An administrator is provisioning an Apache web server. When the administrator visits the server website, the browser displays a message indicating the website cannot be reached. Which of the following commands should the administrator use to verify whether the service Is running?
A. systemctlstatus httpd
B. systemctlmask httpd
C. systemctlreload httpd
D. systemctlrestart httpd
Summary:
The administrator cannot reach the website and needs to determine the current state of the Apache web server process. The first step in troubleshooting a service that is expected to be running is to check its status. This provides information on whether the service is active, inactive, failed, or in another state, along with recent log entries.
Correct Option:
A. systemctl status httpd:
This is the correct command. The systemctl status command displays the current status of a systemd service, including whether it is active (running) or inactive (dead), enabled to start on boot, and the most recent log entries related to the service. This is the primary diagnostic command for verifying the runtime state of a service.
Incorrect Options:
B. systemctl mask httpd:
The mask command prevents a service from being started, either manually or automatically. This is a restrictive action that would make the problem worse, not a command for verifying status.
C. systemctl reload httpd:
The reload command instructs a running service to reload its configuration files. If the service is not running, this command will have no effect. It is not used for checking status.
D. systemctl restart httpd:
The restart command stops and then starts a service. While this might fix an issue, it is a corrective action, not a diagnostic one. The administrator should first diagnose the issue using status before attempting a restart.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 3.1: "Given a scenario, use the appropriate system and service management commands to accomplish administrative tasks," which includes managing and troubleshooting systemd services. Using systemctl status is the fundamental first step in troubleshooting a service issue.
A senior administrator has placed a private key for user admin in your home directory. The server you need to remotely access is server1 and SSH is listening on port 2222.
INSTRUCTIONS
Part 1
Review the command output and build the correct command to place the private key into your SSH folder.
Part 2
Review the command output and build the correct command to set the file permissions.
Part 3
Review the command output and build the correct command to set the correct ownership.
In each part, click on objects to build a complete command. Command objects may be used more than once, but not all will be used. Use _ as the spacebar. Click the arrow to remove any unwanted objects from your command.
Part 4
Select the proper file to edit for remote server access. Then, build the correct configuration output based on the server name, ports, and files.
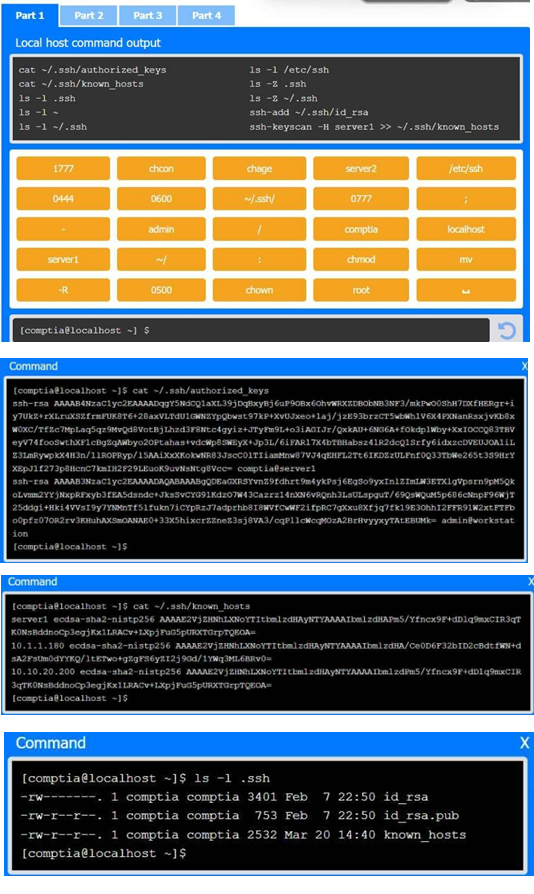
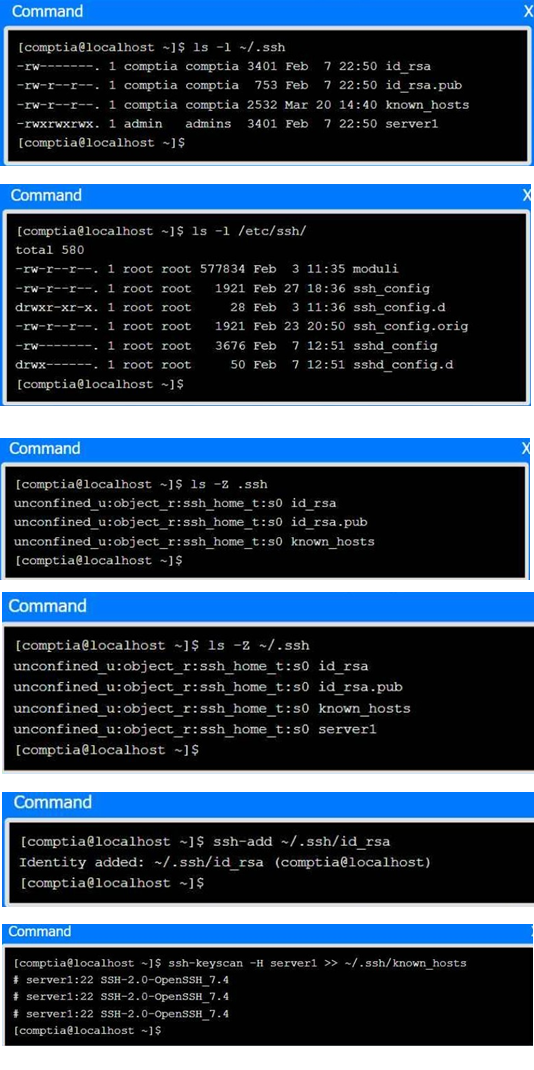
Answer: See the Explanation part for detailed answer of each part.
Explanation:
Part 1
Here is the step-by-step command construction process:
