Which two policy components are required to block traffic in real time using a dynamic user group (DUG)? (Choose two.)
A. A Deny policy for the tagged traffic
B. An Allow policy for the initial traffic
C. A Decryption policy to decrypt the traffic and see the tag
D. A Deny policy with the "tag" App-ID to block the tagged traffic
Explanation:
Dynamic User Groups (DUGs) in Palo Alto Networks firewalls are used to dynamically assign users to groups based on tags pushed from external systems like Cortex XSOAR, XDR, or via the XML API. These allow for real-time enforcement of security policies without requiring user logout/login or group refreshes.
To block traffic in real time using DUGs, the following policy components are needed:
🔹 A. A Deny policy for the tagged traffic
This is the actual policy that references the Dynamic User Group and blocks traffic for users dynamically added to the group.
Once a user is tagged (e.g., as "malicious" or "violator"), this rule becomes effective immediately, blocking their access based on the DUG membership.
🔹 B. An Allow policy for the initial traffic
Before the user is tagged and added to the DUG, they still need to be allowed to generate traffic so they can be evaluated or monitored.
This initial allow policy ensures the traffic is visible and can be tagged (e.g., by a monitoring or detection system like Cortex XDR).
❌ Why the other options are incorrect:
C. A Decryption policy to decrypt the traffic and see the tag:
Tags and DUG membership are independent of traffic decryption. DUG enforcement is based on user identity and tag, not packet content.
D. A Deny policy with the "tag" App-ID to block the tagged traffic:
Tags are not App-IDs. A tag is an identifier for grouping users in DUGs, not an application signature. So there is no "tag" App-ID.
🔍 Reference:
Palo Alto Networks – Dynamic User Groups:
Dynamic User Groups (DUGs) Overview
Best Practices for DUG Implementation:
Palo Alto Live Community – Using Dynamic User Groups to Quarantine Users
A remote administrator needs access to the firewall on an untrust interface. Which three options would you configure on an interface Management profile to secure management access? (Choose three)
A. HTTPS
B. SSH
C. Permitted IP Addresses
D. HTTP
E. User-IO
Explanation:
When allowing management access on an external-facing interface (like untrust), it is critical to limit the exposure to reduce the attack surface. The Interface Management Profile is the primary tool for this, controlling how and from where the firewall can be managed.
A. HTTPS & B. SSH:
These are the secure protocols you would enable to allow the remote administrator to actually access the firewall's WebUI (HTTPS) and Command Line Interface (SSH). You should disable insecure protocols like HTTP and Telnet.
C. Permitted IP Addresses:
This is the most crucial security control. Instead of allowing management access from any IP address on the internet, this setting restricts access to only the specific, known IP address (or range) from which the administrator will be connecting. This dramatically reduces the attack surface, preventing random scanners and attackers from even reaching the login prompts for HTTPS or SSH.
Why the other options are incorrect:
D. HTTP:
This is an insecure protocol that transmits credentials and data in plaintext. It should never be enabled for management access, especially on an untrust interface. Enabling HTTP would be a severe security misconfiguration.
E. User-IO:
This service is related to the firewall's physical console port access. It is used for out-of-band management when you are physically connected to the device with a keyboard and monitor. It is completely irrelevant for securing remote network-based management access over the untrust interface.
Best Practices:
Always disable HTTP and Ping on untrust interfaces.
Use certificate-based authentication for HTTPS/SSH if possible.
Reference:
Palo Alto Interface Management Profile Docs
Exhibit.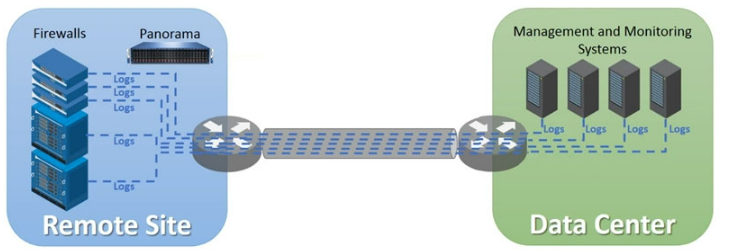
An organization has Palo Alto Networks NGFWs that send logs to remote monitoring and
security management platforms The network team has reported excessive traffic on the
corporate WAN How could the Palo Alto Networks NGFW administrator reduce WAN traffic
while maintaining support for all the existing monitoring/security platforms?
