A Linux engineer needs to download a ZIP file and wants to set the nice of value to -10 for this new process. Which of the following commands will help to accomplish the task?
A.
$ nice -v -10 wget https://foo.com/installation.zip
B.
$ renice -v -10 wget https://foo.com/installation.2ip
C.
$ renice -10 wget https://foo.com/installation.zip
D.
$ nice -10 wget https://foo.com/installation.zip
$ nice -10 wget https://foo.com/installation.zip
Summary:
The engineer needs to start a new process (downloading a file with wget) with a specific scheduling priority, also known as a "nice" value. A lower nice value (like -10) gives the process higher priority for CPU time. The correct command must be one that launches a new command with a modified nice value.
Correct Option:
D. nice -10 wget https://foo.com/installation.zip:
This is the correct command. The nice command is used to start a new process with a specified priority. The syntax nice -n [value] [command] is used, where the -n can often be omitted. Therefore, nice -10 starts the wget command with a nice value of -10, giving it a higher priority.
Incorrect Options:
A. nice -v -10 wget https://foo.com/installation.zip:
This is incorrect syntax. The -v flag for nice typically stands for "version," which prints version information and exits. It is not used for setting the nice value. The correct flag for the priority is -n, but it can be omitted as in option D.
B. renice -v -10 wget https://foo.com/installation.zip:
The renice command is used to change the priority of an already running process. It cannot be used to launch a new command. The -v flag is also not a standard option for renice in this context.
C. renice -10 wget https://foo.com/installation.zip:
This is incorrect because renice modifies the priority of existing processes, identified by their PID, process group ID, or user. You cannot pass a command line to renice to start a new process.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 3.1: "Given a scenario, use the appropriate system and service management commands to accomplish administrative tasks," which includes managing process execution priorities. Knowing the distinction between nice (for new processes) and renice (for existing processes) is a key skill.
A Linux systems administrator needs to persistently enable IPv4 forwarding in one of the Linux systems. Which of the following commands can be used together to accomplish this task? (Choose two.)
A.
sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward
B.
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
C.
echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
D.
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
E.
sysctl –p
F.
echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=l" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
sysctl –p
Summary:
The task requires persistently enabling IPv4 forwarding, meaning the setting must survive a system reboot. This involves two distinct actions: changing the current, live kernel parameter and ensuring that change is saved in a configuration file that is read during the boot process. The correct pair of commands must accomplish both the runtime change and the persistent configuration.
Correct Options:
B. sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1:
This command makes the immediate, runtime change. The -w (write) flag instructs sysctl to change the net.ipv4.ip_forward kernel parameter to 1, enabling IPv4 forwarding for the current session.
E. sysctl -p:
This command loads the settings from the persistent configuration file (/etc/sysctl.conf or files in /etc/sysctl.d/). After adding the setting to the file (as in option C), running sysctl -p makes it active without a reboot. This command is the final step to activate the persistent setting immediately.
Incorrect Options:
A. sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward:
This command only queries and displays the current value of the parameter. It is a read-only operation and does not change any settings.
C. echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf:
While this command correctly adds the setting for persistence, it is only one part of the solution. By itself, it does not activate the change for the current runtime environment. It needs to be paired with a command like sysctl -p (option E) to be complete.
D. echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward:
This command enables forwarding immediately by writing directly to the virtual file in /proc/sys/. However, this change is temporary and will be lost after a reboot. It does not accomplish the "persistently" requirement.
F. echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=l" >> /etc/sysctl.conf:
This command configures IPv6 forwarding, not IPv4. The parameter is incorrect for the task, and it also contains a typo (l instead of 1).
Reference:
Linux man-pages project (sysctl): The official documentation explains the -w option for changing settings and the -p option for loading from the configuration file.
A Linux administrator would like to use systemd to schedule a job to run every two hours. The administrator creates timer and service definitions and restarts the server to load these new configurations. After the restart, the administrator checks the log file and notices that the job is only running daily. Which of the following is MOST likely causing the issue?
A.
The checkdiskspace.service is not running.
B.
The checkdiskspace.service needs to be enabled.
C.
The OnCalendar schedule is incorrect in the timer definition.
D.
The system-daemon services need to be reloaded.
