Topic 1: Exam Pool A
Which configuration enables a Cisco router lo send information to a TACACS+ server for individual EXEC commands associated with privilege level 15?
A. Router(config)# aaa accounting commands 15 default start-stop group tacacs+
B. Router(config)# aaa authorization exec default group tacacs+
C. Router(config)# aaa authorization commands 15 default group tacacs+
D. Router(config)# aaa accounting exec default start-stop group tacacs+
Summary
The question is about configuring accounting for specific commands on a Cisco router. AAA accounting is used to track what users are doing, such as logging the commands they execute. The requirement is to log individual EXEC commands that are associated with a specific privilege level (level 15, which is the highest) and send those logs to a TACACS+ server. The correct command must specify accounting for "commands" at a specific privilege level.
Correct Option
A. Router(config)# aaa accounting commands 15 default start-stop group tacacs+
This command is the only one that correctly enables accounting for individual commands at a specific privilege level.
aaa accounting:
This keyword enables the logging and tracking of user activity.
commands 15:
This specifies that the accounting should be applied to commands executed at privilege level 15.
default start-stop group tacacs+: This directs the router to record the start and stop time of each level 15 command and send that record to the TACACS+ server group.
Incorrect Options
B. Router(config)# aaa authorization exec default group tacacs+
This command configures authorization, not accounting. It determines whether a user is allowed to start an EXEC shell session (e.g., gain access to the CLI) after they have authenticated. It does not log which commands the user runs during that session.
C. Router(config)# aaa authorization commands 15 default group tacacs+
This command configures authorization for commands, not accounting. It checks with the TACACS+ server to see if the user is permitted to run each level 15 command. While it involves commands, its purpose is access control, not logging the commands that were actually executed.
D. Router(config)# aaa accounting exec default start-stop group tacacs+
This command configures accounting for the EXEC session itself, not for the individual commands within it. It would log when a user starts and stops a CLI session (e.g., logs in and logs out), but it would not record a history of the specific commands they typed.
Reference
Cisco IOS Security Command Reference - aaa accounting - The official command reference for aaa accounting details the syntax, including the commands and start-stop keywords, explaining how to enable accounting for commands at a specified privilege level.
Which two mechanisms are used with OAuth 2.0 for enhanced validation? (Choose two.)
A. custom headers
B. authentication
C. authorization
D. request management
E. accounting
Summary
OAuth 2.0 is an authorization framework that allows applications to obtain limited access to user accounts. To enhance the security of this process beyond the initial grant, two primary mechanisms are used to ensure that access tokens are presented by the legitimate client application to which they were issued, and not intercepted by an attacker. These mechanisms validate the client's identity in different ways.
Correct Options
A. Custom headers
One common method for enhanced validation is the use of a custom header, such as the X-Client-ID header.
By including the client identifier in a header, the authorization server can perform an additional check to ensure the request is coming from the expected application, providing an extra layer of security beyond the access token alone.
B. Authentication
OAuth 2.0 supports client authentication, where the client application proves its identity to the authorization server.
This is typically done using a client secret (a password for the app), a public/private key pair (using JWT assertions), or other credentials. This ensures that only the legitimate, registered client can exchange an authorization code for an access token or refresh a token.
Incorrect Options
C. Authorization
Authorization is the core purpose of the entire OAuth 2.0 framework itself. It is the process of granting permissions (scopes) to a client. It is not a specific mechanism used for enhanced validation; it is the primary outcome that the validation mechanisms help to secure.
D. Request management
This is a vague term and not a standard security mechanism within the OAuth 2.0 specification. While managing requests is part of any protocol, it is not defined as a specific feature for client or token validation like the other options.
E. Accounting
Accounting refers to the tracking and logging of user activities for auditing and billing purposes (as part of the AAA framework: Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting). OAuth 2.0 is concerned with delegation of access (authorization) and does not include a standardized accounting component.
