What payload is returned by a Database SELECT operation that does not match any rows in the database?
A. false
B. null
C. Exception
D. Empty Array
Explanation:
When a Database SELECT returns no matching rows, Mule’s Database connector yields an empty list (empty array) as the payload rather than null, false, or an exception.
Refer to the exhibit.
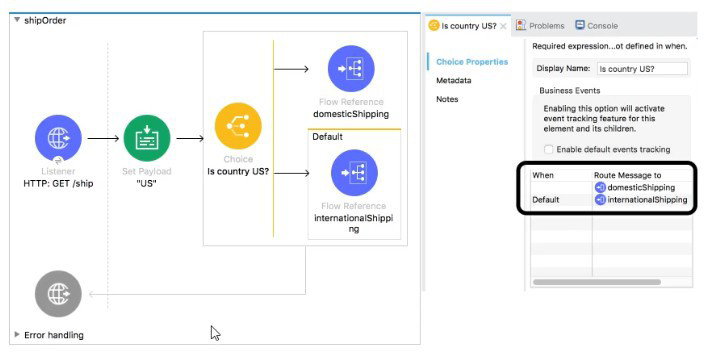
What is a valid expression for the Choice router’s when expression to route events to the documenticShipping flow?
A. 0#[ payload = 'US' ]
B. #[ payload == 'US' J
C. #[ if(payload = 'US') J
D. #[ if(payload == "US") ]
Explanation: Choice Router The Choice router dynamically routes messages through a flow according to a set of DataWeave expressions that evaluate message content. Each expression is associated with a different routing option. The effect is to add conditional processing to a flow, similar to an if/then/else code block in most programming languages.
Only one of the routes in the Choice router executes, meaning that the first expression that evaluates to true triggers that route’s execution and the others are not checked. If none of the expressions are true, then the default route executes.
Properties of
Expression in DataWeave language to evaluate input.If the expression evaluates to true, this routing option is used:
< when expression = " # [ vars . language = = ' Spanish ' ] ">
With respect to above information ,
Option 1 is the correct syntax as others are incorrect because of below reasons
* Single = is not the correct syntax to validate the condition. It should be ==
* If keyword is not required in when condition.
What valid RAML retrieves details on a specific by its orderld as a URL parameter?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation:
RAML uses curly braces {} to indicate a URI parameter. To retrieve the details of a specific order by its orderId, you define a parameterized resource like this:
/orders:
/{orderId}:
get:
This tells the API that a GET request to /orders/12345 (for example) will retrieve the details for order ID 12345.
Why the others are incorrect:
B. Incorrect because /orderId: is treated as a literal string, not a URI parameter.
C. Invalid nesting — get should not be above the path segment.
D. Same as C — the path structure is incorrectly ordered.
What is the purpose of the api:router element in APIkit?
A. Creates native connectors using a 3rd party Java library
B. Serves as an API implementation
C. Validates requests against RAML API specifications and routes them to API implementations
D. Validates responses returned from API requests and routes them back to the caller
Explanation:
The APIkit Router is a key message processor that validates requests against the provided definition, enriches messages (for example by adding default values to the messages) and routes requests to a particular flow. Also, the Router raises errors messages if errors occurs while routing, validating or processing the user request.
What MuleSoft API-led connectivity layer is intended to expose part of a backend database without business logic?
A. Data layer
B. Process layer
C. Experience layer
D. System layer
Explanation:
Correct answer is System layer System APIs provide a means for insulating the data consumers from the complexity or changes to the underlying backend systems.
MuleSoft recommends three-layered approach to API-led connectivity, highlighting the three layers:
* System APIs
* Process APIs
* Experience APIs
System APIs are the core systems of record underlying core systems of record (e.g. ERPs, key customer and billing systems, databases, etc.). Process APIs allow you to define a common process which the organization can share, and these APIs perform specific functions, provide access to non-central data, and may be built by either Central IT or Line of Business IT. And finally, the Experience APIs are the means by which data can be reconfigured so that it is most easily consumed by its intended audience, all from a common data source.
The three-layered structure allows for a seamless flow of data from systems of record to new experiences, and allows for reusability of assets rather than point to point connections. This approach provides a distributed and tailored approach to architecture, greater flexibility through loose coupling, and deeper operational visibility into what is being built.
An HTTP Request operation sends an HTTP request with a non-empty JSON object payload to an external HTTP endpoint. The response from the external HTTP endpoint returns an XML body. The result is stored in a target named the Result.
What is the payload at the event processor after the HTTP Request?
