The ability to resolve two separate reflectors perpendicular to the path of the beam describes which type of resolution?
A. Axial
B. Contrast
C. Lateral
D. Temporal
Explanation: Lateral resolution describes the ability of an ultrasound system to distinguish between two structures that are side by side (perpendicular to the path of the ultrasound beam). This type of resolution depends on the beam width; narrower beams provide better lateral resolution. As the ultrasound beam travels deeper into the tissue, it generally widens, which can reduce lateral resolution. Techniques such as focusing the beam can help improve lateral resolution at specific depths by narrowing the beam width.
At which angle to blood flow would the maximum Doppler shift occur?
A. 90 degrees
B. 60 degrees
C. 30 degrees
D. 0 degrees
Explanation: The Doppler shift is highest when the angle between the ultrasound beam and the direction of blood flow is 0 degrees. This is because the cosine of 0 degrees is 1, maximizing the Doppler frequency shift. As the angle increases towards 90 degrees, the cosine value decreases, reducing the Doppler shift.
Which technique averages individual frames together to improve the image?
A. Coded excitation
B. Compression
C. Persistence
D. Harmonic imaging
Explanation: Persistence is a technique used in ultrasound imaging that averages individual frames together to improve the overall image quality. This process helps to reduce noise and improve the signal-to-noise ratio, leading to clearer and more stable images. By averaging multiple frames, transient artifacts are minimized, and the continuity of structures is better visualized. Persistence is particularly useful in imaging static or slow-moving structures.
Which is a method to reduce noise?
A. Increase frequency
B. Decrease beam width
C. Decrease depth
D. Increase persistence
Explanation: Persistence is a form of temporal averaging where consecutive frames are averaged to reduce random noise, resulting in a smoother image. Increasing persistence effectively reduces noise by averaging out transient noise artifacts while preserving the true signal. This improves image quality, although it may also reduce the temporal resolution, making it less suitable for rapidly moving structures.
Which ultrasound adjustment allows for an increased frame rate in color flow Doppler?
A. Using continuous wave Doppler
B. Decreasing depth
C. Using multiple focal zones
D. Increasing sector scan width
Which pulsed-wave Doppler adjustment would be appropriate to correct the aliasing seen in this image?
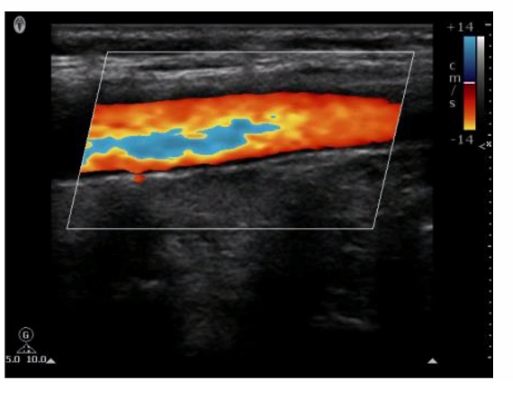
A. Increase the spectral Doppler gain.
B. Decrease the spectral Doppler gain.
C. Increase the Doppler pulse repetition frequency.
D. Decrease the Doppler pulse repetition frequency.
Explanation: Aliasing in pulsed-wave Doppler occurs when the sampled Doppler frequency exceeds the Nyquist limit, which is half of the pulse repetition frequency (PRF). This results in an incorrect representation of the blood flow velocities, causing the waveform to wrap around and appear on the opposite side of the baseline. To correct aliasing, the PRF should be increased, which raises the Nyquist limit and allows for accurate measurement of higher velocities without aliasing. Increasing the PRF effectively reduces the likelihood of aliasing artifacts in the Doppler signal.
Which component of a contrast agent causes a marked mismatch in impedance between the agent and blood?