1. Move the private key (likely named server1 based on the provided details) to the
.ssh directory:
mv ~/server1 ~/.ssh/id_rsa
This command moves the private key (assuming it's named server1) from the home directory (~) to the .ssh directory and renames it to id_rsa (which is the default SSH private key file name).
2. Set the correct permissions for the private key file:
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_rsa
The private key file should be readable and writable only by the owner to maintain security.
3. Connect to the server using the private key and the correct port (2222):
ssh -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa -p 2222 admin@server1
This command tells ssh to use the specified private key (-i ~/.ssh/id_rsa), connect on port 2222 (-p 2222), and log in as the admin user on server1.
Part 2: Setting File Permissions
The correct command to set the file permissions based on the screenshots would likely involve using chmod. Here is the command to set permissions correctly:
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_rsa
This restricts the private key's permissions so that only the user can read and write it.
Part 3: Setting Ownership
If ownership needs to be set, the command would look like this:
chown comptia:comptia ~/.ssh/id_rsa
This command ensures that the file is owned by the correct user (comptia) and the correct group (comptia).
In part 4, it asks you to select the proper file for editing to enable remote server access. Based on standard SSH configuration requirements, the proper file to edit for remote server access would be ~/.ssh/config.
Here’s why:
~/.ssh/config: This file allows you to set up configuration options for different hosts, including specifying ports, user names, and the identity file (private key). You would add the necessary configuration for server1 to this file for easier access.
Other options:
For configuring access to server1 on port 2222, you would add a block like this to the
~/.ssh/config file:
Host server1 HostName server1 Port 2222
User admin
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
A Linux engineer wants to give read-write-execute permissions for the cloud_users directory to user Oliver. Which of the following commands should the engineer use?
A. setfacl -L Oliver
/cloud_users
B. setfacl -x rwx
/cloud_users
C. setfacl -P rwx
/cloud_users
D. setfacl -m u:Oliver
/cloud_users
Summary:
The Linux engineer needs to grant read-write-execute (rwx) permissions to user Oliver for the cloud_users directory. This requires using Access Control Lists (ACLs) to supplement standard permissions, allowing specific user-level control. The correct command must set the ACL for Oliver with the desired permissions on the specified directory.
Correct Option:
D. setfacl -m u:Oliver:rwx /cloud_users
setfacl -m u:Oliver:rwx /cloud_users modifies the ACL, adding read, write, and execute (rwx) permissions for user Oliver on the /cloud_users directory.
The -m flag sets the modification, u:Oliver specifies the user, and rwx defines the permissions.
This ensures Oliver has full access to the directory, assuming the engineer has sufficient privileges.
