. Users can access their remote desktops and applications from virtually any device and any location with an internet connection.
Incorrect Option
Azure Spot Virtual Machines:
This is a purchasing model for VMs that provides access to unused Azure compute capacity at a significant discount. While you could technically install an OS on a Spot VM and use it as a remote desktop, it is not a managed service for desktop virtualization. It lacks the centralized management, scaling, and broker services that AVD provides.
Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets:
This is a compute resource used to deploy and manage a set of identical, auto-scaling VMs. It is an infrastructure service for building scalable applications, not a dedicated desktop virtualization service. While AVD uses scale sets in its underlying infrastructure, the scale set itself is not the service that delivers virtual desktops.
Reference
Microsoft Learn: What is Azure Virtual Desktop? - The documentation states it is a "desktop and app virtualization service that runs on the cloud" and "enables a secure, remote desktop experience from anywhere."
Match the cloud service to the appropriate description.
To answer, drag the appropriate cloud service from the column on the left to its description
on the right. Each service may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
NOTE: Each correct match is worth one point.

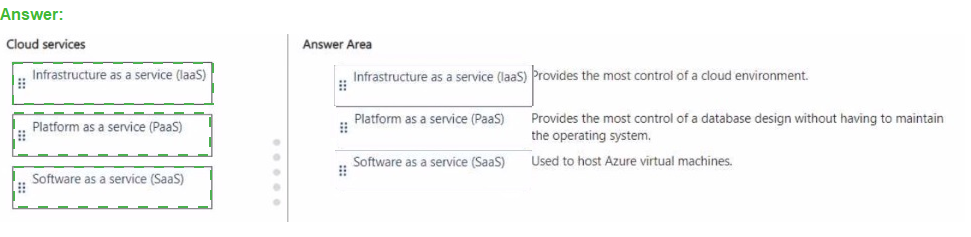
Summary
This question tests your understanding of the three primary cloud service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. The key differentiator is the level of control and management responsibility you have versus what the cloud provider manages for you. IaaS offers the most user control, PaaS abstracts the underlying infrastructure to let you focus on application and data, and SaaS provides a complete managed application.
Matching the Services to Descriptions
1. Provides the most control of a cloud environment.
Answer: i: Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Explanation: IaaS provides the highest level of control and management flexibility. You are responsible for managing the operating system, storage, networking, and applications deployed on the service. The cloud provider only manages the physical hardware, virtualization, and core networking. This is why it is used to host Azure Virtual Machines, as you have full control over the VM's configuration.
2. Provides the most control of a database design without having to maintain the operating system.
Answer: ii: Platform as a service (PaaS)
Explanation: This is a perfect description of PaaS. With a service like Azure SQL Database (a PaaS offering), you have full control over the database design, schemas, queries, and performance tuning. However, Microsoft manages the underlying operating system, software patching, and infrastructure, freeing you from those administrative tasks.
3. Used to host Azure virtual machines.
Answer: i: Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Explanation: Azure Virtual Machines are the foundational compute service of the IaaS category. When you deploy a VM, you are using an IaaS service because you are responsible for managing the guest OS, the software installed on it, and the configuration, while Azure manages the physical host and hypervisor.
Reference
Microsoft Learn: Compare cloud service models
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select
No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Summary
This question tests your understanding of the purpose and capabilities of Azure Service Health. It is a suite of services designed to keep you informed about the health of Azure services and planned maintenance, but it is a monitoring and alerting tool, not a proactive mitigation tool.
Statement 1: From Azure Service Health, an administrator can view the health of all the services deployed to an Azure environment and all the other services available in Azure.
Answer: Yes
Explanation: This statement is true. Azure Service Health provides a personalized dashboard that combines two key views. The Service Issues tab shows the health of the specific Azure services and regions you are using. The Azure Status tab provides a broader view of the global health of all Azure services worldwide, regardless of whether you use them. This gives a comprehensive view from personal to global.
Statement 2: From Azure Service Health, an administrator can create a rule to be alerted if an Azure service fails.