A. The XML response body
B. null
C. The original JSON request body
D. A non-empty Java object
Explanation:
The HTTP Request operation overwrites the payload with the response body from the external endpoint. Since the response is XML, the payload becomes the XML content (Option A).
Why Other Options Are Wrong:
B (null): Incorrect—the response body is non-null XML.
C (Original JSON): Overwritten by the response.
D (Java object): Mule 4 defaults to raw data (XML), not Java objects.
How does APIkit determine the number of flows to generate from a RAML specification?
A. How does APIkit determine the number of flows to generate from a RAML specification?
B. Creates a separate flow for each HTTP method
C. Creates a separate flow for each response status code
D. Creates a separate flow for each resource that contains child resources
Explanation:
When you use APIkit (e.g. via the APIkit Router in Mule applications), it analyzes your RAML spec. It generates flows based on:
Resources (paths)
HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) under each resource
So for each combination of resource + method, APIkit generates a dedicated flow.
Example RAML:
/resources:
get:
description: Get all resources
post:
description: Create a new resource
/resources/{id}:
get:
description: Get a resource by id
put:
description: Update a resource
APIkit would generate these flows:
api-main.raml|/resources|get
api-main.raml|/resources|post
api-main.raml|/resources/{id}|get
api-main.raml|/resources/{id}|put
So 4 flows would be generated.
Why Not The Others?
A. How does APIkit determine the number of flows… → This repeats the question, not an answer.
C. Creates a separate flow for each response status code → Incorrect. Responses only define schemas and codes, not separate flows.
D. Creates a separate flow for each resource that contains child resources →Incorrect. Child resources affect routing but not the number of flows unless they have distinct HTTP methods.
According to Mulesoft, how are Modern APIs treated as?
A. Products
B. SOAP API's
C. Rest API's
D. Code
Explanation:
According to MuleSoft’s API-led connectivity approach and the API Lifecycle concepts, modern APIs are treated as products rather than just technical interfaces or code artifacts.
Why “products”?
They have consumers (internal or external developers, partners, apps, etc.)
They come with documentation and usage agreements
They are versioned, governed, secured
They are monitored for usage and performance
They deliver business value and can even be monetized
So, APIs aren’t merely code (D is wrong), or tied to a protocol like REST or SOAP (B and C are wrong).
Why Not The Others?
B. SOAP APIs → SOAP is one implementation style. Modern APIs can be REST, SOAP, GraphQL, Async APIs, etc.
C. REST APIs → Modern APIs are not defined solely by the REST architectural style.
D. Code → Modern APIs expose business capabilities via contracts; they are much more than just code.
Refer to the exhibits.
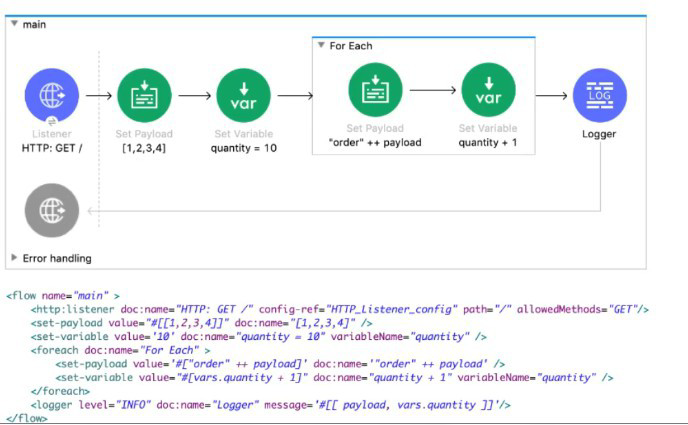
What payload and quantity are togged at the end of the main flow?
A. [[order1, order2, order3, order4], 14]
B. [[1,2,3,4], 10]
C. [[1,2,3,4], 14]
D. [orderlorder2order3order4, 14]
Explanation:
Initial Setup (Before foreach Loop)
Set Payload = [1, 2, 3, 4] → Payload is an array [1, 2, 3, 4].
Set Variable quantity = 10 → vars.quantity is initialized to 10.
Inside the foreach Loop
The loop iterates 4 times (once for each array element: 1, 2, 3, 4).
Each iteration does the following:
Set Payload = "order" ++ payload
Converts the current element (e.g., 1) to a string (e.g., "order1").
But since Set Payload overwrites the payload each time, the final payload after the loop is just the last value ("order4").
Set Variable quantity = quantity + 1
Increments quantity by 1 in each iteration.
Final quantity = 10 + 4 = 14.