Reference
OAuth 2.0 Security Best Current Practice - This IETF document outlines security best practices for OAuth 2.0. It extensively discusses the importance of client authentication (e.g., using client secrets or private keys) and recommends additional measures like sender-constraining tokens, which can be implemented using techniques akin to custom headers to bind the token to a specific client.
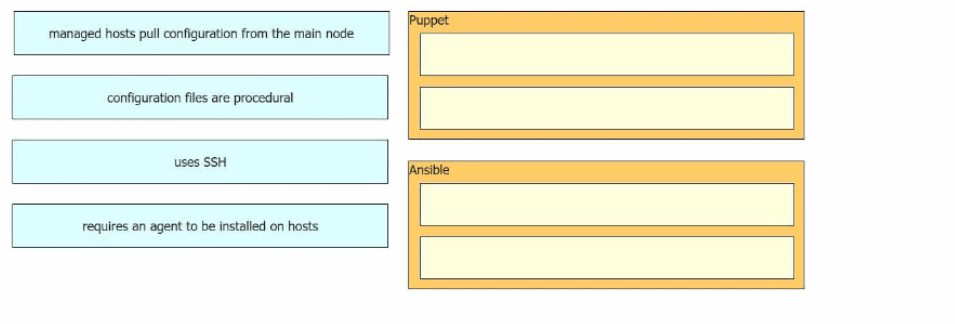
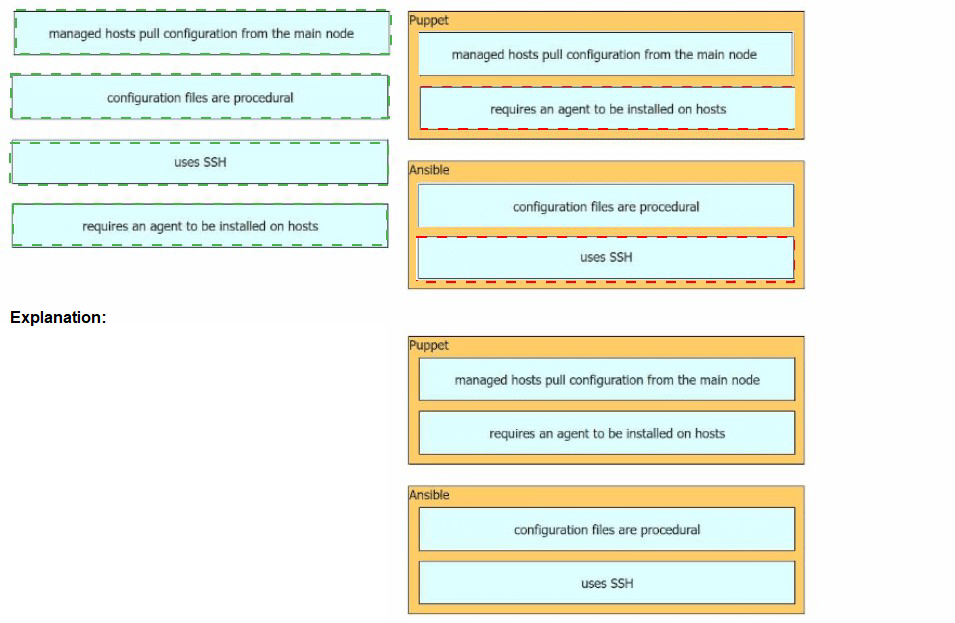
Drag and drop the characteristics from the left onto the corresponding orchestration tool on the right.
Which data is properly formatted with JSON?