Answer: Yes
Explanation: This statement is true. A core feature of Azure Service Health is the ability to create Service Health alerts. You can configure these alerts to notify you (via email, SMS, webhook, etc.) when an Azure service you use is impacted by an incident, when planned maintenance is scheduled, or when a health advisory is issued. This allows for proactive response to service problems.
Statement 3: From Azure Service Health, an administrator can prevent a service failure from affecting a specific virtual machine.
Answer: No
Explanation:This statement is false. Azure Service Health is a communication and monitoring service. Its purpose is to inform you about service issues, not to prevent them. It cannot be used to take automated remediation actions, such as moving a VM to a different host or region to avoid an outage. Preventing service failure requires architectural decisions like deploying resources across Availability Zones or regions, which is configured outside of Service Health.
Reference
Microsoft Learn: What is Azure Service Health?
Microsoft Learn: Create Activity Log alerts on service notifications
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.
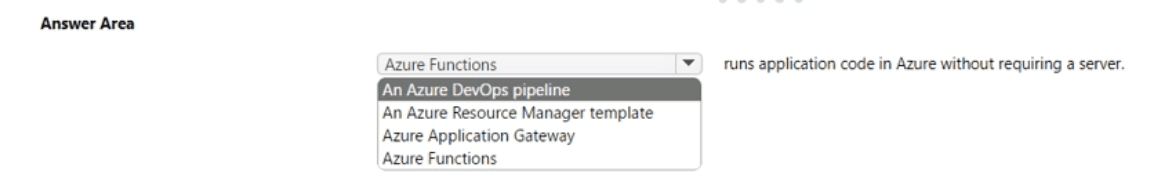
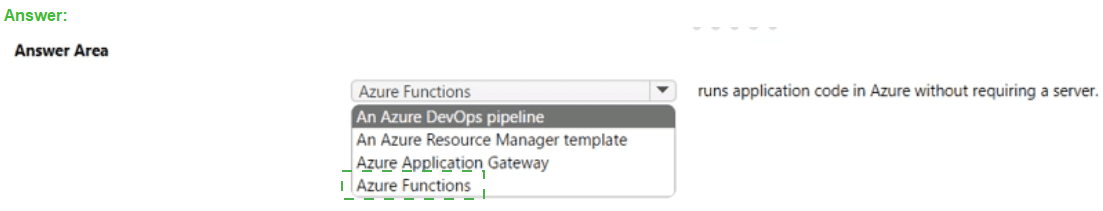
Summary:
This question tests your knowledge of serverless compute services in Azure. The key phrase is "without requiring a server," which is the core concept of a serverless architecture. In this model, the cloud provider fully manages the underlying infrastructure, allowing developers to focus solely on deploying their code.
Correct Option:
Azure Functions:
This is the correct answer. Azure Functions is a serverless compute service that allows you to run small pieces of code (functions) in response to events without worrying about the underlying application infrastructure. You do not need to provision or manage virtual machines, and you are only billed for the compute resources consumed while your code is running, making it a true "serverless" platform.
Incorrect Option:
An Azure Resource Manager template:
This is an infrastructure-as-code (IaC) service used to define and deploy Azure resources in a declarative JSON format. It is a tool for provisioning infrastructure (including servers), not for running application code without a server.
Azure Application Gateway:
This is a web traffic load balancer that manages traffic to web applications. It is a networking service for routing, SSL termination, and web application firewall (WAF) protection, not a platform for executing application code.
Reference
Microsoft Learn: What is Azure Functions? - The documentation states: "Azure Functions is a serverless solution that allows you to write less code, maintain less infrastructure, and save on costs... Azure handles all the infrastructure to run your code at scale."