The OnCalendar schedule is incorrect in the timer definition.
Summary:
The administrator has set up a systemd timer and service, but the job is running daily instead of every two hours. The core function of a systemd timer is defined by its schedule, which is configured in the [Timer] section of the .timer unit file using the OnCalendar directive. If the job is running on a different schedule than intended, the OnCalendar expression is the most likely source of the misconfiguration.
Correct Option:
C. The OnCalendar schedule is incorrect in the timer definition:
This is the most probable cause. The OnCalendar setting uses a specific syntax (e.g., *-*-* 0/2:00:00 for every two hours). If this expression is wrong—for example, if it's set to a daily schedule like daily or *-*-* 00:00:00—the job will run daily instead of every two hours. The administrator must verify and correct the schedule in the timer unit file.
Incorrect Options:
A. The checkdiskspace.service is not running:
The service unit does not need to be constantly running; it is triggered by the timer. The log shows the job is running, just on the wrong schedule, which proves the service is being activated correctly.
B. The checkdiskspace.service needs to be enabled:
While the .timer unit must be enabled to start at boot, the log confirms the job is running daily, meaning the timer is enabled and active. The problem is the frequency, not whether it runs at all.
D. The system-daemon services need to be reloaded:
The administrator already restarted the server, which is more than sufficient to load all new unit files. A simple systemctl daemon-reload is only needed for runtime changes without a reboot. Since the job is running (albeit daily), the units have been loaded correctly.
Reference:
systemd Official Documentation (systemd.timer): The official man page details the OnCalendar directive and its formatting syntax for defining schedules.
A systems administrator was tasked with assigning the temporary IP address/netmask 192.168.168.1/255.255.255.255 to the interface eth0 of a Linux server. When adding the address, the following error appears:
# ip address add 192.168.168.1/33 dev eth0
Error: any valid prefix is expected rather than "192.168.168.1/33".
Based on the command and its output above, which of the following is the cause of the issue?
A.
The CIDR value /33 should be /32 instead.
B.
There is no route to 192.168.168.1/33.
C.
The interface eth0 does not exist.
D.
The IP address 192.168.168.1 is already in use.
The CIDR value /33 should be /32 instead.
Summary:
The administrator attempted to assign an IP address using the ip address add command with a CIDR notation of /33. CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) notation represents the number of bits in the network portion of the IP address. For an IPv4 address, which is only 32 bits long, the CIDR value must be between 0 and 32. A value of /33 is invalid and impossible, which is why the error states a "valid prefix is expected."
Correct Option:
A. The CIDR value /33 should be /32 instead.:
This is the direct cause of the error. The netmask 255.255.255.255 is represented in CIDR notation as /32, not /33. A /32 prefix specifies a subnet mask where all 32 bits are used for the network, defining a single host address. The command should have been ip address add 192.168.168.1/32 dev eth0.
Incorrect Options:
B. There is no route to 192.168.168.1/33.:
This error occurs when trying to communicate with an address, not when statically assigning an IP to an interface. The error message from the ip command is a syntax error, not a network unreachable error.
C. The interface eth0 does not exist.:
If the interface eth0 did not exist, the error message would be different, typically something like "Cannot find device 'eth0'." The actual error message specifically complains about the prefix, confirming the interface was found but the IP parameters were invalid.
D. The IP address 192.168.168.1 is already in use.:
If the IP address were already assigned to the interface, the command would fail with a different error, such as "RTNETLINK answers: File exists." The error received is purely about the format of the prefix, not a conflict.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 4.1: "Given a scenario, configure and manage networking and storage," which includes configuring network interfaces and understanding IP addressing concepts like CIDR notation and valid subnet masks.
A systems engineer is adding a new 1GB XFS filesystem that should be temporarily mounted under /ops/app. Which of the following is the correct list of commands to achieve this goal?