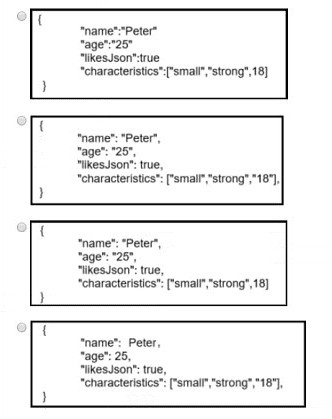
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Summary:
The question tests JSON syntax validation. Proper JSON requires double quotes around all keys and string values, proper comma placement, and correct bracket/bracing. Only one option follows RFC 8259 JSON standards with consistent double-quoted keys/values and correct object structure without trailing commas or syntax errors.
Correct Option:
C. Option C
All keys ("name", "age", "likes", "characteristics") use double quotes ✓
All string values use double quotes ✓
Numeric value "25" properly unquoted ✓
Boolean "true" properly unquoted ✓
Correct comma placement, no trailing comma ✓
Perfectly valid JSON per RFC 8259 standards
Incorrect Options:
A. Option A
Missing closing quote on "likes" value: likesJson (should be "likesJson")
Invalid JSON syntax - parser fails on unterminated string
B. Option B
Trailing comma after "strong" before closing bracket
JSON RFC 8259 prohibits trailing commas in objects/arrays
Parser error: Expected ':' after property name
D. Option D
Missing comma between "25" and "likes" properties
Parser error: Unexpected token l in JSON at position XX
Invalid property separator breaks object structure
Reference:
Cisco ENCOR 350-401 Official Cert Guide, Volume 1, Chapter 5: Automation and Programmability
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/training-events/training-certifications/exams/current-list/encor-350-401.html
JSON RFC 8259: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc8259
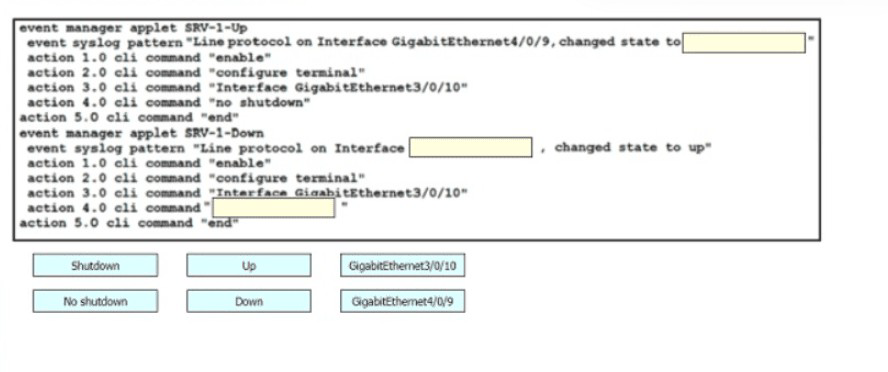
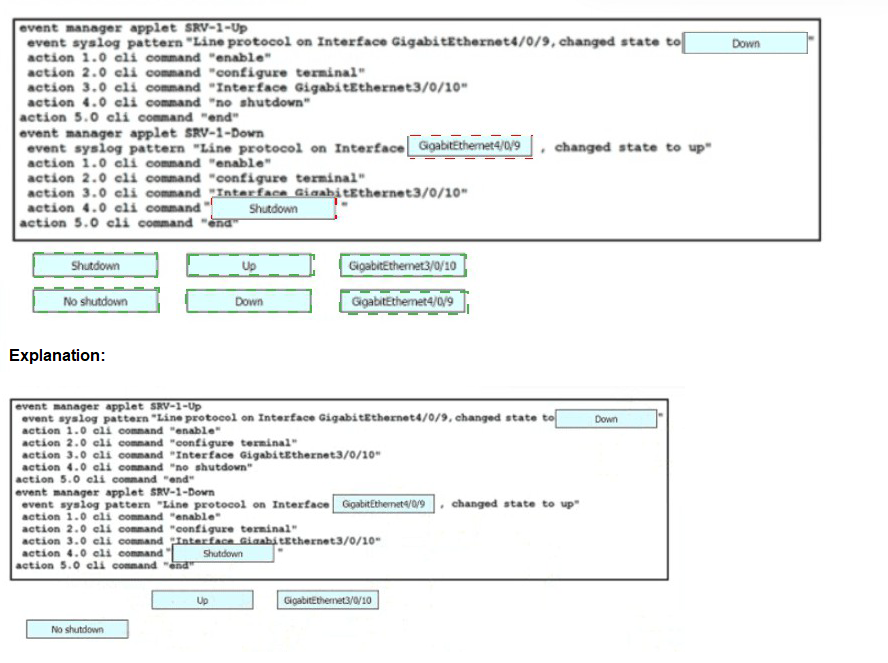
Drag and drop the snippets onto the blanks within the code to construct a script that brings up the failover Ethernet port if the primary port goes down and also shuts down the failover port when the primary returns to service. Not all options are used.