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select
No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
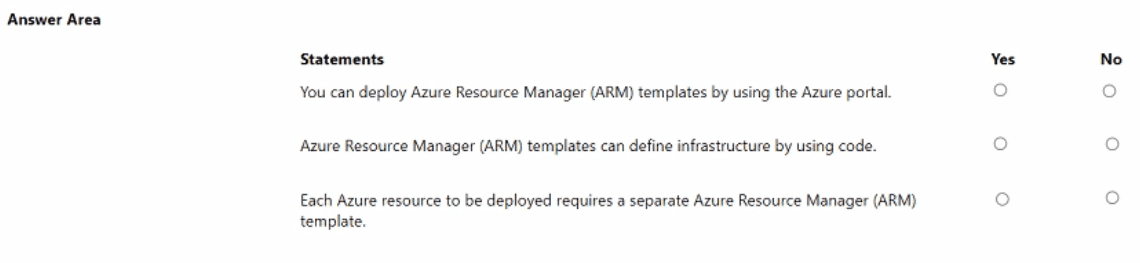

Summary
This question tests your understanding of the capabilities and usage of Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates. ARM templates are a form of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) used to define and deploy collections of Azure resources in a consistent and repeatable manner.
Statement 1: You can deploy Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates by using the Azure portal.
Answer: Yes
Explanation: This statement is true. The Azure portal provides a user-friendly interface for deploying ARM templates. You can use the "Custom deployment" option, which allows you to either build your own template or upload a JSON template file, fill in the required parameters, and initiate the deployment directly from the browser. ARM templates can also be deployed via PowerShell, Azure CLI, and REST API.
Statement 2: Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates can define infrastructure by using code.
Answer: Yes
Explanation: This statement is true and describes the core purpose of ARM templates. They are a declarative JSON or Bicep file that defines the infrastructure and configuration for your Azure solution. By using code to define your environment, you can version, review, and reliably replicate your deployments, which is a fundamental practice of Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
Statement 3: Each Azure resource to be deployed requires a separate Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template.
Answer: No
Explanation: This statement is false. A key strength of ARM templates is the ability to deploy an entire solution, consisting of multiple interdependent resources, in a single, coordinated operation. A single ARM template can define a complex environment including virtual networks, virtual machines, storage accounts, and databases, and manage the dependencies between them.
Reference
Microsoft Learn: What are ARM templates?
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select
No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Summary
This question tests your understanding of Azure Storage's core features, including data redundancy, geo-replication, and scalability. It's important to distinguish between data replication for durability within a region and a formal backup strategy, as well as to know the high scalability limits of the service.
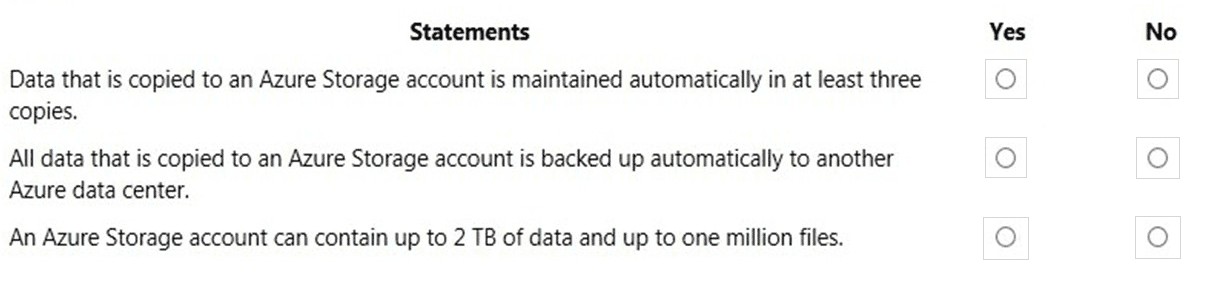
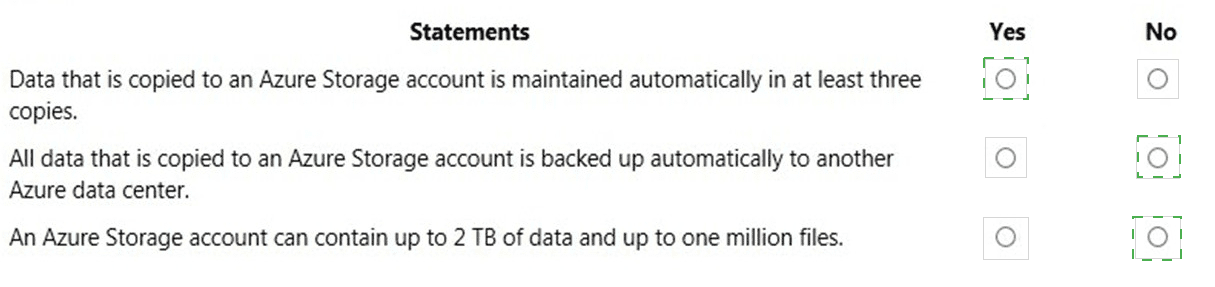
Statement 1: Data that is copied to an Azure Storage account is maintained automatically in at least three copies.
