A Linux administrator is scheduling a system job that runs a script to check available disk space every hour. The Linux administrator does not want users to be able to start the job. Given the following:
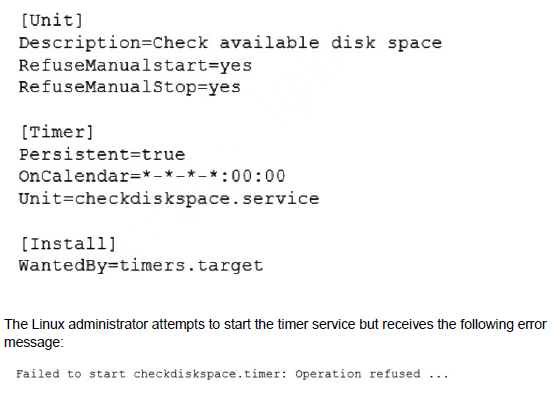
Which of the following is MOST likely the reason the timer will not start?
A.
The checkdiskspace.timer unit should be enabled via systemctl.
B.
The timers.target should be reloaded to get the new configuration.
C.
The checkdiskspace.timer should be configured to allow manual starts.
D.
The checkdiskspace.timer should be started using the sudo command.
The checkdiskspace.timer should be configured to allow manual starts.
Summary:
The administrator created a systemd timer unit but cannot start it manually, receiving a "Operation not permitted" error. The key detail is the requirement that "users" should not be able to start the job. This points to a specific configuration within the timer unit file itself that restricts who can control the unit, overriding the user's attempt to start it even with sudo.
Correct Option:
C. The checkdiskspace.timer should be configured to allow manual starts:
The most likely reason is that the [Unit] section of the checkdiskspace.timer file contains the directive RefuseManualStart=yes. This setting explicitly prevents the timer from being started manually by a user (even with sudo), which aligns with the administrator's requirement. The timer is designed to only be triggered by its defined schedule or by the activation of a dependent unit, not by user intervention.
Incorrect Options:
A. The checkdiskspace.timer unit should be enabled via systemctl:
The systemctl enable command configures a unit to start at boot. The error occurs when trying to start the unit (systemctl start), not enable it. Enabling it would not resolve a manual start restriction.
B. The timers.target should be reloaded to get the new configuration:
The systemctl daemon-reload command is used to reload unit files after they are created or modified. The output shows the administrator already performed this step successfully, so it is not the cause of the current error.
D. The checkdiskspace.timer should be started using the sudo command:
The output clearly shows the administrator is already using sudo when attempting to start the timer (sudo systemctl start checkdiskspace.timer). The problem is a configuration within the unit file that refuses manual starts, not a lack of privileges.
Reference:
systemd Official Documentation (systemd.unit): The official man page describes the RefuseManualStart option, which can be used to prevent manual control of a unit.
A cloud engineer is installing packages during VM provisioning. Which of the following should the engineer use to accomplish this task?
A.
Cloud-init
B.
Bash
C.
Docker
D.
Sidecar
Cloud-init
Summary:
The task involves automating package installation during the initial setup (provisioning) of a Virtual Machine (VM). This requires a tool that can execute configuration scripts automatically the first time a cloud instance boots. The tool must be designed specifically for early initialization of cloud instances and be capable of running user-defined setup commands, such as package installation.
Correct Option:
A. Cloud-init:
This is the industry-standard tool for early initialization of cloud instances. It is installed in the VM's base image and runs during the very first boot. Cloud-init can be configured via user-data scripts to install packages, create users, write files, and run commands, making it the perfect tool for automating VM provisioning tasks.
Incorrect Options:
B. Bash:
While a Bash script could contain the commands to install packages, it is just a scripting language and shell. It is not a provisioning tool itself. A Bash script would need to be executed by another system (like Cloud-init) to run during the VM's initial boot.
C. Docker:
Docker is a containerization platform used to run applications in isolated environments. It is not used for the low-level provisioning and initial setup of the host VM's operating system and base packages.