A. Any configuration on an M-500 would address the insufficient bandwidth concerns
B. Forward logs from external sources to Panorama for correlation, and from Panorama send them to the NGFW
C. Configure log compression and optimization features on all remote firewalls
D. Forward logs from firewalls only to Panorama and have Panorama forward logs to other external services
Explanation:
In the image, we see multiple firewalls at a remote site sending logs directly to both Panorama and to various management and monitoring systems at the data center, which consumes significant WAN bandwidth.
To reduce WAN traffic while maintaining the existing log visibility:
🔄 Centralize log forwarding:
Send logs only once across the WAN — from the firewalls to Panorama — and let Panorama handle the log forwarding to all other systems (SIEM, monitoring tools, etc.).
This drastically cuts down on duplicate log traffic over the WAN.
🔍 Why the other options are incorrect:
A. Any configuration on an M-500 would address the insufficient bandwidth concerns:
❌ Incorrect. The M-500 is a Panorama appliance, and its configuration affects log storage/management but doesn't inherently reduce WAN bandwidth unless used properly in architecture like option D.
B. Forward logs from external sources to Panorama for correlation, and from Panorama send them to the NGFW:
❌ Reversed logic. Logs go from NGFWs to Panorama, not the other way around.
C. Configure log compression and optimization features on all remote firewalls:
❌ PAN-OS does not support log compression across WAN links for remote log forwarding. So this option is not feasible.
🧠 Best Practice:
Use Panorama in "Log Collector mode" or dedicated log collectors to centralize logs.
Use Panorama’s Log Forwarding feature to relay logs to external monitoring and SIEM systems.
This keeps only one copy of each log traveling across the WAN, minimizing traffic and duplication.
📚 Reference:
Palo Alto Networks – Log Forwarding
Palo Alto Networks – Best Practices for Distributed Log Collection
Refer to the exhibit.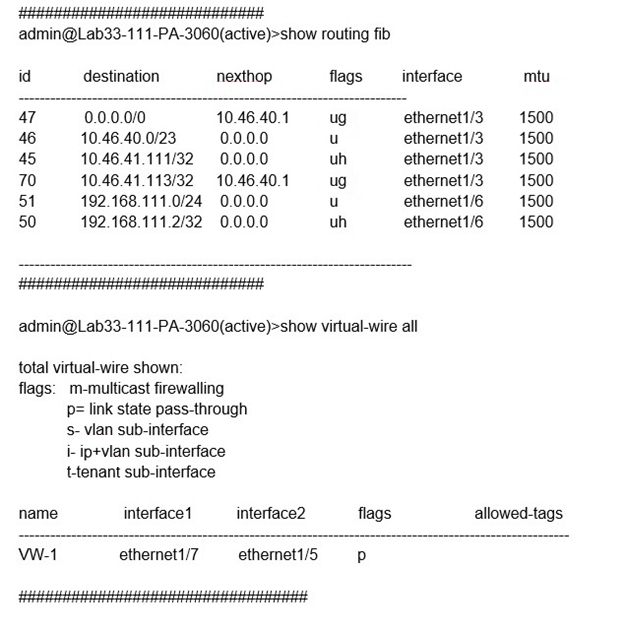
Which will be the egress interface if the traffic's ingress interface is ethernet1/7 sourcing
from 192.168.111.3 and to the destination 10.46.41.113?
A. ethernet1/6
B. ethernet1/3
C. ethernet1/7
D. ethernet1/5
Explanation:
1. Understanding the Traffic Flow
Ingress Interface: ethernet1/7 (Virtual Wire member, as seen in show virtual-wire all).