Which NGFW mode block flows crossing the firewall?
A. Passive
B. Tap
C. Inline tap
D. Inline
Summary
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) can operate in different deployment modes that determine how they interact with network traffic. The key distinction is whether the firewall is positioned directly in the traffic path or is monitoring a copy of the traffic from a separate device like a switch span port. Only a mode that places the firewall directly in the active forwarding path has the ability to block traffic in real-time.
Correct Option
D. Inline
Inline mode places the NGFW directly in the live network path between two network segments (e.g., between a router and a core switch).
Because all traffic must pass through the firewall, it can actively inspect and enforce policy.
If a packet or flow is found to be malicious or in violation of a security policy, the firewall can block it by dropping the packets, preventing them from reaching their destination.
This is the primary operational mode for enforcing security policy and blocking threats.
Incorrect Options
A. Passive
In Passive mode, the NGFW receives a copy of the traffic from a network tap or a SPAN port on a switch. It is not in the direct data path.
While it can analyze traffic and send alerts, it cannot block flows because it only sees a copy; the original traffic continues unimpeded through the network.
B. Tap
"Tap" mode is synonymous with Passive mode. The firewall is connected to a network tap, which provides a copy of all traffic for monitoring and analysis.
Like Passive mode, it is used for visibility and threat detection but lacks the capability to intercept and drop malicious traffic.
C. Inline Tap
Inline Tap mode (sometimes called "Inline Passive") is a hybrid. The firewall is deployed physically in the path, but it operates by forwarding all traffic, even if it would normally be blocked.
Its primary purpose is to gather extensive data and logs without affecting network availability. While it can be configured to send TCP resets to terminate sessions, it does not actively drop or block packets at the network layer like a true Inline firewall. The traffic flow is not blocked; it is allowed to pass while being monitored.
Reference
Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense Deployment Guide - Inline vs. Passive Modes - This official deployment guide explains the different modes, explicitly stating that Inline mode is required for blocking traffic, while Passive modes are used for monitoring.
Which two methods are used to assign security group tags to the user in a Cisco Trust Sec architecture? (Choose two.)
A. modular QoS
B. policy routing
C. web authentication
D. DHCP
E. IEEE 802.1x
Summary
Cisco TrustSec (CTS) uses Security Group Tags (SGTs) to classify endpoints and users with a security group identifier. This classification is the first critical step in implementing security policies based on group membership (e.g., "Contractors," "Finance") rather than just IP addresses. The assignment of an SGT can happen at the point of network access through various enforcement mechanisms.
Correct Options
C. Web authentication
Web Authentication (WebAuth) is a method where a user is assigned an SGT after successfully authenticating via a captive portal web page.
This is commonly used for guest access or on networks where 802.1X is not feasible. Once the user provides valid credentials, the network device (like a switch or wireless controller) assigns a pre-configured SGT (e.g., "Guest-SGT") to the user's traffic.
E. IEEE 802.1x
IEEE 802.1X is the primary and most robust method for assigning SGTs in a wired or wireless environment.