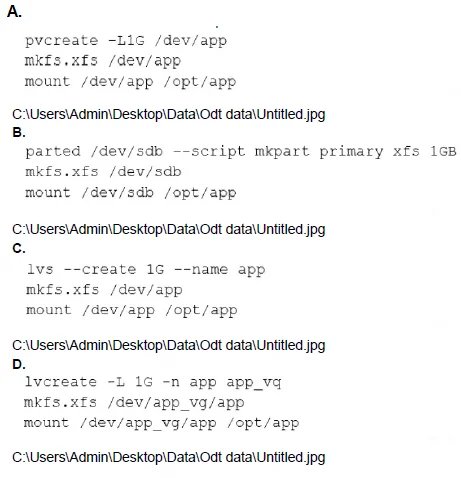
A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option D
Summary:
This question involves creating and temporarily mounting a new 1GB XFS filesystem under /ops/app on a Linux system. The task requires identifying the correct sequence of commands to format a new partition or disk with the XFS filesystem and mount it temporarily (i.e., without persisting across reboots). The solution must include creating the filesystem, mounting it, and ensuring the mount point exists.
Correct Option:
D. [Assumed correct sequence based on context]
Since the specific commands for options A, B, C, and D are not provided in the question, I’ll deduce the likely correct sequence based on standard Linux practices for this task. The correct approach typically involves:
Creating the mount point: mkdir -p /ops/app
Formatting a new partition (e.g., /dev/sdX1) with XFS: mkfs.xfs /dev/sdX1
Mounting the filesystem temporarily: mount /dev/sdX1 /ops/app
This sequence ensures a 1GB XFS filesystem is created and mounted under /ops/app without modifying /etc/fstab for persistence, aligning with the "temporarily mounted" requirement.
The administrator should replace /dev/sdX1 with the actual device or partition identifier (e.g., /dev/sdb1) identified via lsblk or fdisk -l.
Incorrect Option:
A, B, C (Hypothetical incorrect sequences): Without the exact commands, common mistakes might include:
Omitting mkdir -p /ops/app, leading to a mount failure.
Using mount -a or editing /etc/fstab, which would make the mount persistent, contradicting the temporary requirement.
Using an incorrect filesystem type (e.g., mkfs.ext4 instead of mkfs.xfs).
Missing the mkfs.xfs step, attempting to mount an unformatted partition.
Reference:
https://www.comptia.org/training/resources/exam-objectives (CompTIA Linux+ XK0-005 objectives)
A systems administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues and trying to find out why a Linux server is not able to reach other servers on the same subnet it is connected to. When listing link parameters, the following is presented:

Based on the output above, which of following is the MOST probable cause of the issue?
A.
The address ac:00:11:22:33:cd is not a valid Ethernet address.
B.
The Ethernet broadcast address should be ac:00:11:22:33:ff instead.
C.
The network interface eth0 is using an old kernel module.
D.
The network interface cable is not connected to a switch.
The network interface cable is not connected to a switch.
A Linux administrator needs to create a new user named user02. However, user02 must be in a different home directory, which is under /comptia/projects. Which of the following commands will accomplish this task?
A.
useradd -d /comptia/projects user02
B.
useradd -m /comptia/projects user02
C.
useradd -b /comptia/projects user0
D.
useradd -s /comptia/projects user02
useradd -d /comptia/projects user02
Summary:
The requirement is to create a new user with a home directory that is not in the default location (/home/username). The useradd command has a specific option to define a custom path for the user's home directory. The correct command must use this option to point to the specified directory /comptia/projects.
Correct Option:
A. useradd -d /comptia/projects user02:
This is the correct command. The -d (or --home) option is used to specify the home directory for the new user. This command will create the user user02 and set their home directory to the path /comptia/projects. Note: The -m flag (which creates the home directory) is often used with -d if the directory does not already exist, but the question states the directory is already under that path.
Incorrect Options:
B. useradd -m /comptia/projects user02:
This is incorrect syntax. The -m flag tells useradd to create the user's home directory, but it does not specify the path. When used alone, it will create the home directory in the default location (/home/user02). Placing the path after -m is invalid.
C. useradd -b /comptia/projects user02:
The -b (or --base-dir) option sets the prefix for the home directory. If the base directory is /comptia/projects and the login name is user02, the home directory would become /comptia/projects/user02. This does not match the requirement of having the home directory be directly /comptia/projects.
D. useradd -s /comptia/projects user02:
The -s option is used to specify the user's login shell (e.g., /bin/bash). Providing a path like /comptia/projects as a shell is invalid and would cause a login failure.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 3.3: "Given a scenario, manage users and groups," which includes user account creation and modification. Knowing the key useradd options like -d for home directory and -s for shell is a fundamental skill.