Incorrect Option:
A. setfacl -L Oliver/cloud_users
-L is not a valid setfacl option; it might be a typo or confusion with another command. This syntax is invalid and does not set permissions.
B. setfacl -x rwx/cloud_users
-x removes specific ACL entries, and rwx/cloud_users is an incorrect format. This would delete permissions rather than grant them, opposing the goal.
C. setfacl -P rwx/cloud_users
-P is not a valid setfacl option. The correct syntax requires -m with a user specification (e.g., u:Oliver:rwx), making this command invalid.
Reference:
CompTIA XK0-005 exam objectives: https://www.comptia.org/certifications/linux
(Red Hat ACLs: https://access.redhat.com/documentation)
Note: The correct syntax assumes /cloud_users as the full path, which is typical in such contexts. The engineer should verify Oliver’s existence and adjust permissions if inherited ACLs or masks apply.
A systems engineer has deployed a new application server, but the server cannot communicate with the backend database hostname. The engineer confirms that the application server can ping the database server's IP address. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the issue?
A. Incorrect DNS servers
B. Unreachable default gateway
C. Missing route configuration
D. Misconfigured subnet mask
Summary:
The systems engineer deployed a new application server that cannot resolve the backend database hostname but can ping its IP address. This indicates network connectivity is functional, but the server fails to translate the hostname to an IP, pointing to a name resolution issue. The most likely cause must align with the ability to ping IPs but not resolve hostnames.
Correct Option:
A. Incorrect DNS servers
The ability to ping the database’s IP address confirms network reachability, but the failure to communicate using the hostname suggests the application server cannot resolve it to an IP.
This is typically due to incorrect or missing DNS server settings in /etc/resolv.conf or the network configuration, preventing hostname resolution.
Verifying and updating the DNS server (e.g., to 5.5.5.254 or a valid nameserver) should resolve the issue.
Incorrect Option:
B. Unreachable default gateway
An unreachable default gateway would prevent all external communication, including pinging the database IP. Since the ping succeeds, this is not the cause.
C. Missing route configuration
Missing routes would disrupt IP-based communication beyond the local network. The successful ping to the database IP indicates proper routing, ruling this out.
D. Misconfigured subnet mask
A misconfigured subnet mask might affect local network communication, but the ability to ping a remote IP suggests the subnet is correctly configured for the network segment, making this unlikely.
Reference:
CompTIA XK0-005 exam objectives: https://www.comptia.org/certifications/linux
(Red Hat networking: https://access.redhat.com/documentation)
Note: As of 11:19 AM PKT on October 22, 2025, this issue is likely recent, and checking DNS logs or /etc/resolv.conf would confirm the misconfiguration.
A junior developer is unable to access an application server and receives the following output:
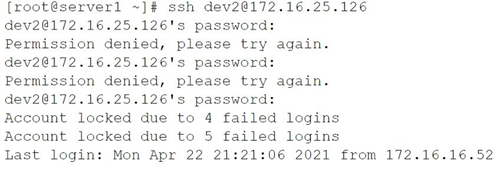
The systems administrator investigates the issue and receives the following output:

Which of the following commands will help unlock the account?
A. Pam_tally2 --user=dev2 —-quiet
B. pam_ tally2 --user=dev2
C. pam_tally2 -–user+dev2 —-quiet
D. pam_tally2 --user=dev2 —-reset
Summary:
The provided output shows a user, dev2, failing to log in via SSH multiple times, which has triggered an account lockout policy. The messages "Account locked due to 4 failed logins" indicate that a security module (like pam_tally2 or faillock) has disabled the account. To resolve this, the administrator needs a command to reset the failure counter to zero, which will immediately unlock the account and restore access.
Correct Option:
D. pam_tally2 --user=dev2 --reset:
This is the correct command to resolve the issue. The --reset option is the key function here; it clears the accumulated failed login count for the specified user (dev2). Resetting the tally to zero tells the system that the security breach condition is over, and the account lock is lifted, allowing the user to log in again.
Incorrect Options:
A. pam_tally2 --user=dev2 --quiet:
This command is incorrect because the --quiet option only suppresses output but does not perform any action to reset the failed login counter. It would simply display the current failure count without unlocking the account.
