Topic 2, Exam Pool B
An engineer configured SNMP notifications sent to the management server using authentication and encrypting data with DES. An error in the response PDU is received as "UNKNOWNUSERNAME. WRONGDIGEST". Which action resolves the issue?
A.
Configure the correct authentication password using SNMPv3 authPriv .
B.
Configure the correct authentication password using SNMPv3 authNoPriv.
C.
Configure correct authentication and privacy passwords using SNMPv3 authNoPriv.
D.
Configure correct authentication and privacy passwords using SNMPv3 authPriv.
Configure correct authentication and privacy passwords using SNMPv3 authPriv.
In which two ways does the IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table operate? (Choose two.)
A.
by IPv6 routing protocols to securely build neighborships without the need of authentication
B.
by the recovery mechanism to recover the binding table in the event of a device reboot
C.
by IPv6 HSRP to make sure neighbors are authenticated before being used as gateways
D.
by various IPv6 guard features to validate the data link layer address
E.
by storing hashed keys for IPsec tunnels for the built-in IPsec features
by the recovery mechanism to recover the binding table in the event of a device reboot
by various IPv6 guard features to validate the data link layer address
Explanation:
Overview of the IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table A database table of IPv6 neighbors connected to the device is created from information
sources such as NDP snooping. This database, or binding table, is used by variousIPv6 guard features to validate the link-layer address (LLA), the IPv4 or IPv6 address, and the prefix binding of the neighbors to prevent spoofing and redirect attacks.
IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table Recovery MechanismThe IPv6 first-hop security binding table recovery mechanism enables the binding table to recover in the event of a device reboot.
When configuring Control Plane Policing on a router to protect it from malicious traffic, an engineer observes that the configured routing protocols start flapping on that device. Which action in the Control Plane Policy prevents this problem in a production environment while achieving the security objective?
A.
Set the conform-action and exceed-action to transmit initially to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy in the output direction
B.
Set the conform-action and exceed-action to transmit initially to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy in the input direction
C.
Set the conform-action to transmit and exceed-action to drop to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy m the input direction
D.
Set the conform-action to transmit and exceed-action to drop to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy m the output direction
Set the conform-action and exceed-action to transmit initially to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy in the input direction
Refer to the exhibit.
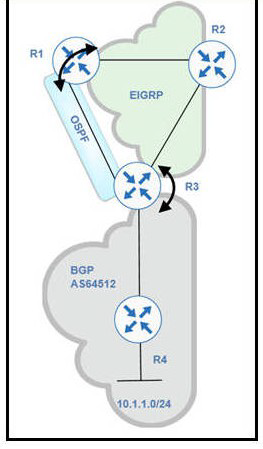
BGP and EIGRP are mutually redistributed on R3, and EIGRP and OSPF are mutually redistributed on R1. Users report packet loss and interruption of service to applications hosted on the 10.1.1.0724 prefix. An engineer tested the link from R3 to R4 with no packet loss present but has noticed frequent routing changes on R3 when running the debug ip
route command. Which action stabilizes the service?
A.
Tag the 10.1.1.0/24 prefix and deny the prefix from being redistributed into OSPF on R1.
B.
Repeat the test from R4 using ICMP ping on the local 10.1.1.0/24 prefix, and fix any Layer 2 errors on the host or switch side of the subnet. ^ C. Place an OSPF distribute-list outbound on R3 to block the 10.1.10/24 prefix from being advertised back to R3.
C.
Reduce frequent OSPF SPF calculations on R3 that cause a high CPU and packet loss on traffic traversing R3.
Tag the 10.1.1.0/24 prefix and deny the prefix from being redistributed into OSPF on R1.
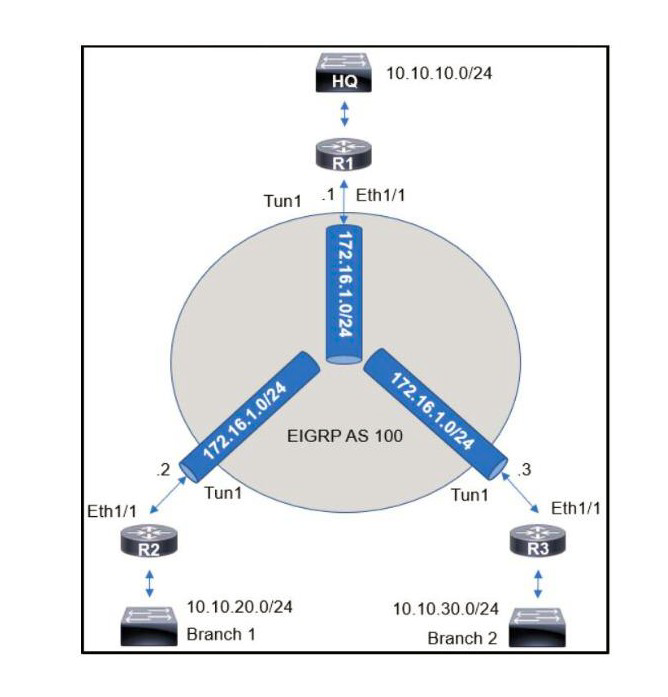
An engineer sets up a DMVPN connection to connect branch 1 and branch 2 to HQ branch 1 and branch 2 cannot communicate with each other. Which change must be made to resolve this issue?