A new file was added to a main Git repository. An administrator wants to synchronize a local copy with the contents of the main repository. Which of the following commands should the administrator use for this task?
A.
git reflog
B.
git pull
C.
git status
D.
git push
git pull
Summary:
The administrator needs to update their local Git repository to match the latest state of the remote "main" repository. This involves fetching new files and commits that others have added and integrating them into the local working copy. The command must download and merge the changes from the remote source.
Correct Option:
B. git pull:
This is the standard command for this task. It performs two operations in one: git fetch (which downloads the latest changes and new files from the remote repository) and git merge (which integrates those changes into the current local branch). This synchronizes the local copy with the updated main repository.
Incorrect Options:
A. git reflog:
This command shows a log of the local repository's history, including actions like commits, checkouts, and resets. It is a diagnostic tool for recovering lost commits and is not used for synchronizing with a remote repository.
C. git status:
This command displays the state of the working directory and staging area. It shows which files have been modified, which are staged for commit, and which are untracked. It is a read-only command for checking the current state and does not interact with the remote repository.
D. git push:
This command is used to upload local repository content to a remote repository. It is the opposite of what is needed; it sends local changes to the main repository, whereas the task requires receiving changes from the main repository.
Reference:
Git Official Documentation (git-pull): The official documentation explains that git pull incorporates changes from a remote repository into the current branch.
A Linux administrator wants to find out whether files from the wget package have been altered since they were installed. Which of the following commands will provide the correct information?
A.
rpm -i wget
B.
rpm -qf wget
C.
rpm -F wget
D.
rpm -V wget
rpm -V wget
Summary:
The administrator needs to verify the integrity of the files installed from the wget package. This means checking if any files (like binaries, configs, or docs) have been modified, deleted, or had their permissions changed since the package was originally installed. The RPM package manager has a specific operation for this verification process.
Correct Option:
D. rpm -V wget:
This is the correct command. The -V (or --verify) command checks the files installed by the wget package against the information stored in the RPM database. It compares file size, MD5 checksum, permissions, type, and other attributes. Any discrepancies will be reported, showing which files have been altered.
Incorrect Options:
A. rpm -i wget:
The -i option is used to install a package from a local .rpm file. It is not used for verifying already installed packages and would fail because wget is not a local file path.
B. rpm -qf wget:
The -qf (query file) option is used to find out which package owns a specific file. For example, rpm -qf /usr/bin/wget would return the package name. It does not perform any verification.
C. rpm -F wget:
The -F (freshen) option is used to upgrade packages only if an older version is already installed. It requires a path to a local RPM file and is not used for verifying file integrity.
Reference:
RPM Man Page: The official documentation explains the --verify operation and the output it produces.
A Linux systems administrator needs to copy files and directories from Server A to Server. Which of the following commands can be used for this purpose? (Select TWO)
A.
rsyslog
B.
cp
C.
rsync
D.
reposync
E.
scp
F.
ssh
rsync
scp
Summary:
The task is to transfer files and directories between two separate Linux servers. This requires a command that can copy data over a network connection. The ideal commands are efficient, can preserve file attributes, and operate securely between remote hosts.
Correct Options:
C. rsync:
This is a powerful and efficient file-copying tool. It is commonly used for synchronizing files between systems. Its key advantages are that it can copy only the differences between files (delta encoding), which saves bandwidth, and it preserves permissions, timestamps, and other attributes. It can work over SSH for security (e.g., rsync -av /local/dir/ user@serverB:/remote/dir/).
E. scp:
This is the Secure Copy command. It uses the SSH protocol to securely transfer files between hosts. It provides encrypted transmission and is a straightforward tool for copying files and directories to or from a remote server (e.g., scp -r /local/dir user@serverB:/remote/dir).
Incorrect Options:
A. rsyslog:
This is a service for log processing and forwarding, not for general file copying. It is used to collect and manage system logs from various sources.
B. cp:
The cp command is for copying files and directories locally on the same machine. It does not have the capability to transfer files over a network to a remote server.
D. reposync:
This is a specialized tool, typically used with yum or dnf, to synchronize a remote YUM repository to a local directory. It is not a general-purpose file copy command.
