Topic 1: Exam Pool A
Which solution simplifies management of secure access to network resources?
A. TrustSec to logically group internal user environments and assign policies
B. ISE to automate network access control leveraging RADIUS AV pairs
C. RFC 3580-based solution to enable authenticated access leveraging RADIUS and AV pairs
D. 802 1AE to secure communication in the network domain
Summary
The question focuses on a solution that simplifies management of secure access. While several options provide secure access, the key is centralized automation and policy abstraction. This involves moving away from managing complex, device-specific configurations (like ACLs) and instead using a central policy server to define access based on user and device identity, which is then automatically enforced across the network.
Correct Option
A. TrustSec to logically group internal user environments and assign policies
Cisco TrustSec is designed specifically to simplify policy management. It achieves this by decoupling policy from the network topology and IP addresses.
It uses Security Group Tags (SGTs) to logically group users and endpoints (e.g., "Employees," "Contractors," "Finance-Servers").
Access policies (Security Group Access Control Lists or SGACLs) are then defined once based on these groups (e.g., "Contractors cannot access Finance-Servers").
This is much simpler than managing thousands of IP-based ACLs on individual devices, as the policy follows the user/device regardless of their location in the network.
Incorrect Options
B. ISE to automate network access control leveraging RADIUS AV pairs
While Cisco ISE is the policy engine that enables TrustSec, this answer is too narrow. It focuses on the low-level mechanism (RADIUS AV pairs) that ISE uses to communicate with network devices. The question is about the overarching solution that simplifies management, which is the TrustSec architecture that ISE implements.
C. RFC 3580-based solution to enable authenticated access leveraging RADIUS and AV pairs
RFC 3580 defines standard RADIUS attributes for enforcing VLAN assignment and basic access. This is a foundational technology for 802.1X but is a manual, standards-based component. It lacks the higher-level abstraction and simplification offered by the group-based policy model of TrustSec.
D. 802.1AE to secure communication in the network domain
IEEE 802.1AE (MACsec) provides link-layer encryption for data confidentiality and integrity between devices. It is a protocol for securing data in-transit on the wire. It does not simplify the management of access to resources; it secures the path after access has been granted.
Reference
Cisco TrustSec Solution Overview - The official solution page for TrustSec explains its core value proposition: "Simplify policy management" by using group-based policies that are independent of IP addresses, which directly answers the question.
An engineer must create an EEM script to enable OSPF debugging in the event the OSPF neighborship goes down. Which script must the engineer apply?
A. event manager applet ENABLE_OSPF_DEBUG
event syslog pattern "%OSPF-1-ADJCHG: Process 5. Nbr 1.1.1.1 on SerialO/0 from
FULL to DOWN"
action 1.0 cli command "debug ip ospf event"
action 2.0 cli command "debug ip ospf adj"
action 3.0 syslog priority informational msg "ENABLE_OSPF_DEBUG
B. event manager applet ENABLEOSPFDEBUG
event syslog pattern "%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 5, Nbr 1.1.1.1 on SerialO/0 from
LOADING to FULL"
action 1.0 cli command "debug ip ospf event"
action 2.0 cli command "debug ip ospf adj"
action 3.0 syslog priority informational msg "ENABLE JDSPF_DEBUG"
C. event manager apple! ENABLE OSPFDEBUG
event syslog pattern "%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 5. Nbr 1.1.1.1 on SerialO/0 from
LOADING to FULL"
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "debug ip ospf event"
action 3.0 cli command "debug ip ospf adj"
action 4.0 syslog priority informational msg "ENABLE_OSPFJ} EBUG"
D. event manager applet ENABLE_OSPF_DEBUG
event syslog pattern "%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 6. Nbr 1.1.1.1 on SerialO/0 from
FULL to DOWN"
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "debug ip ospf event"
action 3.0 cli command "debug ip ospf adj"
action 4.0 syslog priority informational msg "ENABLE_OSPF_DEBUG'*
Summary
The requirement is to create an EEM applet that triggers when an OSPF neighborship goes down and then enables debugging. The correct script must have two key components: 1) An event that matches the exact syslog message generated when a neighbor transitions to the "DOWN" state, and 2) A series of actions that enter the correct commands to enable the necessary OSPF debug.