During the EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) exchange, the user's credentials are validated by an authentication server (like Cisco ISE). The server can return an SGT as part of the authorization result, which the network device (the authenticator) then applies to all traffic from that user.
Incorrect Options
A. Modular QoS
Modular QoS (MQC) is a framework for implementing quality of service policies to manage bandwidth, delay, jitter, and loss. While QoS policies can be applied based on an SGT, MQC is not a method used to assign the SGT to a user in the first place.
B. Policy routing
Policy-Based Routing (PBR) is a technique for overriding the default routing behavior and steering traffic based on defined policies. Similar to QoS, PBR can use an SGT as a match condition for its policy, but it is not a mechanism for assigning the SGT to the user's session.
D. DHCP
While it is technically possible in some legacy or specific implementations to assign an SGT based on an IP address learned via DHCP, this is not a primary or dynamic method tied to user identity. The SGT is bound to the IP address, not the user, which is less secure and scalable than methods like 802.1X that assign the SGT directly to the authenticated session.
Reference
Cisco TrustSec Configuration Guide, Security Group Tag Assignment - This official configuration guide details the various methods for SGT assignment, explicitly listing 802.1X and Web Authentication as key methods.
Which three methods does Cisco Catalyst Center (formerly DNA Center) use to discover devices? (Choose three.)
A. SNMP
B. a specified range of IP addresses
C. NETCONF
D. LLDP
E. ping
F. CDP
Summary
Cisco Catalyst Center (formerly DNA Center) performs network discovery to build an inventory of the devices it will manage. Discovery is the first step in the provisioning process. It uses a combination of Layer 3 reachability protocols to find devices and Layer 2 protocols to gather detailed topology and neighbor information about them.
Correct Options
B. a specified range of IP addresses
This is a fundamental discovery method. You provide Catalyst Center with one or more IP address ranges or subnets.
Catalyst Center then uses this list as a target for its discovery probes (like ICMP ping and SNMP) to find and identify devices within those network segments.
D. LLDP
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral Layer 2 protocol used by Catalyst Center to discover detailed information about directly connected neighbors.
After a device is initially found via an IP range, Catalyst Center uses LLDP to learn about physical connectivity, device capabilities, and to build an accurate network topology map.
F. CDP
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Cisco-proprietary Layer 2 protocol that serves the same essential purpose as LLDP but is specific to Cisco devices.
Catalyst Center uses CDP to gather rich information from neighboring Cisco devices, such as model, software version, and IP addresses, which greatly enhances the discovery process and topology rendering
Incorrect Options
A. SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is not primarily a discovery method in this context. Instead, it is a data collection protocol used after a device has been discovered via an IP range.
Once a device responds to a ping, Catalyst Center uses SNMP to read its Management Information Base (MIB) to collect detailed inventory data (serial number, IOS version, interface details, etc.).
C. NETCONF
NETCONF is a protocol used for device configuration and management, not for initial network discovery. It is used by Catalyst Center for advanced provisioning and Day-N operations on devices that support it, but it relies on the device already being discovered and reachable.
E. ping
Ping (ICMP Echo) is the underlying mechanism used to check the reachability of an IP address within a specified range. However, it is not listed as a separate "discovery method" in the Catalyst Center GUI. It is the tool used to fulfill the "IP Address Range" discovery method. A device must respond to ping to be considered "reachable" before Catalyst Center proceeds to probe it with SNMP, CDP, etc.
Reference
Cisco Catalyst Center User Guide - Discover Your Network - The official user guide for Catalyst Center details the discovery process, explicitly stating that you define discovery jobs using "IP address ranges or subnets" and that the system uses protocols like CDP and LLDP to build the network topology.
Which mobility role is assigned to a client in the client table of the new controller after a Layer 3 roam?
A. anchor
B. foreign
C. mobility
D. transparent
Summary
In a Cisco wireless network with multiple controllers in a mobility group, a Layer 3 roam occurs when a client moves to a new subnet controlled by a different WLC. To maintain the client's IP address and session, the controllers establish a mobility tunnel. The original controller that the client first associated with maintains its role, while the new controller takes on a specific, different role to facilitate the connection.