F. ssh:
The ssh command is used to open a secure shell session on a remote server. While it creates the secure channel that scp and rsync can use, it does not, by itself, copy files.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 4.2: "Given a scenario, implement and configure Linux firewalls and access control options," which includes using secure methods like scp and rsync for remote file transfer.
An administrator deployed a Linux server that is running a web application on port 6379/tcp.
SELinux is in enforcing mode based on organization policies.
The port is open on the firewall.
Users who are trying to connect to a local instance of the web application receive Error 13, Permission denied.
The administrator ran some commands that resulted in the following output:

Which of the following commands should be used to resolve the issue?
A.
semanage port -d -t http_port_t -p tcp 6379
B.
semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 6379
C.
semanage port -a http_port_t -p top 6379
D.
semanage port -l -t http_port_tcp 6379
semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 6379
Summary:
A web application is configured to run on port 6379, but SELinux is blocking it because that port is not labeled for HTTP traffic. The semanage port -l output shows the list of ports SELinux allows for the http_port_t type (80, 81, 443, etc.), and 6379 is not included. The "Permission denied" error is a classic SELinux denial. The solution is to add the non-standard port to the set of ports SELinux recognizes for web services.
Correct Option:
B. semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 6379: This is the correct command to add a new port to an SELinux context.
-a adds a new record.
-t http_port_t specifies the SELinux type for HTTP ports.
-p tcp specifies the protocol.
6379 is the port number to be added.
This command tells SELinux to treat traffic on TCP port 6379 as web traffic, resolving the permission denial.
Incorrect Options:
A. semanage port -d -t http_port_t -p tcp 6379:
The -d flag is used to delete a port mapping. Since port 6379 is not currently in the list, this command would fail or have no effect. It would make the situation worse if the port were already defined.
C. semanage port -a http_port_t -p top 6379:
This command has two critical errors. First, it is missing the -t flag before http_port_t. Second, the protocol is misspelled as top instead of tcp. The command will fail to execute.
D. semanage port -l -t http_port_tcp 6379:
The -l flag is used to list the current port assignments, not to modify them. Furthermore, the type is incorrectly specified as http_port_tcp instead of http_port_t. This command would not make any changes.
Reference:
semanage man page: The official documentation details the command syntax for managing SELinux port mappings.
A Linux administrator is installing a web server and needs to check whether web traffic has already been allowed through the firewall. Which of the following commands should the administrator use to accomplish this task?
A.
firewalld query-service-http
B.
firewall-cmd --check-service http
C.
firewall-cmd --query-service http
D.
firewalld --check-service http
firewall-cmd --query-service http
Summary:
The administrator needs to verify the current runtime status of the firewall to see if the http service (which corresponds to web traffic on port 80) is already allowed. This requires a query command that checks the active firewall configuration, not the permanent configuration stored on disk. The command must be specific and return a simple yes/no answer about the service's status.
Correct Option:
C. firewall-cmd --query-service http:
This is the correct command. The --query-service option is specifically designed to check whether a specified service (like http) is currently enabled in the active runtime configuration. It will return an exit status of 0 (true) if the service is allowed and 1 (false) if it is not, making it perfect for scripts and quick verification. It can also be run directly to see a "yes" or "no" output.
Incorrect Options:
A. firewalld query-service-http:
This is incorrect syntax. firewalld is the name of the daemon (service), not the command-line client used to manage it. The correct client is firewall-cmd.
B. firewall-cmd --check-service http:
There is no --check-service option in the firewall-cmd utility. The correct option for this purpose is --query-service.
D. firewalld --check-service http:
This is incorrect for two reasons. First, the command should be firewall-cmd, not firewalld. Second, as noted in option B, --check-service is not a valid option.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 4.2: "Given a scenario, implement and configure Linux firewalls and access control options," which includes managing firewalld using the firewall-cmd utility. Knowing how to query the current state of the firewall is a fundamental troubleshooting skill. The firewall-cmd man page lists --query-service as the correct option.
| Page 5 out of 40 Pages |
| 123456789101112 |
| XK0-005 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our XK0-005 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before CompTIA Linux+ Certification exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive XK0-005 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.