Correct Option
D. event manager applet ENABLE_OSPF_DEBUG event syslog pattern "%OSPF-5-ADJCHG:
Process 6. Nbr 1.1.1.1 on SerialO/0 from FULL to DOWN" action 1.0 cli command "enable" action 2.0 cli command "debug ip ospf event" action 3.0 cli command "debug ip ospf adj" action 4.0 syslog priority informational msg "ENABLE_OSPF_DEBUG'"
Event: The syslog pattern correctly matches the critical part of the message: from FULL to DOWN. This is the specific state change that indicates a neighborship has failed, which is the exact trigger requested.
Actions: The sequence of actions is correct and complete:
action 1.0 cli command "enable": This enters privileged EXEC mode, which is required to execute the debug commands.
action 2.0 and 3.0: These enable the two most relevant OSPF debugs for troubleshooting neighbor adjacency issues: debug ip ospf event and debug ip ospf adj.
Incorrect Options
A.
Event: The event pattern uses %OSPF-1-ADJCHG. OSPF adjacency change messages are typically severity level 5 (Notifications), not level 1 (Alerts). This pattern may not match the actual syslog message generated by the router, causing the applet to never run.
B.
Event: The event pattern triggers on a transition from LOADING to FULL. This indicates a neighborship is being established, not going down. This script would enable debug when the problem is resolving itself, which is the opposite of the requirement.
C.
Event: The event pattern has the same error as Option B; it triggers on the neighbor coming up (from LOADING to FULL), not going down.
Syntax: The applet name has a critical typo (apple! instead of applet), which would cause the configuration to be rejected.
Reference
Cisco IOS EEM Configuration Guide - The official documentation details the syntax for the event syslog and action cli command statements. It confirms that the pattern must match the exact syslog message and that CLI commands are executed in the order specified.
Which next generation firewall feature supports separate security services for multiple departments?
A. state sharing mode to .trade the user data sessions and replication to the neighbor firewall using a failover link
B. Layer 3 mode with resource tracking capabilities and automatic configuration synchronization between the nodes and security zones
C. multicontext mode with specific logical or physical interface allocation within each context and grouped into security zones
D. virtual switch mode to provide traffic inspection capabilities for the flows entering the firewall and dropping packets based on policy configuration
Summary
The requirement is to provide separate security services for multiple departments within a single physical firewall. This is a classic use case for virtualization or segmentation at the firewall level. The solution must allow the creation of multiple, logically independent firewalls, each with its own policies, interfaces, and security configurations, to serve different departments as if they were using separate physical appliances.
Correct Option
C. multicontext mode with specific logical or physical interface allocation within each context and grouped into security zones
Multicontext mode (also known as Virtual Firewall or Context mode) is specifically designed for this purpose. It partitions a single physical NGFW into multiple, independent logical firewalls (called security contexts).
Each context can be assigned to a different department, with its own:
Dedicated interfaces (physical or logical/sub-interfaces).
Unique security policies (ACLs, NAT rules, inspection policies).
Isolated routing tables and administrative control.
Grouping interfaces into security zones within each context allows for the application of modern, zone-based policies. This provides complete separation and customized security for each department on a shared hardware platform.
Incorrect Options
A. state sharing mode to trade the user data sessions and replication to the neighbor firewall using a failover link
This describes high availability (HA) or failover functionality. Stateful failover synchronizes session state information between two physical firewalls to provide redundancy in case one fails. It does not create separate security domains for different departments within a single firewall.