A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option D
Refer to the exhibit.
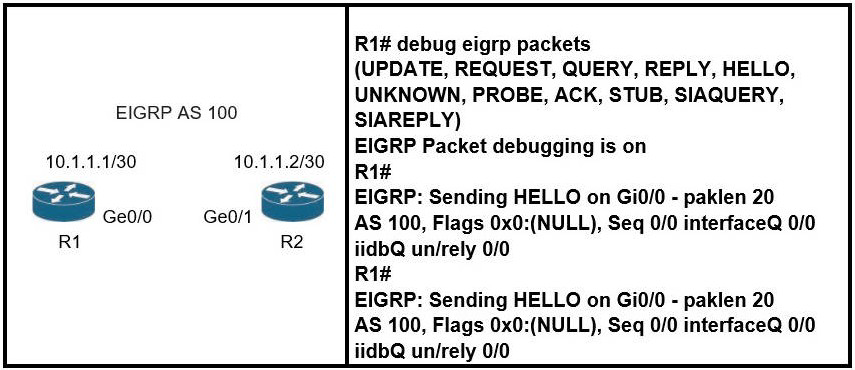
Which action resolves the adjacency issue?
A.
Match the hello interval timers.
B.
Configure the same EIGRP process IDs.
C.
Match the authentication keys.
D.
Configure the same autonomous system numbers.
Configure the same autonomous system numbers.
Explanation:
EIGRP does not have process ID as it uses Autonomous System (AS) numbers only. This is not an authentication problem or we would see this error from the debug:
EIGRP: Ethernet0/0: ignored packet from 10.1.1.3, opcode = 1 (missing authentication or key-chain missing)
If the AS numbers between two routers are different then the neighbor relationship cannot be formed.
Refer to the exhibits.
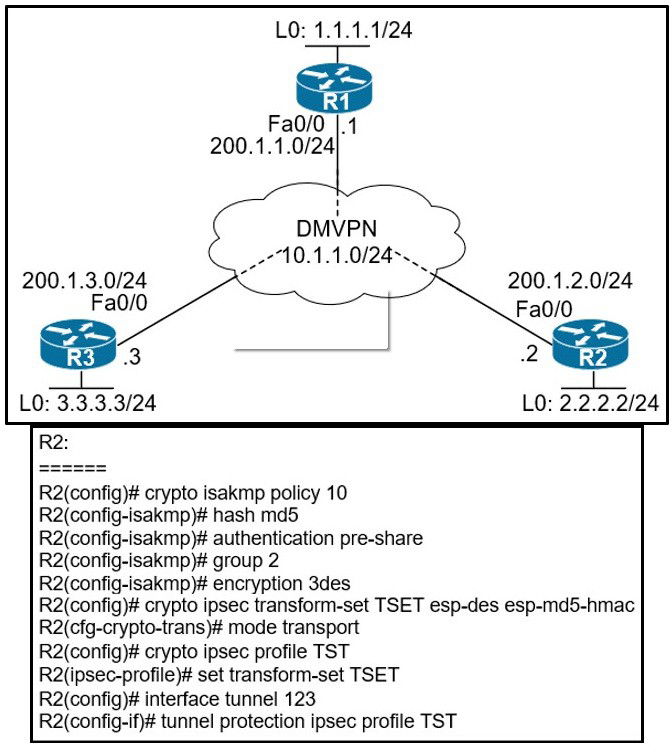
When DMVPN is configured, which configuration allows spoke-to-spoke communication using loopback as a tunnel source?
A.
Configure crypto isakmp key cisco address 0.0.0.0 on the hub.
B.
Configure crypto isakmp key Cisco address 200.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 on the hub.
C.
Configure crypto isakmp key cisco address 200.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 on the spokes.
D.
Configure crypto isakmp key cisco address 0.0.0.0 on the spokes.
Configure crypto isakmp key cisco address 0.0.0.0 on the spokes.
A DMVPN single hub topology is using IPsec + mGRE with OSPF. What should be configured on the hub to ensure it will be the designated router?
A.
tunnel interface of the hub with ip nhrp ospf dr
B.
OSPF priority to 0
C.
route map to set the metrics of learned routes to 110
D.
OSPF priority greater than 1
OSPF priority greater than 1
Refer to Exhibit.