Correct Option
B. Foreign
After a Layer 3 roam, the client is registered with a new Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) in a different subnet.
This new WLC is assigned the Foreign role for that client
The Foreign controller's responsibility is to forward the client's data traffic through a secure EoIP (Ethernet over IP) tunnel, known as a mobility tunnel, back to the client's original WLC.
The original WLC retains the Anchor role, which is the point where the client's traffic enters the wired network, preserving the client's IP address and session state.
Incorrect Options
A. Anchor
The Anchor role is assigned to the original controller that the client first associated with, not the new controller. This role is maintained throughout the client's session to anchor the client's IP subnet and provide consistent policy enforcement.
C. Mobility
"Mobility" is the name of the overall feature and the protocol (Mobility Messages) that the controllers use to communicate. It is not a specific role assigned to a client in the client table.
D. Transparent
"Transparent" is not a valid client mobility role in Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers. The primary roles in a mobility setup are Anchor and Foreign.
Reference
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide, Layer 3 Roaming - This official documentation explains the Layer 3 roaming process and explicitly describes the roles of the Anchor and Foreign controllers in maintaining client connectivity across subnets.
Which features does Cisco EDR use to provide threat detection and response protection?
A. containment, threat intelligence, and machine learning
B. firewalling and intrusion prevention
C. container-based agents
D. cloud analysts and endpoint firewall controls
Summary
Cisco Secure Endpoint (formerly Advanced Malware Protection - AMP for Endpoints) is an Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solution. It goes beyond traditional signature-based antivirus by using advanced techniques to detect, analyze, and respond to sophisticated threats that evade other security layers. Its core value lies in continuous recording, behavioral analysis, and global threat intelligence.
Correct Option
A. containment, threat intelligence, and machine learning
Containment:
This is a critical EDR response action. When a malicious process or file is identified, Cisco Secure Endpoint can automatically isolate or "contain" the endpoint from the network to prevent the threat from spreading, while allowing time for an analyst to investigate.
Threat Intelligence:
The service leverages Cisco's global threat intelligence, Talos, one of the largest commercial threat intelligence teams in the world. This provides context and correlates endpoint activity with known malicious campaigns, IPs, domains, and file hashes.
Machine Learning:
It uses machine learning models to analyze file behavior and attributes to detect never-before-seen (zero-day) malware and suspicious activities without relying solely on known signatures.
Incorrect Options
B. firewalling and intrusion prevention
While a host-based firewall and intrusion prevention (IPS) are valuable security features, they are typically associated with traditional security suites or IPS solutions, not the core, defining features of a modern EDR platform like Cisco Secure Endpoint. EDR focuses on detection and response post-breach, whereas IPS is a preventative control.
C. container-based agents
This is a deployment or isolation technology, not a primary feature for threat detection. The endpoint agent's analysis may occur in a secure, containerized environment, but "container-based agents" is not a marketed core capability for threat detection and response.
D. cloud analysts and endpoint firewall controls
While Cisco Secure Endpoint does include a cloud-based management console and may have firewall controls, this option is misleading. "Cloud analysts" refers to human-driven services (Managed Detection and Response), which is a separate offering. The core product's automated protection is not primarily defined by these features.
Reference
Cisco Secure Endpoint Data Sheet - The official data sheet for Cisco Secure Endpoint explicitly lists its key capabilities, including "Behavioral Analytics and Machine Learning," "Global Threat Intelligence," and "Orchestrated Containment," which directly correspond to the features in the correct answer.
How does Cisco DNA Center perform a network discovery?