B. Layer 3 mode with resource tracking capabilities and automatic configuration synchronization between the nodes and security zones
"Layer 3 mode" is a standard routing deployment for a firewall. "Resource tracking" is often used for monitoring interface status for failover, and "automatic configuration synchronization" is again an HA feature. This describes a resilient single-context firewall, not a segmented multi-tenant one.
D. virtual switch mode to provide traffic inspection capabilities for the flows entering the firewall and dropping packets based on policy configuration
Virtual Wire or Transparent (Layer 2) mode deploys the firewall as a "bump in the wire" that is not a routed hop. While it can inspect and drop traffic, it operates as a single, flat security domain. It does not support the creation of multiple, separate virtual firewalls with independent policies for different departments.
Reference
Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense Configuration Guide, Multiple Context Mode - The official documentation explains that multiple context mode creates multiple virtual firewalls, each with its own configuration and security policies, which is the exact feature that supports separate services for multiple departments.
Which task Is mandatory when provisioning a device through the plug-and-play workflow in Cisco DNA Center?
A. site assignment
B. slack serial number assignment
C. golden image upgrade
D. template configuration application
Summary
Cisco DNA Center's Plug and Play (PnP) workflow automates the onboarding of new devices. The process involves claiming a device, which binds its serial number to the DNA Center inventory. However, for the device to receive its final configuration and become operational in the network, it must be placed within the logical site hierarchy. This step is essential for applying the correct IP addressing, policies, and configurations specific to its physical location.
Correct Option
A. site assignment
Site assignment is a mandatory step in the PnP provisioning workflow.
The site hierarchy in DNA Center defines the network's physical and logical structure (e.g., Building > Floor).
Assigning a device to a specific site is crucial because it determines which IP address pools, configurations, and policies are applied to the device based on its location.
Without a site assignment, DNA Center does not know which context-specific configuration (like an IP address from the correct pool) to push to the device, preventing it from being fully provisioned.
Incorrect Options
B. slack serial number assignment
This appears to be a typo or distractor. "Slack" is a collaboration tool and is not part of the DNA Center PnP process. The device's serial number is used to claim the device, but "assigning" it via Slack is not a step in the workflow.
C. golden image upgrade
While a common best practice, upgrading the device's OS image to a "golden" standard is not mandatory for basic PnP provisioning. The primary goal of PnP is to get the device configured and on the network. An image upgrade can be part of the workflow, but the device can be provisioned with its existing OS version.
D. template configuration application
Applying a configuration template is a highly common and powerful feature of PnP, but it is not strictly mandatory. A device can be provisioned using a CLI template or by other means. The absolute mandatory step that provides the necessary context for any configuration (whether via template or not) is assigning the device to a site.
Reference
Cisco DNA Center User Guide - Provision a Device Using Plug and Play - The official user guide for DNA Center's PnP workflow will consistently show that assigning a device to a site is a required step in the provisioning process to provide the device with its location-specific configuration.
In Cisco CatalystCenter(formerly DNA Center) Inventory, the Software Version of a networkdevice displays a status of OUTDATED. What does It me?
A. There is a later software version available on Cisco Catalyst Center (formerly DNA Center).
B. The current software image does not match the selected Golden image for this type of network device.
C. The current type of software image does not match the type of the network device.
D. There is a later software version available at www.cisco.com website.
Summary
The "OUTDATED" status in the Catalyst Center inventory is a result of its integrated Software Image Management (SWIM) feature. Catalyst Center maintains a repository of software images and allows administrators to define a "golden" or standard image for specific device models or roles. The status is an internal comparison between the image running on the device and the standard defined within the Catalyst Center system itself.
Correct Option
B. The current software image does not match the selected Golden image for this type of network device.
This status is generated by Catalyst Center's internal compliance checking.
An administrator defines a "Golden Image" (the desired standard version) for a specific device type or group within the Catalyst Center software repository.
Catalyst Center then compares the version running on each device against this predefined standard.