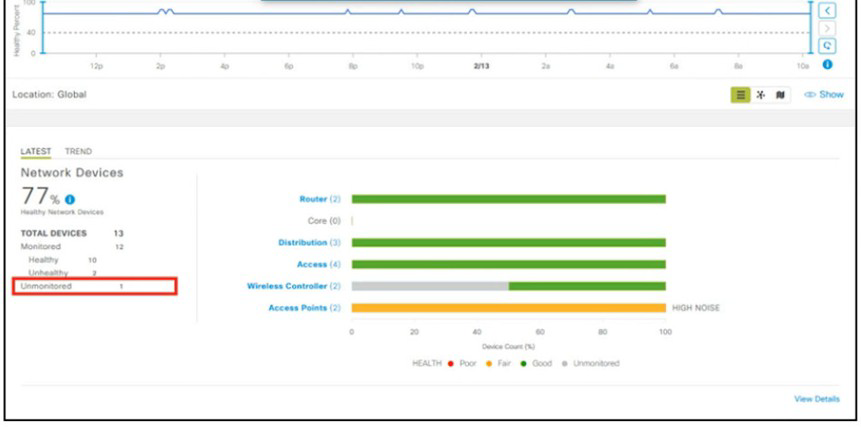
A network administrator added one router in the Cisco DNA Center and checked its discovery and health from the Network Health Dashboard. The network administrator observed that the router is still showing up as unmonitored. What must be configured on the router to mount it in the Cisco DNA Center?
A.
Configure router with NetFlow data
B.
Configure router with the telemetry data
C.
Configure router with routing to reach Cisco DNA Center
D.
Configure router with SNMPv2c or SNMPv3 traps
Configure router with the telemetry data
STION NO: 186
Refer to the exhibit.
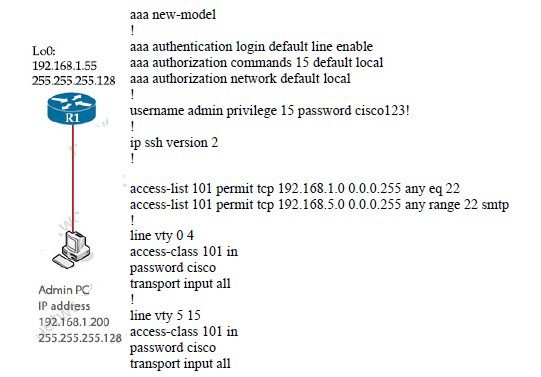
The administrator successfully logs into R1 but cannot access privileged mode commands. What should be configured to resolve the issue?
A.
aaa authorization reverse-access
B.
secret cisco123! at the end of the username command instead of password cisco123!
C.
matching password on vty lines as cisco123!
D.
enable secret or enable password commands to enter into privileged mode
enable secret or enable password commands to enter into privileged mode
Refer to the exhibit.

The neighbor is not coming up. Which two sets of configurations bring the neighbors up? (Choose two.)
A.
R2
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.1
router bgp 200
neighbor 10.1.1.1 tti-security hops 1
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0
B.
R2
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.1
router bgp 200
neighbor 10.1.1.1 disable-connected-check
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0
C.
R2
ip route 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.2
router bgp 100neighbor 10.1.1.2 ttl-security hops 1
neighbor 10.1.1.2 update-source loopback 0
D.
ip route 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.2
router bgp 100
neighbor 10.1.1.1 ttl-security hops 1
neighbor 10.1.1.2 update-source loopback 0
E.
ip route 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.2
router bgp 100
neighbor 10.1.1.2 disable-connected-check
neighbor 10.1.1.2 update-source Loopback0
R2
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.1
router bgp 200
neighbor 10.1.1.1 disable-connected-check
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0
ip route 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.2
router bgp 100
neighbor 10.1.1.2 disable-connected-check
neighbor 10.1.1.2 update-source Loopback0
Refer to the exhibit.
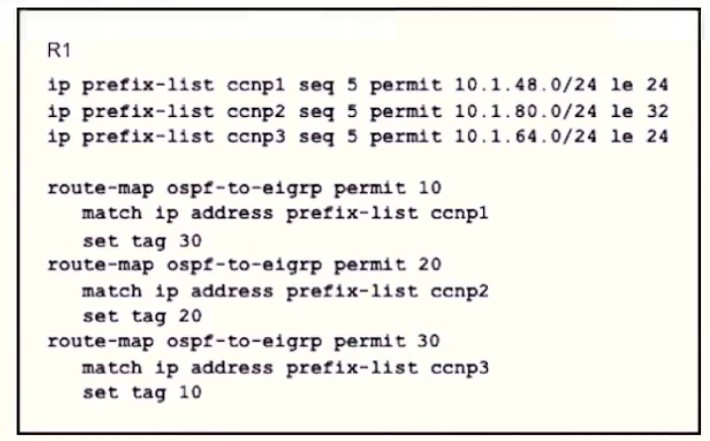
An engineer wanted to set a tag of 30 to route 10 1.80.65/32 but it failed How is the issue fixed?
A.
Modify route-map ospf-to-eigrp permit 30 and match prefix-list ccnp2.
B.
Modify route-map ospf-to-eigrp permit 10 and match prefix-list ccnp2.
C.
Modify prefix-list ccnp3 to add 10.1.64.0/20 le 24
D.
Modify prefix-list ccnp3 to add 10.1.64.0/20 ge 32
Modify route-map ospf-to-eigrp permit 10 and match prefix-list ccnp2.
| Page 17 out of 47 Pages |
| 101112131415161718192021222324 |
| 300-410 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our 300-410 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (300-410 ENARSI) exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive 300-410 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.