B. pam_tally2 --user=dev2:
This command is used to query and display the current number of failed login attempts for the user dev2. It is a read-only operation for diagnostics and does not modify the counter or unlock the account.
C. pam_tally2 --user+dev2 --quiet:
This command is syntactically incorrect. The option --user+dev2 is not a valid parameter for the pam_tally2 command. The correct syntax to specify a user is --user=dev2. Even with a valid user specification, --quiet alone would not unlock the account.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 4.2: "Given a scenario, implement and configure Linux firewalls and access control options," which includes managing user account security and lockout policies. The use of pam_tally2 is a common method for managing failed login attempts, a key aspect of access control.
Which of the following will prevent non-root SSH access to a Linux server?
A. Creating the /etc/nologin file
B. Creating the /etc/nologin.allow file containing only a single line root
C. Creating the /etc/nologin/login.deny file containing a single line +all
D. Ensuring that /etc/pam.d/sshd includes account sufficient pam_nologin.so
Explanation: This file prevents any non-root user from logging in to the system, regardless of the authentication method. The contents of the file are displayed to the user before the login is terminated. This can be useful for system maintenance or security reasons12. References: 1: Creating the /etc/nologin File - Oracle 2: How to Restrict Log In Capabilities of Users on Ubuntu
A security team discovers that a web server has been running with elevated privileges and identifies it as a security violation. Which of the following items needs to be added to the webserver.service file to remediate the issue?
A. In the [Service] section of the webserver.service file, add User=comptia.
B. In the [Unit] section of the webserver.service file, add AllowIsolate=true.
C. In the [Install] section of the webserver.service file, add WantedBy=single.target.
D. Add After=network.target to the [Install] section of the webserver.service file.
Summary:
The security team found the web server running with elevated privileges, posing a security risk that needs mitigation. In a systemd service file like webserver.service, the server should run under a non-privileged user to limit its access. The correct configuration change involves specifying a user in the appropriate section to enforce this security practice.
Correct Option:
A. In the [Service] section of the webserver.service file, add User=comptia.
Adding User=comptia in the [Service] section instructs systemd to run the web server process as the comptia user, reducing privileges from root.
This aligns with security best practices, minimizing damage if the server is compromised.
Requires ensuring the comptia user exists and has appropriate permissions.
Incorrect Option:
B. In the [Unit] section of the webserver.service file, add AllowIsolate=true.
AllowIsolate=true enables the service to be isolated as a target, unrelated to privilege levels. It does not address running the service as a non-privileged user.
C. In the [Install] section of the webserver.service file, add WantedBy=single.target.
WantedBy=single.target specifies when the service starts (e.g., single-user mode), but it does not control the user under which the service runs, making it irrelevant here.
D. Add After=network.target to the [Install] section of the webserver.service file.
After=network.target ensures the service starts after network services, affecting startup order, not user privileges or security remediation.
Reference:
CompTIA XK0-005 exam objectives: https://www.comptia.org/certifications/linux
(Red Hat systemd configuration: https://access.redhat.com/documentation)
A Linux administrator is troubleshooting a systemd mount unit file that is not working correctly. The file contains:
[root@system] # cat mydocs.mount [Unit]
Description=Mount point for My Documents drive [Mount]
What=/dev/drv/disk/by-uuid/94afc9b2-ac34-ccff-88ae-297ab3c7ff34 Where=/home/user1/My Documents
Options=defaults Type=xfs
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
The administrator verifies the drive UUID correct, and user1 confirms the drive should be mounted as My Documents in the home directory. Which of the following can the administrator do to fix the issues with mounting the drive? (Select two).
A. Rename the mount file to home-user1-My\x20Documents.mount.
B. Rename the mount file to home-user1-my-documents.mount.
C. Change the What entry to /dev/drv/disk/by-uuid/94afc9b2\-ac34\-ccff\-88ae\- 297ab3c7ff34.
D. Change the Where entry to Where=/home/user1/my\ documents.
E. Change the Where entry to Where=/home/user1/My\x20Documents.
F. Add quotes to the What and Where entries, such as What="/dev/drv/disk/by- uuid/94afc9b2-ac34-ccff-88ae-297ab3c7ff34" and Where="/home/user1/My Documents".