If the versions do not match, the device is flagged as "OUTDATED," indicating it is not compliant with the internal corporate software policy set in Catalyst Center.
Incorrect Options
A. There is a later software version available on Cisco Catalyst Center (formerly DNA Center).
While this is often true, it is not the specific meaning of the "OUTDATED" status. The status is a direct result of a policy violation (mismatch with the Golden Image), not a simple notification that a newer file exists in the repository. A device could be running an older version but not be "OUTDATED" if no Golden Image has been set for it.
C. The current type of software image does not match the type of the network device.
This describes an incompatible image, which would likely cause the device to fail to boot or operate correctly. Catalyst Center would report a more critical error (like a failure) during a compliance check, not simply an "OUTDATED" status.
D. There is a later software version available at www.cisco.com website.
The "OUTDATED" status is an internal comparison within the Catalyst Center system against its own repository and policies. It does not perform a real-time check against the public Cisco.com website to determine this status. The external availability of a newer version is irrelevant to the internal policy compliance flag.
Reference
Cisco Catalyst Center Administrator Guide, Manage Software Images - The official guide explains the Golden Image concept and how Catalyst Center uses it to report on device image compliance, which is the direct source of the "OUTDATED" status.
What does the LAP send when multiple WLCs respond to the CISCO_CAPWAPCONTROLLER. localdomain hostname during the CAPWAP discovery and join process?
A. broadcast discover request
B. join request to all the WLCs
C. unicast discovery request to each WLC
D. Unicast discovery request to the first WLS that resolves the domain name
Summary
During the CAPWAP discovery process, a Lightweight AP (LAP) uses several methods to find potential Wireless LAN Controllers (WLCs). One method is a DNS lookup for the domain CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER.localdomain. If multiple WLCs are registered under this hostname, the DNS server returns the IP addresses of all of them. The AP must then initiate communication with each controller to gather information and decide which one to join.
Correct Option
C. unicast discovery request to each WLC
When the DNS lookup for CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER.localdomain returns multiple IP addresses, the AP has a list of potential controllers.
The AP does not broadcast or join at this stage. Instead, it sends a unicast CAPWAP Discovery Request message individually to the IP address of each WLC that was in the DNS response.
Each WLC that receives this request will reply with a CAPWAP Discovery Response, providing the AP with information (like controller load and capacity) that the AP uses to select the best WLC to send a final Join Request.
Incorrect Options
A. broadcast discover request
A broadcast discovery is a separate, initial discovery method (specifically, a CAPWAP broadcast on the local subnet). It is not the method used when the AP has already obtained a specific list of WLC IP addresses via DNS.
B. join request to all the WLCs
The AP sends a Join Request only to the single, best WLC it selects after evaluating all the Discovery Responses. Sending a Join Request to all WLCs would attempt to register with multiple controllers simultaneously, which is not how the process works.
D. Unicast discovery request to the first WLS that resolves the domain name
The AP does not just contact the first WLC in the list. It sends a unicast discovery request to every WLC IP address it received from the DNS server. This allows it to gather information from all available controllers and make an informed decision based on factors like controller load, rather than just picking the first one arbitrarily.
Reference
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide, AP Join Process - This official documentation details the CAPWAP discovery and join process, explaining that the AP discovers controllers through multiple methods, including DNS, and then sends unicast discovery requests to the discovered addresses.
What is a characteristic of the Cisco Catalyst Center (formerly DNA Center) Template Editor feature?
A. It facilitates software upgrades to network devices from a central point.
B. It facilitates a vulnerability assessment of the network devices.
C. It uses a predefined configuration through parameterized elements or variables.
D. It provides a high-level overview of the health of every network device.
Summary
The Cisco Catalyst Center Template Editor is a feature within the Design workflow used for network provisioning and Day-N configuration. Its primary purpose is to automate the deployment of device configurations by creating reusable configuration snippets. Instead of manually configuring each device, an administrator creates a template with variables, and Catalyst Center replaces these variables with specific values for each device.