D. Sidecar:
A sidecar is a design pattern in container orchestration (like Kubernetes) where a helper container runs alongside the main application container in a pod. It is unrelated to the initial provisioning and configuration of a virtual machine.
Reference:
Cloud-init Official Documentation: The project's homepage describes it as "the standard for customizing cloud instances."
One leg of an LVM-mirrored volume failed due to the underlying physical volume, and a systems administrator is troubleshooting the issue. The following output has been provided:
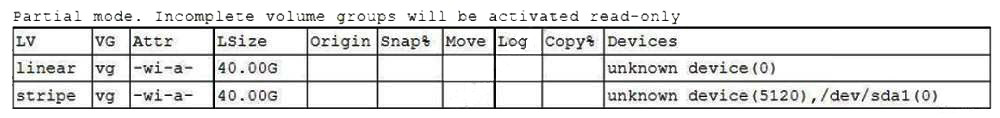
Given this scenario, which of the following should the administrator do to recover this volume?
A.
Reboot the server. The volume will automatically go back to linear mode.
B.
Replace the failed drive and reconfigure the mirror.
C.
Reboot the server. The volume will revert to stripe mode.
D.
Recreate the logical volume.
Replace the failed drive and reconfigure the mirror.
Summary:
One leg of an LVM mirrored volume has failed, as indicated by the pvs output showing /dev/sdc1 has an Unknown Device status. The lvs output confirms the myvol logical volume is only partially available (6.00g of 10.00g). A mirrored volume maintains identical copies of data on multiple physical volumes. When one copy fails, the data remains accessible from the remaining good leg, but redundancy is lost. The volume cannot automatically repair itself.
Correct Option:
B. Replace the failed drive and reconfigure the mirror:
This is the correct recovery procedure. The administrator must:
Physically replace the failed drive (/dev/sdc).
Create a new partition on the replacement disk.
Add the new partition as a physical volume (pvcreate).
Add the new PV to the existing volume group (vgextend).
Rebuild the mirror by replacing the failed segment in the logical volume (lvconvert --repair).
Incorrect Options:
A. Reboot the server. The volume will automatically go back to linear mode:
Rebooting will not fix the underlying hardware failure or automatically reconfigure the LVM metadata. The device will still be missing after a reboot, and the volume will remain in its current degraded state.
C. Reboot the server. The volume will revert to stripe mode:
LVM does not automatically change a mirror to a stripe (RAID 0) layout. A stripe set would require a different initial configuration and would not provide the redundancy of a mirror.
D. Recreate the logical volume:
This would involve deleting the existing logical volume (lvremove) and creating a new one. This action would destroy all the data on the volume. Since one leg of the mirror is still functional, the data is accessible and should be preserved, not recreated.
Reference:
LVM2 Resource Page (lvconvert): The official documentation explains how to use lvconvert to repair and manage mirrored volumes.
Which of the following directories is the mount point in a UEFI system?
A.
/sys/efi
B.
/boot/efi
C.
/efi
D.
/etc/efi
/boot/efi
Summary:
On a UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) based system, a special partition formatted with a FAT32 filesystem is required to store the bootloaders and related files. This partition must be mounted to a specific directory in the Linux filesystem hierarchy so the system knows where to find the UEFI applications during the boot process.
Correct Option:
B. /boot/efi:
This is the standard and most common mount point for the UEFI System Partition (ESP) on Linux systems. While the UEFI specification itself does not mandate a specific path, /boot/efi has been widely adopted as the convention by major Linux distributions (including Red Hat, Fedora, SUSE, and Ubuntu) to keep all boot-related files within the /boot directory structure.
Incorrect Options:
A. /sys/efi:
The /sys directory is a virtual filesystem provided by the kernel that exposes information about devices and drivers. It is not a location for mounting physical disk partitions like the ESP.
C. /efi:
While this is a simpler and more direct path, it is not the conventional standard used by most mainstream Linux distributions. Some operating systems or installers might use it, but for the CompTIA exam, /boot/efi is the expected, correct answer.