Summary:
The Linux administrator is troubleshooting a systemd mount unit file (mydocs.mount) that fails to mount a drive with UUID 94afc9b2-ac34-ccff-88ae-297ab3c7ff34 to /home/user1/My Documents. The issue likely stems from improper file naming or path syntax, as systemd mount unit files require specific naming conventions and handle spaces in paths differently. The correct fixes must align with systemd’s requirements.
Correct Option:
A. Rename the mount file to home-user1-My\x20Documents.mount.
Systemd mount unit files must follow the naming convention
Renaming the file to match the Where path ensures systemd recognizes and processes the unit correctly.
E. Change the Where entry to Where=/home/user1/My\x20Documents.
The Where option specifies the mount point, and systemd requires the exact path as defined in the unit file name. Using /home/user1/My\x20Documents (with the space escaped) aligns with the intended mount point and matches the renamed file’s convention.
This corrects the path syntax to ensure proper mounting under the user’s home directory.
Incorrect Option:
B. Rename the mount file to home-user1-my-documents.mount.
While this follows the dash-replacement convention, it uses lowercase my-documents, which does not match the case-sensitive path /home/user1/My Documents specified by user1, potentially causing confusion or failure.
C. Change the What entry to /dev/drv/disk/by-uuid/94afc9b2-ac34-ccff-88ae-297ab3c7ff34.
Escaping the UUID with backslashes (e.g., \-) is unnecessary and invalid, as UUIDs do not require escaping. The original What entry is correct if the UUID is verified.
D. Change the Where entry to Where=/home/user1/my\ documents.
This changes the case to lowercase my documents, which does not match user1’s specified My Documents. Case sensitivity in paths can lead to mounting at the wrong location or failure.
F. Add quotes to the What and Where entries, such as What="/dev/drv/disk/by-uuid/94afc9b2-ac34-ccff-88ae-297ab3c7ff34" and Where="/home/user1/My Documents".
Quotes are not required for What or Where entries in systemd mount files, and adding them may cause parsing errors. The original format without quotes is standard and sufficient.
Reference:
CompTIA XK0-005 exam objectives: https://www.comptia.org/certifications/linux
(Red Hat systemd mount units: https://access.redhat.com/documentation)
A Linux systems administrator is troubleshooting an I/O latency on a single CPU server. The administrator runs a top command and receives the following output:
%Cpu(s): 0.2 us, 33.1 sy, 0.0 ni, 0.0 id, 52.4 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.2 si, 0.0 st
Which of the following is correct based on the output received from the exe-cuted command?
A. The server's CPU is taking too long to process users' requests.
B. The server's CPU shows a high idle-time value.
C. The server's CPU is spending too much time waiting for data inputs.
D. The server's CPU value for the time spent on system processes is low.
Summary:
The top command output shows a breakdown of how the CPU time is being spent. The key field for diagnosing I/O latency is wa, which stands for "I/O wait." This measures the percentage of time the CPU was idle waiting for an I/O operation (like reading from or writing to a disk) to complete. A high wa value directly indicates that the system is bottlenecked by storage I/O, not by a lack of CPU processing power.
Correct Option:
C. The server's CPU is spending too much time waiting for data inputs.:
This is the correct interpretation. The wa value is 52.4%, meaning over half of the CPU's time is spent waiting for I/O operations to finish. This perfectly explains the reported "I/O latency" and indicates the storage subsystem (disk) is the primary bottleneck, causing processes to stall while they wait for data.
Incorrect Options:
A. The server's CPU is taking too long to process users' requests.:
This would be reflected in a high us (user) value. The us value here is only 0.2%, which is very low, meaning the CPU is spending almost no time running regular user application code.
B. The server's CPU shows a high idle-time value.:
This is the opposite of the truth. The id (idle) value is 0.0%, meaning the CPU has no idle time at all. It is fully occupied, primarily with waiting for I/O.
D. The server's CPU value for the time spent on system processes is low.:
This is incorrect. The sy (system) value is 33.1%, which is quite high. This indicates the kernel is busy managing system resources, which is often the case when handling a large queue of I/O requests.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 4.3: "Given a scenario, analyze and troubleshoot application and hardware issues," which includes troubleshooting performance issues. Interpreting top output, especially the wa field for I/O wait, is a fundamental skill for diagnosing storage bottlenecks.