Answer: Yes
Explanation: This statement is true. By default, Locally Redundant Storage (LRS) is the minimum replication option for an Azure Storage account. LRS synchronously stores three copies of your data within a single datacenter in the primary region. This protects against hardware failures like a drive crash. All other redundancy options (GRS, ZRS, etc.) provide even higher durability.
Statement 2: All data that is copied to an Azure Storage account is backed up automatically to another Azure data center.
Answer: No
Explanation: This statement is false. While redundancy options like Geo-Redundant Storage (GRS) do replicate data to a secondary region, this is replication, not a backup. The key distinction is that a backup is a point-in-time copy protected from accidental deletion or corruption. If data is deleted or overwritten in the primary region, it is also deleted or overwritten in the secondary region. A separate backup solution, like Azure Backup, is required for protection against these scenarios.
Statement 3: An Azure Storage account can contain up to 2 TB of data and up to one million files.
Answer: No
Explanation: This statement is false and significantly understates the capacity of Azure Storage. A standard general-purpose v2 storage account has a maximum capacity of 5 PiB (over 5,000 TB). The limits for the number of files are also vastly higher. For example, an Azure File Share supports millions of files, and an Azure Blob Container has no practical limit on the number of blobs. The stated limits of 2 TB and one million files are far too low.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Azure Storage redundancy
Microsoft Learn: Azure Storage scalability and performance targets
You plan to map a network drive from several computers that run Windows 10 to Azure
Storage. You need to create a storage solution in Azure for the planned mapped drive.
What should you create?
A. an Azure SQL database
B. a virtual machine data disk
C. a Files service in a storage account
D. a Blobs service in a storage account
Summary
This question tests your knowledge of which Azure storage service provides a true network file share that is accessible via the standard Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. Mapping a network drive in Windows requires a service that presents a shared folder, which is distinct from database services, raw disk storage, or object storage designed for applications.
Correct Option
C. a Files service in a storage account:
This is the correct answer. Azure Files offers fully managed file shares in the cloud that are accessible using the standard SMB protocol. These shares can be mapped as a network drive on Windows, macOS, and Linux machines, just like a traditional file server. It is the ideal service for this scenario, providing a centralized, cloud-based location for file sharing.
Incorrect Option
A. an Azure SQL database:
This is a relational database service used for storing, processing, and querying structured data. It cannot be mapped as a network drive and is accessed via SQL commands, not the SMB file-sharing protocol.
B. a virtual machine data disk:
This is a virtual hard disk (VHD) attached to a specific Azure virtual machine. While you could share a folder from that VM, the disk itself is not a directly accessible network share. This solution would require you to manage the VM and its OS, which is not necessary when a managed service like Azure Files exists.
D. a Blobs service in a storage account:
Azure Blob Storage is an object storage service designed for storing massive amounts of unstructured data, such as text or binary data. It is accessed via REST APIs and does not natively support the SMB protocol for mapping as a network drive. While the Azure Blob Storage feature "NFS 3.0" exists, the standard and recommended way to map a drive from Windows is via SMB with Azure Files.