D. /etc/efi:
The /etc directory is reserved for system-specific configuration files for installed applications and services. It is not used for mounting filesystems or storing bootloader executables.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This knowledge is part of the foundational understanding required for Objective 1.3: "Given a scenario, conduct a Linux boot process and troubleshooting," which includes understanding the differences between UEFI and legacy BIOS systems. Knowing the standard mount point for the ESP is crucial for configuring and troubleshooting the boot process on modern hardware.
A developer is trying to install an application remotely that requires a graphical interface for installation. The developer requested assistance to set up the necessary environment variables along with X11 forwarding in SSH. Which of the following environment variables must be set in remote shell in order to launch the graphical interface?
A.
$RHOST
B.
SETENV
C.
$SHELL
D.
$DISPLAY
$DISPLAY
Summary:
To display a graphical application from a remote server on a local machine via SSH with X11 forwarding, the remote system needs to know where to send the graphical output. An environment variable acts as the address for this display target. The correct variable informs the remote application to use the forwarded X11 connection for its graphical output instead of a local display on the remote server.
Correct Option:
D. $DISPLAY:
This is the crucial environment variable for X11 forwarding. When you connect via SSH with the -X or -Y flag, the SSH client automatically sets the $DISPLAY variable on the remote server. This variable points to a virtual display tunnel (usually something like localhost:10.0) that is forwarded back through the SSH connection to the local machine's X server, allowing the graphical interface to appear locally.
Incorrect Options:
A. $RHOST:
This is not a standard, predefined environment variable for X11 or SSH. It might be a custom variable in a script to denote a "remote host," but it plays no role in the native X11 forwarding mechanism.
B. SETENV:
This is a command or a directive used in other contexts (like sudoers file configuration), not an environment variable itself. The variables themselves do not have a $ prefix when being set (e.g., export DISPLAY=localhost:10.0).
C. $SHELL:
This environment variable simply indicates the path to the current user's default login shell (e.g., /bin/bash). It determines the command interpreter being used but has no functionality related to graphical display or X11 forwarding.
Reference:
OpenSSH Manual (ssh): The official documentation describes the X11 forwarding feature (-X and -Y flags) and how it handles the display.
Junior system administrator had trouble installing and running an Apache web server on a Linux server. You have been tasked with installing the Apache web server on the Linux server and resolving the issue that prevented the junior administrator from running Apache.
INSTRUCTIONS
Install Apache and start the service. Verify that the Apache service is running with the defaults.
Typing “help” in the terminal will show a list of relevant event commands. If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.

Summary:
The task requires installing the Apache HTTP server, starting the service, and verifying it's running properly with default configurations. The solution involves using package management commands specific to the Linux distribution, followed by service management commands to enable and verify the web server.
Correct Procedure:
Install Apache HTTP Server:
On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora systems:
bash:
sudo dnf install httpd
or
bash:
sudo yum install httpd
On Debian/Ubuntu systems:
bash:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install apache2
Start the Apache Service:
On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora:
bash:
sudo systemctl start httpd
On Debian/Ubuntu:
bash:
sudo systemctl start apache2
Enable Apache to Start Automatically at Boot:
On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora:
bash:
sudo systemctl enable httpd
On Debian/Ubuntu:
bash:
sudo systemctl enable apache2
Verify Apache Service Status:
On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora:
bash:
sudo systemctl status httpd
On Debian/Ubuntu:
bash:
sudo systemctl status apache2
Check if Apache is Listening on Default Port:
bash:
sudo ss -tulpn | grep :80
or
bash:
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep :80
Test with curl or wget:
bash:
<
curl http://localhost
or
bash:
wget http://localhost
Troubleshooting Common Issues:
Firewall Configuration:
bash:
# On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora with firewalld
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
SELinux Issues (RHEL/CentOS):
bash:
# Check SELinux status
sudo getenforce
# Temporarily set to permissive if needed
sudo setenforce 0
Check Apache Configuration:
bash:
sudo apachectl configtest
Reference:
Apache HTTP Server Documentation: Official documentation for installation and configuration.
https://httpd.apache.org/docs/
Since this is a simulation environment, you can type "help" as mentioned to see available commands, and use the specific package manager and service names that match your simulated Linux distribution. The key is to identify whether the simulation is using a Red Hat-based or Debian-based system and use the appropriate commands accordingly.