A. using SNMP
B. using ICMP
C. through a DHCP server
D. using CDP with a seed IP address
Summary
Cisco DNA Center (now Catalyst Center) uses a comprehensive, multi-protocol process to discover and profile network devices. The process begins by defining a discovery job with specific parameters, most importantly a starting point or range of IP addresses. The system then uses a sequence of protocols to first find devices and then collect detailed information from them.
Correct Option
D. using CDP with a seed IP address
This is the most accurate description of the initial phase of a typical discovery process.
A seed IP address is configured as the starting point for the discovery. This is typically the IP address of a known, core network device like a distribution switch or a router.
DNA Center then uses Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), a Layer 2 protocol, to query this seed device for its directly connected neighbors.
This creates a "chain of discovery" where DNA Center learns about neighboring devices from the seed and then uses that information to discover further devices, effectively crawling the network topology.
Incorrect Options
A. using SNMP
SNMP is critical, but it is not the primary discovery method. SNMP is used after a device has been found (via the seed/CDP process or an IP range) to gather detailed inventory information like serial numbers, IOS versions, and interface configurations. It is a data collection protocol, not the initial finding mechanism.
B. using ICMP
ICMP (ping) is a component, but not the complete process. Ping is used to check the reachability of an IP address within a specified range. However, discovery is not performed only with ICMP. ICMP merely confirms a device is online before DNA Center proceeds to use CDP, SNMP, and other protocols to actually identify and profile it
C. through a DHCP server
While DNA Center can potentially use DHCP logs as one of many data sources for endpoint visibility, it is not the primary method for discovering network infrastructure devices like switches and routers. Network devices typically have static IP addresses and are not discovered via DHCP.
Reference
Cisco Catalyst Center User Guide - Create a Discovery - The official user guide explains the discovery process, detailing how to configure a discovery job using a seed device and the protocols (like CDP) used to explore the network from that starting point.
A customer has several small branches and wants to deploy a Wi-Fi solution with local management using CAPWAP. Which deployment model meets this requirement?
A. local mode
B. SD-Access wireless
C. autonomous
D. Mobility Express
Summary
The requirement specifies two key points: a solution for small branches and the use of CAPWAP with local management. CAPWAP is the protocol used between a lightweight access point (LAP) and a Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). "Local management" means the WLC function must be on-site at the branch, not centralized in a data center. The solution must be cost-effective and designed for a smaller scale.
Correct Option
D. Mobility Express
Mobility Express is a controller-based solution specifically designed for small to medium-sized deployments, such as branch offices.
It uses the CAPWAP protocol between access points.
The key feature is that the WLC function is virtualized and runs on one of the access points (a Master AP) locally at the branch, fulfilling the "local management" requirement.
This provides all the benefits of a centralized WLC (like ease of management and policy enforcement) but in a low-cost, on-premises form factor ideal for branches.
Incorrect Options
A. Local mode
"Local mode" is an operational mode for a lightweight access point (LAP) in a traditional controller-based architecture, not a deployment model itself. The LAP in local mode connects to a physical, external WLC. This WLC could be centralized, not necessarily local to the branch, and would be an expensive over-provisioning for a small branch.
B. SD-Access wireless
SD-Access is an enterprise-grade, intent-based networking solution that uses CAPWAP. However, it relies on a centralized Cisco DNA Center for management and policy orchestration and typically uses physical or virtual WLCs in a central location. It does not provide the simple, standalone local management required for several independent small branches.
C. Autonomous
Autonomous deployment uses standalone, "thick" or "fat" access points that operate independently. While this provides local management, it does not use the CAPWAP protocol. Autonomous APs run their own IOS and are managed individually, which becomes difficult to scale and manage across several branches compared to a controller-based solution like Mobility Express.
Reference
Cisco Mobility Express Data Sheet - The official data sheet describes Mobility Express as a "controllerless" solution for small and medium-sized networks where the controller is embedded within an access point, using CAPWAP for communication with other APs. This directly matches the requirement for local CAPWAP-based management in small branches.
| Page 1 out of 30 Pages |