Final Payload & Quantity
Payload:
If the flow accumulates results (e.g., using map or appending to a variable), the payload would be ["order1", "order2", "order3", "order4"].
However, since the question’s flow overwrites the payload each time, the final payload is just "order4".
Quantity: 14 (as calculated above).
Why Option D is Correct (Assuming Accumulation)
The question likely expects concatenated strings ("order1order2order3order4") due to how MuleSoft handles payloads in loops.
If Set Payload appended instead of overwrote, the result would be a merged string.
Thus, [order1order2order3order4, 14] is the closest match.
Why Other Options Are Wrong?
A. [[order1, order2, order3, order4], 14] → Incorrect because the payload is not an array after the loop.
B. [[1,2,3,4], 10] → Ignores loop transformations.
C. [[1,2,3,4], 14] → Incorrect payload (should be modified by the loop).
An organization's Center for enablement (C4E)has built foundational assets (API specifications and implementation templates, common frameworks, and best practices guides) and published them to Anypoint Exchange.
What is a metric related to these foundational assets that helps the organization measure the success of it's C4E efforts?
A. Utilization counts of foundational assets in production applications
B. Correlation of each foundational asset with the counts of developers that download such asset
C. Correlation of key performance indicators (KPI) of production applications with foundational assets
D. Count how many Lines Of Business (LoBs) onsumed each foundational asset
Explanation:
Below are the Key performance indicators (KPIs), to measure and track the and success ofthe C4E and its activities, as well as the growth and health of the application network. Most of the metrics can be extracted automatically, through REST APIs, from Anypoint Platform.
• # of assets published to Anypoint Exchange
• # of interactions with Anypoint Exchange assets
• # of APIs managed by Anypoint Platform
• # of System APIs managed by Anypoint Platform
• # of API clients registered for access to APIs
• # of API implementations deployed to Anypoint Platform
• # of API invocations
• # or fraction of lines of code covered by automated tests in CI/CD pipeline
• Ratio of info/warning/critical alerts to number of API invocations
Refer to the exhibits. APIKit router is used to generate the flow components for RAML pecification.
The Mule application must be available to REST clients using the two URL's
http://localhost:8081/internal and http://localhost:8081/external
How many APIKit Router components are generated to handle requests to every endpoint defined in RAML specification?
1. Library.raml
2./books
3. get:
4. post:
5./order:
6. get
7. patch 8./members
9. get:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 5
Explanation:
APIkit generates only one APIKit Router component per Mule application, regardless of the number of endpoints or URLs exposed. Here’s why:
APIKit Router’s Role:
The APIKit Router is the single entry point for all API requests.
It routes incoming requests to the correct flow based on the HTTP method and resource path defined in the RAML.
Generated Flows vs. Routers:
While APIkit creates multiple flows (one per HTTP method, e.g., GET /books, POST /books), it uses only one Router to direct traffic to these flows.
The Router inspects the request’s path/method and forwards it to the appropriate flow.
Multiple URLs (e.g., /internal, /external)
If the application listens on multiple base paths (e.g., http://localhost:8081/internal and http://localhost:8081/external), this is configured in the HTTP Listener, not the APIKit Router.
The same Router handles both paths, delegating to the correct flows based on the RAML spec.
Your RAML Example:
The RAML defines 4 endpoints (/books, /orders, /members with GET/POST/PATCH).
APIkit generates 4+ flows (1 per method) but only 1 Router to manage them all.
Why Not Other Options?
B (2) or C (3): Incorrect. The number of Routers is not tied to endpoints or URLs.
D (5): Matches the number of HTTP methods but misrepresents the Router’s role.
What is minimal requirement in a flow for a Mule application to compile?
A. Event Source
B. Event Processors
C. Error handlers
D. Source and processors both
Explanation:
In Mule, a flow must be syntactically valid XML (or YAML in Mule 4.6+), and it must contain at least one element that is a valid component for it to compile and deploy.
A Mule flow technically does not require an event source to compile. You can have a flow with only processors and no inbound connector.
Example:
< flow name = " myFlow " >
< set - payload value = " Hello World " >
< / set - payload > < / flow >
This will compile and deploy, even though there’s no listener or event source. It simply can’t be invoked externally unless triggered internally by another flow or component.
Why Not Other Options?
A. Event Source → Not required for compilation. You can have a flow without an event source.
C. Error handlers → Optional. You can compile a flow without an error handler.
D. Source and processors both → Incorrect. Only processors are technically required for compilation.
| Page 8 out of 20 Pages |
| Previous |