Correct Option
C. It uses a predefined configuration through parameterized elements or variables.
This is the core characteristic of the Template Editor. It allows you to create a "master" configuration template with placeholders for device-specific information.
These placeholders, or variables (e.g., {{hostname}}, {{loopback_ip}}), are defined using a specific syntax.
When the template is applied to a device or a group of devices, Catalyst Center prompts for the values for these variables, allowing a single template to be customized and deployed to many different devices automatically.
Incorrect Options
A. It facilitates software upgrades to network devices from a central point.
This describes the Software Image Management (SWIM) feature of Catalyst Center. While templates can be part of a Day-0 provisioning workflow that includes an upgrade, the Template Editor itself is for configuration, not for managing and distributing software images.
B. It facilitates a vulnerability assessment of the network devices.
This describes a function of the Assurance component in Catalyst Center. It uses telemetry and analytics to identify security vulnerabilities and network issues, which is a separate function from the configuration provisioning done by the Template Editor.
D. It provides a high-level overview of the health of every network device.
This is also a function of the Assurance component. The Health dashboard in Catalyst Center provides this overview by collecting and analyzing data from devices, which is unrelated to the configuration template creation and deployment tool.
Reference
Cisco Catalyst Center User Guide, Create a Template - The official user guide for creating templates explains how to use variables and parameterized elements to create flexible configurations for deployment to multiple devices.
What is one advantage of using a data modeling language to develop an API client application?
A. Increase in compatibility
B. easier feature extensibility
C. stronger security properties
D. lower resource requirements
Summary
A data modeling language like YANG defines a strict contract for the structure, semantics, and constraints of the data exchanged via an API. This contract is shared between the server (network device) and the client (management application). When the API evolves, this model makes it easier to understand and integrate new features, data nodes, and capabilities without breaking existing client functionality or requiring a complete redesign.
Correct Option
B. easier feature extensibility
A data model acts as a formal, versioned schema for the API. When new features are added to the device (e.g., a new protocol or configuration knob), they are added as new nodes in the data model.
An API client built to consume the model can be designed to be more adaptable. It can discover new parts of the model, handle them gracefully, or be updated more reliably because the changes are structured and documented.
This structured approach makes it significantly easier to extend the API with new features over time compared to less structured methods like screen-scraping CLI output.
Incorrect Options
A. Increase in compatibility
While data models can improve interoperability, "compatibility" is often a result of adhering to standards, not a direct advantage of the modeling language itself. In fact, introducing new features in a model can sometimes create compatibility challenges with older clients that do not understand the new schema.
C. stronger security properties
Security is primarily achieved through the transport protocol (e.g., TLS), authentication, and authorization mechanisms (e.g., OAuth, API keys). A data model defines structure, not security. While it can help validate input to prevent certain errors, it does not inherently provide "stronger security properties."
D. lower resource requirements
Using a data modeling language does not necessarily lead to lower resource requirements (CPU, memory) on the client or server. In some cases, processing structured data (like XML or JSON) according to a complex model might even require more resources than parsing simple, non-modelled data.
Reference
RFC 8342 - Network Management Datastore Architecture (NMDA) - This IETF RFC, which uses YANG data models, discusses how a defined architecture and data models provide a coherent framework for representing network configuration and state, which inherently supports extensibility and evolution of managed elements.