A. Viscous liquid
B. Serous liquid
C. Solid
D. Gas
Explanation: Contrast agents used in ultrasound imaging typically consist of microbubbles filled with gas. The significant mismatch in acoustic impedance between the gas in the microbubbles and the surrounding blood creates strong reflectors of the ultrasound waves, enhancing the echogenicity of blood and improving the visibility of blood flow and tissue perfusion. The high contrast provided by the gas-filled microbubbles makes them particularly effective as ultrasound contrast agents.
What is the primary reason to use compression?
A. Increase line density
B. Reduce the focal region
C. Improve the axial resolution
D. Adjust the contrast resolution
Explanation:
How is intensity of an ultrasound beam measured?
A. Hydrophone
B. Doppler equation
C. Autocorrelation
D. Reynold's number
Explanation: The intensity of an ultrasound beam is measured using a hydrophone. A hydrophone is a specialized device that detects and measures the acoustic pressure of the ultrasound waves in water or tissue-mimicking materials. It is highly sensitive and can measure the variations in pressure, which are used to calculate the intensity and other acoustic parameters of the ultrasound beam.
Which statement characterizes the primary difference between image A and image B?
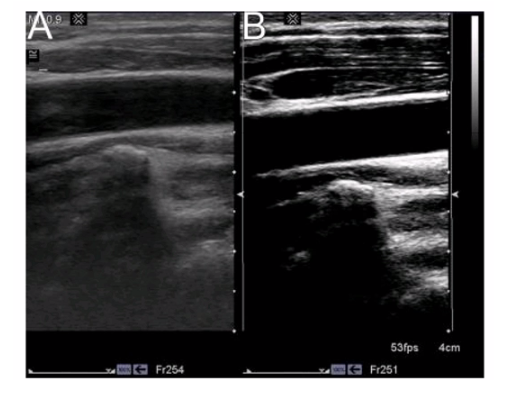
A. Image A demonstrates a better axial resolution.
B. Image A demonstrates a lower overall gain setting.
C. Image A demonstrates a shallower field of view.
D. Image A demonstrates a wider scale of contrast.
Explanation: The primary difference between Image A and Image B is the overall gain setting. Gain controls the amplification of the received echoes. A lower gain setting results in a darker image with less overall brightness, which is evident in Image A compared to Image B. Image B appears brighter, indicating a higher gain setting that amplifies the echoes more, making the structures appear more prominently.
Which target group is used to evaluate transverse distance measurement accuracy in this tissue-mimicking phantom image?
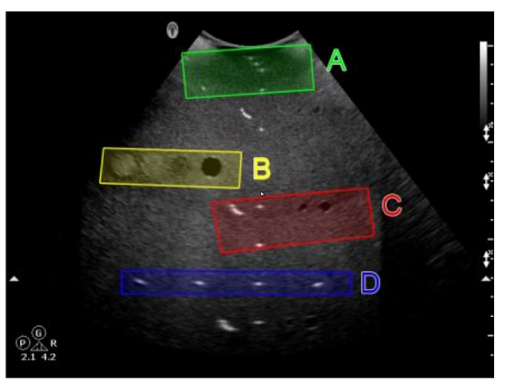
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation: In the tissue-mimicking phantom image, Option D (blue box) is used to evaluate transverse distance measurement accuracy. Phantoms are used to simulate human tissue and provide a standardized way to test the accuracy and precision of ultrasound machines. Transverse distance measurement accuracy is assessed by measuring known distances between targets in the phantom. The blue box (Option D) typically contains targets positioned to specifically test the accuracy of transverse measurements, ensuring that the ultrasound system provides reliable and precise distance readings.
Which resolution is degraded when utilizing multiple transmit focal zones?
A. Temporal
B. Lateral
C. Axial
D. Elevational
Explanation: When utilizing multiple transmit focal zones, the ultrasound system must perform multiple transmissions at each focal depth. This process requires more time for data acquisition, which in turn decreases the frame rate. A lower frame rate directly impacts temporal resolution, which is the ability to accurately depict moving structures over time. Thus, using multiple focal zones improves lateral resolution but degrades temporal resolution.
| Page 2 out of 9 Pages |
| Previous |