Reference
Microsoft Learn: What is Azure Files? - The documentation states: "Azure Files offers fully managed file shares in the cloud that are accessible via the industry standard Server Message Block (SMB) protocol."
Fill in the blank (_________________) is a highly secure loT solution that includes a microcontroller unit (MCU) and a customized Linux operating system.
Summary
This question describes a specific type of Azure IoT service: one that provides a pre-configured, secure, and integrated solution that includes both hardware (a microcontroller) and a customized operating system. This description points to a managed appliance designed to simplify the IoT journey, not a general-purpose application platform.
Correct Answer
Azure Sphere
Explanation
The correct answer is Azure Sphere. It is a comprehensive, highly secure IoT solution that includes three core components:
Azure Sphere Certified Microcontroller (MCU): The hardware unit that runs the OS and your application.
Azure Sphere OS: A custom, security-hardened Linux-based operating system that runs on the MCU.
Azure Sphere Security Service: A cloud-based service that provides continuous, renewable security for every Azure Sphere device.
This integrated approach of hardware, OS, and cloud service is what makes Azure Sphere unique and fits the description perfectly.
Incorrect Option
Azure IoT Central:
This is an incorrect answer. Azure IoT Central is a fully managed SaaS (Software as a Service) solution used to build, deploy, and manage enterprise-grade IoT applications. It is a high-level application platform that runs in the cloud and does not include or provide a microcontroller unit (MCU) or a customized Linux OS for devices.
Reference
Microsoft Learn: What is Azure Sphere? - The documentation states: "Azure Sphere is a secured, high-level application platform with built-in communication and security features for internet-connected devices. It comprises a secured, connected, crossover microcontroller (MCU), a custom high-level Linux-based operating system (OS), and a cloud-based security service that provides continuous, renewable security."
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
You have several virtual machines in an Azure subscription. You create a new subscription.
The virtual machines cannot be moved to the new subscription.
Instructions: Review the underlined text. If it makes the statement correct, select “No
change is needed”. If the statement is incorrect, select the answer choice that makes the
statement correct.
A. No change is needed
B. The virtual machines can be moved to the new subscription
C. The virtual machines can be moved to the new subscription only if they are all in the same resource group
D. The virtual machines can be moved to the new subscription only if they run Windows Server 2016.
Evaluation
The underlined text states: "The virtual machines cannot be moved to the new subscription."
This statement is incorrect.
Azure provides the capability to move most resources, including virtual machines, between different subscriptions. This is a common administrative task for reorganizing management, billing, or governance structures. The move can be initiated using the Azure portal, PowerShell, Azure CLI, or REST API.
Correct Answer
B. The virtual machines can be moved to the new subscription
Explanation of Other Options
A. No change is needed:
This is incorrect because the original statement is false. Virtual machines can be moved.
C. The virtual machines can be moved to the new subscription only if they are all in the same resource group:
This is incorrect. While it is often easier to move an entire resource group, you can move individual resources, including single VMs, between subscriptions. They do not all need to be in the same resource group to be moved.
D. The virtual machines can be moved to the new subscription only if they run Windows Server 2016:
This is incorrect. The ability to move a VM is a platform feature and is independent of the guest operating system (Windows, Linux, or any specific version) installed on the VM.
Reference
Microsoft Learn: Move resources to a new resource group or subscription - The documentation explicitly states: "You can move resources to a new subscription... You can move virtual machines (VM) to a new subscription..."
You have an Azure subscription.
You need to review your secure score.
What should you use?
A. Azure Monitor
B. Azure Advisor
C. Help - support
D. Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Summary:
This question tests your knowledge of the Azure service that is specifically designed for cloud security posture management. The "secure score" is a metric that measures your security posture by comparing your resource configurations against built-in security benchmarks and providing a numerical score and actionable recommendations to improve it.
Correct Option:
D. Microsoft Defender for Cloud:
This is the correct answer. Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides a secure score, which is a key feature for assessing and improving your security posture. It continuously assesses your resources, subscriptions, and organization against Azure Security Benchmark and other standards. It then calculates a percentage score and provides a prioritized list of security recommendations to help you harden your environment and increase your score.