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
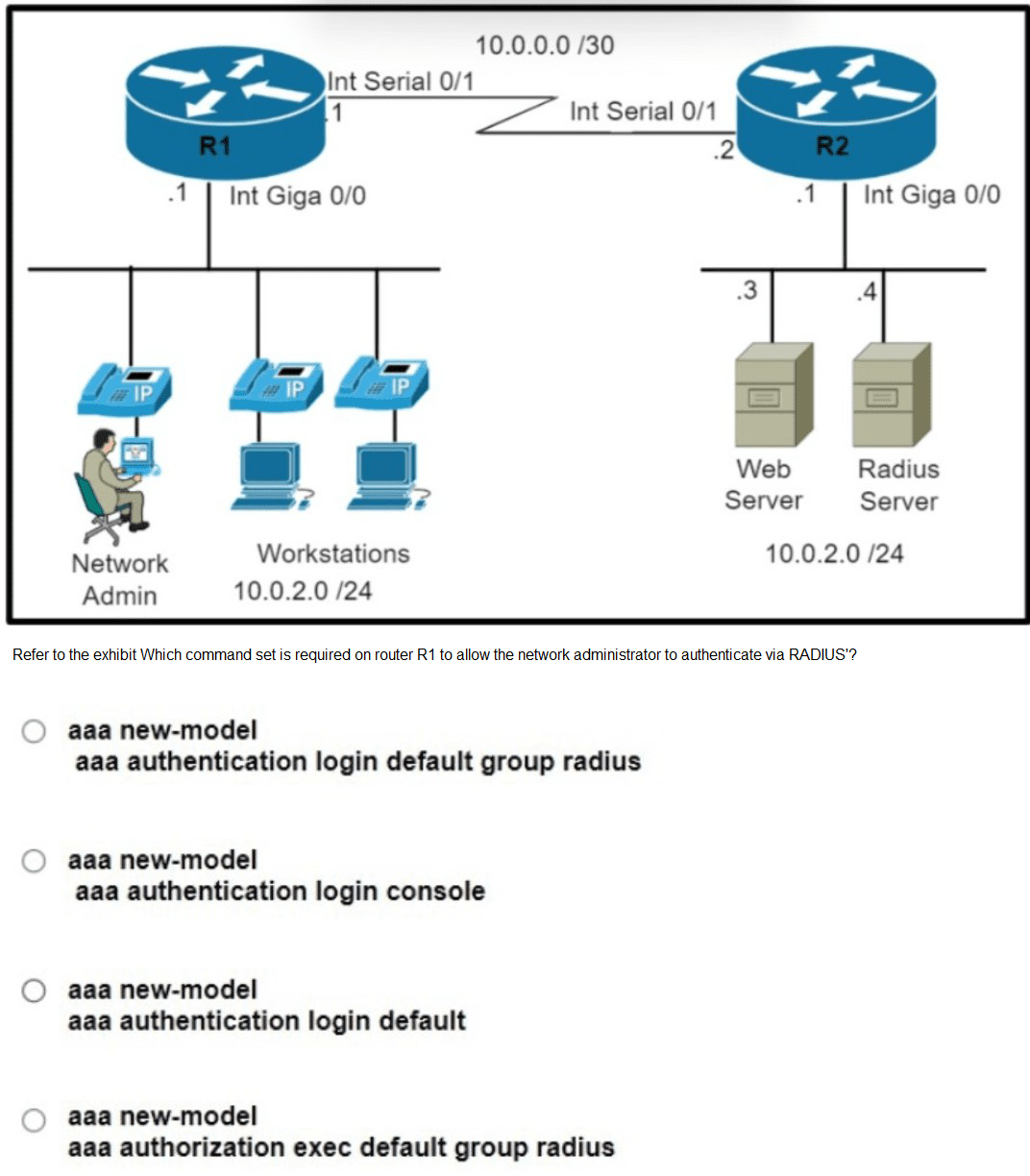
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Which characteristic applies to Cisco SD-Access?
A. It uses dynamic routing the discover and provision access switches.
B. It uses VXLAN for the control plane
C. It uses VXLAN for the data plane
D. It uses dynamic routing to discover and provision border switches
Which two actions are recommended as security best practices to protect REST API? (Choose two.)
A. Use SSL for encryption.
B. Enable out-of-band authentication.
C. Enable dual authentication of the session.
D. Use TACACS+ authentication.
E. Use a password hash.
| Page 2 out of 30 Pages |
| Previous |