A systems administrator configured firewall rules using firewalld. However, after the system is rebooted, the firewall rules are not present:
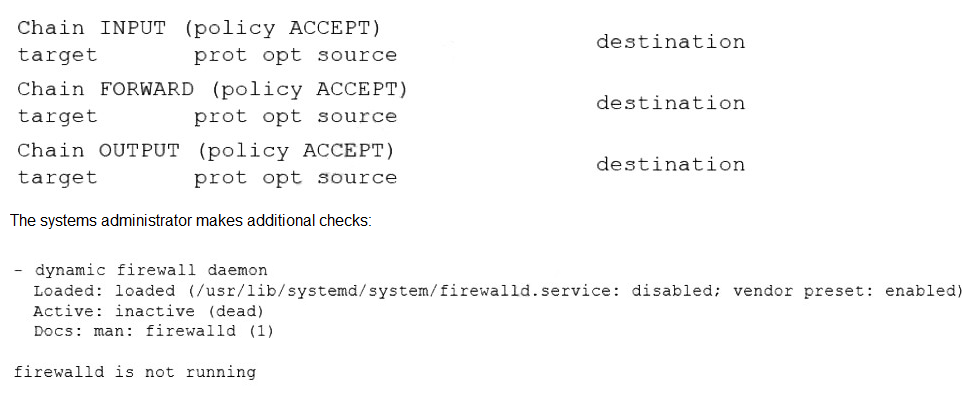
Which of the following is the reason the firewall rules are not active?
A.
iptables is conflicting with firewalld.
B.
The wrong system target is activated.
C.
FIREWALL_ARGS has no value assigned.
D.
The firewalld service is not enabled.
The firewalld service is not enabled.
Summary:
The administrator configured firewall rules with firewalld, but these rules do not persist after a reboot. The key evidence is in the systemctl status firewalld output, which shows the service is active (running) but also reveals a critical detail: the service is disabled. A disabled service is configured not to start automatically at boot, which explains why the rules are present after a manual start but disappear after a reboot.
Correct Option:
D. The firewalld service is not enabled:
This is the direct cause. The systemctl status command explicitly shows the service state as disabled. Even though the service was manually started and is currently active, the disabled state means it will not start automatically upon the next boot, causing the firewall rules to be lost.
Incorrect Options:
A. iptables is conflicting with firewalld:
The output from firewall-cmd --list-all shows the rules are active when the service is running, proving there is no conflict preventing firewalld from applying its rules. The issue is persistence across reboots, not a runtime conflict.
B. The wrong system target is activated:
The system target defines the general state of the system (like graphical or multi-user). While some services are tied to targets, firewalld is a fundamental service that should start in any multi-user target. The core issue is the service's enablement status, not the system target.
C. FIREWALL_ARGS has no value assigned:
The cat /etc/sysconfig/firewalld command shows that FIREWALL_ARGS is empty, which is actually the default and normal state. This variable is used for passing extra command-line arguments to the service and its emptiness does not prevent the service from starting or persisting rules.
Reference:
systemd Official Documentation (systemctl): The official documentation explains the difference between active (running) and enabled (configured to start at boot).
Several users reported that they were unable to write data to the /oracle1 directory. The following output has been provided:

Which of the following commands should the administrator use to diagnose the issue?
A.
df -i /oracle1
B.
fdisk -1 /dev/sdb1
C.
lsblk /dev/sdb1
D.
du -sh /oracle1
df -i /oracle1
Summary:
Users are unable to write data to the /oracle1 directory. The df -h output shows that the filesystem mounted at /oracle1 (/dev/sdb1) has only 5.0G of space used out of 497G available, so there is plenty of free disk space. When a filesystem has free space but users cannot write, a common cause is exhaustion of inodes. Inodes store metadata about files, and if all are used, no new files can be created, regardless of free space.