Source IP: 192.168.111.3 (part of subnet 192.168.111.0/24, locally attached to ethernet1/6).
Destination IP: 10.46.41.113 (routed via 10.46.40.1 on ethernet1/3, per the FIB table).
2. Virtual Wire Behavior
The show virtual-wire all output shows:
VW-1 binds ethernet1/7 (ingress) to ethernet1/5 (egress).
Flags: p (link state pass-through), meaning traffic bypasses Layer 3 routing.
Critical Point: Virtual Wire interfaces forward traffic directly between paired interfaces without routing.
3. Why Not Other Options?
A. ethernet1/6 → Incorrect. This is the L3 interface for 192.168.111.0/24, but traffic enters via Virtual Wire (ethernet1/7).
B. ethernet1/3 → Incorrect. This is the L3 egress for 10.46.41.113, but Virtual Wire bypasses routing.
C. ethernet1/7 → Incorrect. This is the ingress interface, not egress.
4. Key Takeaway
Virtual Wire (transparent mode) forwards traffic at Layer 2 between paired interfaces. Since ethernet1/7 is paired with ethernet1/5, traffic exits via ethernet1/5.
Reference:
Palo Alto Admin Guide (Virtual Wire):
Virtual Wire interfaces do not participate in routing; traffic flows directly between paired interfaces.
A firewall administrator wants to be able at to see all NAT sessions that are going ‘through a firewall with source NAT. Which CLI command can the administrator use?
A. show session all filter nat-rule-source
B. show running nat-rule-ippool rule "rule_name
C. show running nat-policy
D. show session all filter nat source
Explanation:
Why This Command?
The show session all filter nat source command displays all sessions where source NAT is applied.
It filters sessions specifically for source NAT translations, which is what the administrator needs.
Breakdown of the Command:
show session all → Displays all active sessions.
filter nat source → Filters to show only sessions with source NAT.
Why Not the Other Options?
A. show session all filter nat-rule-source → Incorrect syntax (no such filter exists).
B. show running nat-rule-ippool rule "rule_name" → Shows NAT pool configuration, not active NAT sessions.
C. show running nat-policy → Displays configured NAT policies, not live NAT sessions.
Additional Useful NAT Commands:
show session all filter nat → Shows all NAT sessions (source & destination).
show running nat-policy → Lists configured NAT rules.
show session id
Reference:
Palo Alto Networks CLI Reference Guide (under Session Monitoring & NAT Commands).
A superuser is tasked with creating administrator accounts for three contractors. For compliance purposes, all three contractors will be working with different device-groups in their hierarchy to deploy policies and objects. Which type of role-based access is most appropriate for this project?
A. Create a Dynamic Read only superuser
B. Create a Dynamic Admin with the Panorama Administrator role
C. Create a Device Group and Template Admin
D. Create a Custom Panorama Admin
Explanation:
The Device Group and Template Admin role is specifically designed for delegated administration in Panorama. It allows you to assign access to specific device groups and templates, which is exactly what’s needed when contractors are working in separate hierarchies and must manage policies and objects independently.
This role ensures compliance and separation of duties, as each contractor can only see and modify the device groups and templates assigned to them — no cross-access.
❌ Why the others are incorrect:
A. Dynamic Read only superuser:
This role provides read-only access across the system. It’s unsuitable for contractors who need to deploy policies and objects, which requires write permissions.
B. Dynamic Admin with the Panorama Administrator role:
This grants full access to Panorama, including all device groups and templates. It violates the principle of least privilege and compliance boundaries, as contractors would see and potentially modify areas outside their scope.
D. Custom Panorama Admin:
While flexible, it requires manual configuration of granular permissions. It’s more error-prone and less efficient than using the purpose-built Device Group and Template Admin role, which simplifies scoped access.
📚 References:
Palo Alto Networks TechDocs:
Role-Based Access Control in Panorama
What would allow a network security administrator to authenticate and identify a user with a new BYOD-type device that is not joined to the corporate domain?