Incorrect Option:
A. Azure Monitor:
This is a service for collecting, analyzing, and acting on telemetry from your cloud and on-premises environments. It is focused on performance monitoring, application insights, and log analytics, not on providing a centralized security assessment or secure score.
B. Azure Advisor:
This service provides personalized best practice recommendations to improve the reliability, security, performance, and cost of your resources. While it does provide some security recommendations, it does not provide the unified, centralized secure score metric that is a core feature of Microsoft Defender for Cloud
C. Help + support:
This section of the Azure portal is for managing support tickets, service health, and billing issues. It does not provide any tools for security assessment or a secure score.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: What is Microsoft Defender for Cloud?
Microsoft Learn: Secure score in Microsoft Defender for Cloud
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
You have an Azure virtual network named VNET1 in a resource group named RG1.
You assign an Azure policy specifying that virtual networks are not an allowed resource
type in RG1. VNET1 is deleted automatically.
Instructions: Review the underlined text. If it makes the statement correct, select “No
change is needed”. If the statement is incorrect, select the answer choice that makes the
statement correct.
A. No change is needed.
B. is moved automatically to another resource group
C. continues to function normally
D. is now a read-only object
Evaluation:
The underlined text states: "VNET1 is deleted automatically."
This statement is incorrect.
An Azure Policy that enforces a "not allowed resource types" rule is a deny policy. Its effect is preventative, not remedial. It prevents the creation of new non-compliant resources in the specified scope (like RG1). It does not automatically delete or modify existing resources that are already present and non-compliant.
Correct Answer:
C. continues to function normally
Explanation of Other Options:
A. No change is needed:
This is incorrect because the original statement is false. The policy does not automatically delete the virtual network.
B. is moved automatically to another resource group:
This is incorrect. Azure Policy does not have the capability to automatically move resources between resource groups. Resource movement is a manual or scripted operation.
D. is now a read-only object:
This is incorrect. While the resource is non-compliant with the policy, its operational status is not affected. You can still manage and configure the virtual network (e.g., add subnets, peer it to other VNets). The policy only blocks the creation of new ones.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Understand how Azure Policy works - The documentation explains that policies with a "Deny" effect prevent the creation of non-compliant resources. It does not state that they delete existing resources.
Microsoft Learn: Azure Policy definition structure - Deny - The "Deny" effect is used "to prevent a resource request that doesn't match defined standards through policy." It acts on resource creation requests.
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
Resource groups provide organizations with the ability to manage the compliance of Azure
resources across multiple subscriptions.
Instructions: Review the underlined text. If it makes the statement correct, select “No
change is needed”. If the statement is incorrect, select the answer choice that makes the
statement correct.
A. No change is needed
B. Management groups
C. Azure policies
D. Azure App Service plans
Summary:
Resource groups are logical containers for organizing Azure resources within a single subscription, not for managing compliance across multiple subscriptions. Azure Policy evaluates and enforces compliance rules at scale across subscriptions. Management groups organize subscriptions for governance, but the specific function of compliance management is performed by Azure Policy.
Correct Option:
C. Azure policies
Azure Policy enforces organizational standards and assesses compliance across resources in multiple subscriptions.
Uses policy definitions to audit, deny, or remediate non-compliant resources at scale.
Integrates with management groups for hierarchical policy application.
Incorrect Option:
A. No change is needed
Incorrect; resource groups are scoped to one subscription and cannot manage cross-subscription compliance.
They group resources for lifecycle and access control, not policy enforcement.
B. Management groups
Organize subscriptions for unified access and policy application, but do not directly manage compliance.
Serve as containers for Azure Policy and RBAC, not the compliance engine.
D. Azure App Service plans
Define hosting environment for web apps; unrelated to compliance or cross-subscription management.
Focus on compute scaling and pricing, not governance.
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/governance/policy/overview
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/governance/management-groups/overview
| Page 1 out of 42 Pages |