An administrator wants to execute a long-running script in the terminal while troubleshooting another issue. Which of the following options will achieve this goal?
A. bash script.sh &
B. source script.sh
C. sh script.sh | jobs
D. nice -10 ./script.sh
Summary:
The administrator needs to start a long-running script but must keep the current terminal session available for other tasks. The solution is to run the script in the background, which allows it to execute independently while returning the shell prompt to the user immediately. This is accomplished by appending the ampersand (&) symbol to the command.
Correct Option:
A. bash script.sh &:
This is the correct command. The ampersand (&) at the end of the command instructs the shell to run the script as a background job. The script will start executing, and the terminal will immediately return a prompt, allowing the administrator to continue working on other tasks while the script runs.
Incorrect Options:
B. source script.sh:
The source command (or . command) executes the script within the current shell environment. It does not run it in the background. The terminal will be occupied until the script finishes, which is the opposite of what is desired.
C. sh script.sh | jobs:
This command is illogical. It attempts to pipe the output of the script to the jobs command. The jobs command lists background jobs but cannot be used to start a job in the background via a pipe. This will not run the script in the background.
D. nice -10 ./script.sh:
The nice command only adjusts the scheduling priority (nice value) of the process. It does not, by itself, run the process in the background. This command would still run the script in the foreground, occupying the terminal.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 3.1: "Given a scenario, use the appropriate system and service management commands to accomplish administrative tasks," which includes managing jobs and processes. Using the & operator to run a process in the background is a fundamental job control skill.
A systems administrator is working on a security report from the Linux servers. Which of the following commands can the administrator use to display all the firewall rules applied to the Linux servers? (Select two).
A. ufw limit
B. iptables —F
C. systemct1 status firewalld
D. firewall—cmd ——1ist—a11
E. ufw status
F. iptables —A
Summary:
The administrator needs to generate a security report that includes the current firewall rules. This requires commands that display the active rule sets for the firewall service running on the servers. The two most common firewall management interfaces on modern Linux systems are firewalld (managed with firewall-cmd) and ufw (Uncomplicated Firewall). The iptables command can also show rules but is often the backend for these higher-level tools.
Correct Options:
D. firewall-cmd --list-all:
This command is used when the system is running the firewalld service. It provides a comprehensive overview of the firewall configuration for the default zone, including services, ports, masquerading, and other settings.
E. ufw status:
This command is used when the system is running the Uncomplicated Firewall (ufw). The ufw status command displays the current status and a list of the active firewall rules. Using ufw status numbered provides an even more detailed view with rule numbers.
Incorrect Options:
A. ufw limit:
This is not a command to display rules. The ufw limit command is used to add a rule that limits connection attempts.
B. iptables -F:
This command flushes (deletes) all rules in the selected iptables chain. It is a destructive command, not one for displaying rules for a report.
C. systemctl status firewalld:
This command shows the operational status of the firewalld service (whether it is running or not) but does not list the actual firewall rules themselves.
F. iptables -A:
This command is used to append a new rule to the end of a selected iptables chain. The -A flag requires a chain name and a rule specification. It is used for modifying rules, not displaying them. The correct iptables command to list rules is iptables -L.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 4.2: "Given a scenario, implement and configure Linux firewalls and access control options," which includes managing firewalld and other firewall services. Knowing the commands to display the current rule set (firewall-cmd --list-all, ufw status, iptables -L) is essential for auditing and reporting.
A Linux administrator would like to measure possible packet loss between a workstation and a remote web application that is running on port 443. Which of the following would be the best command for the administrator to use to display this information?
A. ping -c 50
B. tcpdump -p 443
C. mtr -T -P 443
D. traceroute -p 443
Explanation: mtr (My Traceroute) is a network diagnostic tool that combines the functionality of traceroute and ping. It shows real-time packet loss and latency on a hop-by-hop basis. The -T option uses TCP instead of ICMP, and the -P 443 option specifies the remote port. This provides the best method for checking packet loss on port 443.
| Page 16 out of 40 Pages |
| 101112131415161718192021 |
| XK0-005 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our XK0-005 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before CompTIA Linux+ Certification exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive XK0-005 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.