A. an Authentication policy with 'unknown' selected in the Source User field
B. an Authentication policy with 'known-user' selected in the Source User field
C. a Security policy with 'known-user' selected in the Source User field
D. a Security policy with 'unknown' selected in the Source User field
Explanation:
To authenticate a user on a new BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) that isn't part of the corporate domain, a network security administrator needs to configure an Authentication policy. This policy should be set to match traffic where the source user is 'unknown'.
1.Authentication Policy: This type of policy's primary function is to trigger user authentication. It directs the user to a captive portal or some other form of authentication method before allowing them access to network resources.
2.unknown' User:
When a user with a new device connects to the network, the Palo Alto Networks firewall initially doesn't have any identity information about them. The firewall classifies their traffic as coming from an 'unknown' user.
3.Authentication Workflow:
The user's device attempts to access a resource (e.g., a website).
The firewall's security policy allows the traffic to proceed, but the Authentication policy with the 'unknown' source user matches the session.
This match triggers the authentication mechanism, such as a Captive Portal.
The user is redirected to the portal to enter their credentials.
Once authenticated, the firewall learns the user's identity and can apply more specific security policies to their traffic.
The other options are incorrect:
B. Authentication policy with 'known-user' selected:
This would only apply to users the firewall has already identified. It would not work for a new, unauthenticated BYOD device.
C & D. Security policy with 'known-user' or 'unknown' selected:
A Security policy is used to permit or deny traffic based on applications, users, and zones. While a security policy can be based on user identity, it doesn't trigger the authentication process itself. The authentication policy is what initiates the user's identification.
References:
Palo Alto Networks:
User Identification and Authentication
Palo Alto Networks:
Best Practices
Which GloDalProtecI gateway setting is required to enable split-tunneting by access route, destination domain and application?
A. Tunnel mode
B. Satellite mode
C. IPSec mode
D. No Direct Access to local networks
Explanation:
Why Tunnel Mode?
1.Split-Tunneling Requirements:
Access Route: Defines which traffic goes through the VPN (e.g., corporate subnets).
Destination Domain: Allows tunneling only for specific domains (e.g., *.company.com).
Application: Controls VPN routing per application (e.g., only tunnel Outlook).
Tunnel Mode is the only GlobalProtect gateway setting that supports all three split-tunneling methods simultaneously.
2.How It Works:
In Tunnel Mode, the GlobalProtect client:
Evaluates traffic against split-tunnel rules (routes/domains/apps).
Selectively routes matching traffic through the VPN.
Non-matching traffic (e.g., public web browsing) goes directly to the internet.
Why Not Other Options?
B. Satellite Mode
Used for cloud gateways, not split-tunneling control.
C. IPSec Mode
Legacy VPN (no support for domain/application-based split-tunneling).
D. No Direct Access
Disables split-tunneling entirely (forces all traffic through VPN).
Key Configuration:
Under Network > GlobalProtect > Gateways > [Gateway] > Agent > Split Tunnel:
Enable Tunnel Mode.
Configure:
Access Routes (e.g., 10.0.0.0/8).
Domains (e.g., *.internal.com).
Applications (e.g., ms-outlook.exe).
Reference:
Palo Alto GlobalProtect Admin Guide:
"Tunnel Mode enables granular split-tunneling by access route, domain, and application.
Please match the terms to their corresponding definitions.