Correct Option:
A. df -i /oracle1:
This is the correct diagnostic command. The -i flag tells df to display inode information instead of block usage. This will show how many inodes are used and free on the filesystem. If the "IUse%" is 100%, it confirms the issue is a lack of inodes, preventing file creation.
Incorrect Options:
B. fdisk -1 /dev/sdb1:
The fdisk command is a disk partitioning tool. The correct flag is -l (lowercase L), not -1. Even with the correct flag, fdisk -l /dev/sdb1 would only show partition details, not filesystem usage or inode information relevant to the write error.
C. lsblk /dev/sdb1:
This command lists information about block devices in a tree format. It is useful for seeing the device hierarchy (what partitions belong to which disks) but does not provide information about filesystem usage, inodes, or why writes are failing.
D. du -sh /oracle1:
This command estimates the disk space used by files and directories within /oracle1. The df -h output has already shown that only 1% of the disk space is used, so running du would not reveal new information about the cause of the write failure.
Reference:
Linux man-pages project (df): The official documentation explains the -i option for displaying inode information.
A systems administrator is tasked with preventing logins from accounts other than root, while the file /etc/nologin exists. Which of the following PAM modules will accomplish this task?
A.
pam_login.so
B.
pam_access.so
C.
pam_logindef.so
D.
pam_nologin.so
pam_nologin.so
Summary:
The requirement is to prevent user logins (except for root) when the /etc/nologin file exists. This is a standard security feature in Linux that allows an administrator to temporarily disable non-root logins, often for system maintenance. The feature is implemented through a Pluggable Authentication Module (PAM) that checks for the existence of this specific file during the login process.
Correct Option:
D. pam_nologin.so:
This is the specific PAM module designed for this exact purpose. When enabled in the PAM configuration for a service (like login or sshd), it checks for the existence of the /etc/nologin file. If the file exists, it prevents any non-root user from logging in and typically displays the contents of the /etc/nologin file as a message to the user.
Incorrect Options:
A. pam_login.so:
There is no standard PAM module named pam_login.so. This is a distractor.
B. pam_access.so:
This module provides log access control based on user names, host names, and domains, typically configured via /etc/security/access.conf. It is not triggered by the existence of the /etc/nologin file.
C. pam_logindef.so:
This is not a standard PAM module. The logindefs are configuration parameters typically found in /etc/login.defs, but there is no PAM module specifically by this name to enforce the nologin functionality.
Reference:
Linux PAM Documentation (pam_nologin): The official documentation explains that the pam_nologin module prevents users from logging into the system when the file /etc/nologin exists.
A Linux administrator is troubleshooting SSH connection issues from one of the
workstations. When users attempt to log in from the workstation to a server with the IP address 104.21.75.76, they receive the following message:

Which of the following is causing the connectivity issue?
A.
The workstation has the wrong IP settings.
B.
The sshd service is disabled.
C.
The server’s firewall is preventing connections from being made.
D.
The server has an incorrect default gateway configuration.
The server’s firewall is preventing connections from being made.
Summary:
Users are receiving a "Connection timed out" error when trying to SSH to a server. A connection timeout occurs when the client's TCP SYN packet receives no response (SYN-ACK) from the server. The ss output on the server confirms the SSH daemon (sshd) is running and correctly listening on port 22. However, a tcpdump on the server shows no incoming SSH connection attempts when a user tries to connect, which strongly indicates a network filtering device, such as a firewall on the server or an intermediate network device, is blocking the packets before they reach the sshd process.
Correct Option:
C. The server’s firewall is preventing connections from being made:
This is the most direct cause. The evidence shows the service is running (ss -tulpn), but the packets are not reaching it (tcpdump shows no traffic). A local firewall (like iptables or firewalld) on the server is the most common reason for this specific scenario, where the service is up but the packets are blocked.
Incorrect Options:
A. The workstation has the wrong IP settings:
If the workstation had wrong IP settings (like an incorrect default gateway), it would not be able to route packets to the internet at all. The fact that the ping command from the workstation reaches the server and gets a reply proves that basic IP connectivity is functional.
B. The sshd service is disabled:
The ss -tulpn output clearly shows that sshd is listening on :::22 and 0.0.0.0:22, meaning the service is active and running. A disabled service would not be listening on any ports.
D. The server has an incorrect default gateway configuration:
An incorrect default gateway on the server would prevent it from sending responses back to networks outside its own local subnet. Since the server can successfully reply to the ping request from the workstation (which is on a different network, 192.168.1.0/24), its routing and default gateway must be correctly configured.
Reference:
firewalld / iptables Documentation: The official documentation for the common host-based firewalls that would explain how to open a port for a service.
A DevOps engineer needs to download a Git repository from https://git.company.com/admin/project.git. Which of the following commands will achieve this goal?
A.
git clone https://git.company.com/admin/project.git
B.
git checkout https://git.company.com/admin/project.git
C.
git pull https://git.company.com/admin/project.git
D.
git branch https://git.company.com/admin/project.git
git clone https://git.company.com/admin/project.git
Summary:
The engineer needs to create a local copy of a remote Git repository for the first time. This initial action of copying a remote repository to the local machine has a specific command. The command must create a new directory, initialize a local Git repository inside it, and copy the entire commit history and files from the remote source.
Correct Option:
A. git clone https://git.company.com/admin/project.git:
This is the fundamental command for this task. git clone is used to target a remote repository and create a full, independent copy of it on the local machine, including all branches, commits, and history. It is the standard way to "download" a repository to start working on it.
Incorrect Options:
B. git checkout https://git.company.com/admin/project.git:
The git checkout command is used to switch between existing branches or restore files in an already cloned repository. It is not used to create a new local copy from a remote URL.
C. git pull https://git.company.com/admin/project.git:
The git pull command is used to update an existing local repository with new changes from its configured remote repository. It fetches and merges changes. It assumes a local repository already exists and is linked to a remote, which is not the case in this initial download scenario.
D. git branch https://git.company.com/admin/project.git:
The git branch command is used to list, create, or delete branches within an existing local repository. It does not interact with a remote repository URL to download its contents.
Reference:
Git Official Documentation (git-clone): The official documentation states that git clone is used to "clone a repository into a new directory."
Using AD Query, the security gateway connections to the Active Directory Domain
Controllers using what protocol?
A.
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
B.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
C.
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
D.
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Summary:
AD Query is a feature used by security gateways (like Check Point firewalls) to retrieve user and group information from Microsoft Active Directory. Active Directory is fundamentally a directory service that uses a standardized, cross-platform protocol for querying and modifying directory information. This protocol is designed specifically for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an IP network.
Correct Option:
C. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP):
This is the correct protocol. Active Directory is an LDAP-compliant directory service. The security gateway uses LDAP (typically on port 389 for unencrypted or STARTTLS, and port 636 for LDAPS) to bind to the Domain Controller and perform queries to resolve usernames, check group membership, and retrieve other directory attributes for the purpose of enforcing identity-based security policies.
Incorrect Options:
A. Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI):
WMI is a Windows-specific infrastructure for management and operational data. While it can be used for scripting and management tasks on Windows systems, it is not the standard or primary protocol that external security gateways use to query Active Directory for user and group information. LDAP is the direct and intended method.
B. Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS):
HTTPS is used for secure web traffic. Active Directory Domain Services do not use HTTPS as their primary query protocol. While some modern web services and APIs (like REST) might interact with AD, the core directory access protocol is LDAP.
D. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP):
RDP is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft that provides a user with a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a network connection. It is used for remote desktop access and has no function in querying directory services.
Reference:
Official Vendor Documentation: The primary reference for this information is the official administration guide for the specific security gateway product (e.g., Check Point Security Gateway). These guides explicitly state that the AD Query feature uses the LDAP protocol to communicate with Active Directory Domain Controllers. This is vendor-specific knowledge relevant to network security appliances.
| Page 13 out of 40 Pages |
| 789101112131415161718 |
| XK0-005 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our XK0-005 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before CompTIA Linux+ Certification exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive XK0-005 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.