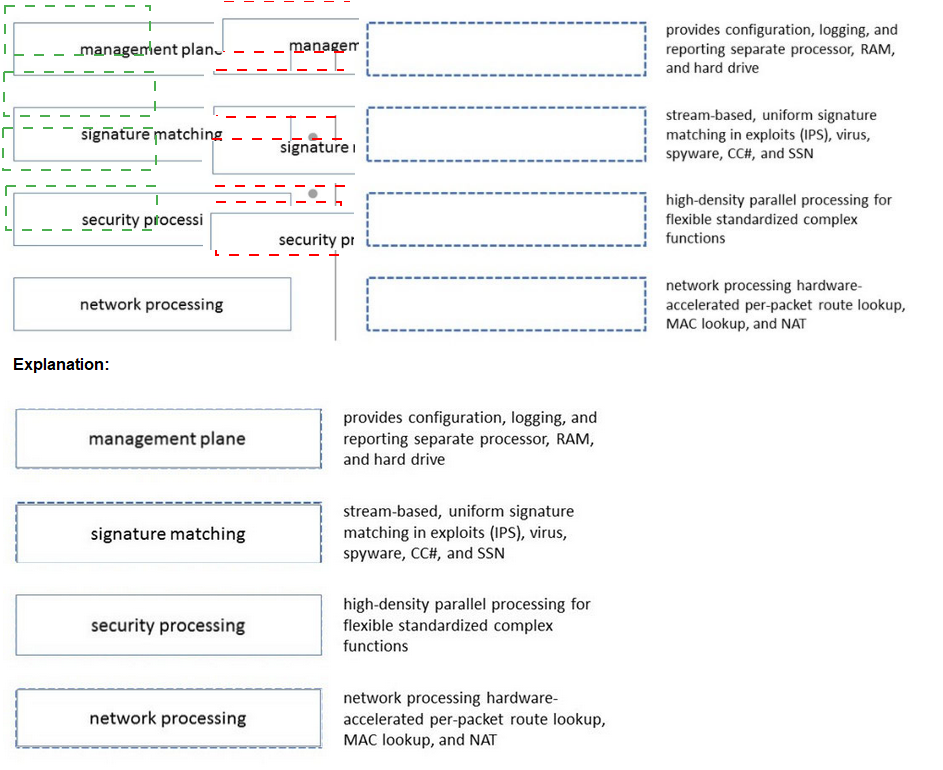
Explanation:
1.management plane:
This plane handles administrative tasks such as configuration, logging, and reporting. It is supported by a separate processor, RAM, and hard drive to ensure these tasks do not interfere with real-time traffic processing.
2.signature matching:
This involves identifying threats using stream-based, uniform signature matching techniques. It targets exploits (via Intrusion Prevention System - IPS), viruses, spyware, command-and-control (C2) traffic, and stolen sensitive data (SSN).
3.security processing:
This plane performs advanced security functions using high-density parallel processing, enabling flexible and standardized handling of complex security tasks across multiple cores or processors.
4.network processing:
This focuses on network-related tasks, leveraging hardware-accelerated processing for per-packet route lookups, MAC address lookups, and Network Address Translation (NAT) to optimize performance.
These mappings align with the Palo Alto Networks firewall architecture, where different planes are dedicated to specific functions, supported by specialized hardware or processing capabilities. This design ensures efficient handling of management, security, and network tasks.
References:
Palo Alto Networks Documentation:
Firewall Architecture Overview
Palo Alto Networks Technical Whitepapers:
Single-Pass Parallel Processing Architecture
An administrator has a Palo Alto Networks NGFW. All security subscriptions and decryption are enabled and the system is running close to its resource limits. Knowing that using decryption can be resource-intensive, how can the administrator reduce the load on the firewall?
A. Use RSA instead of ECDSA for traffic that isn't sensitive or high-priority.
B. Use the highest TLS protocol version to maximize security.
C. Use ECDSA instead of RSA for traffic that isn't sensitive or high-priority.
D. Use SSL Forward Proxy instead of SSL Inbound Inspection for decryption.
Explanation:
Why ECDSA Over RSA?
1.Performance Impact:
ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) is less CPU-intensive than RSA for decryption, especially for bulk traffic.
RSA relies on large prime numbers, requiring more computational power for key exchanges and signing operations.
Switching non-sensitive traffic to ECDSA reduces decryption overhead while maintaining security.
2.Resource Optimization:
The firewall is near capacity, so optimizing decryption efficiency is critical.
ECDSA provides comparable security to RSA with shorter key lengths (e.g., 256-bit ECDSA ≈ 3072-bit RSA)
.
Why Not the Other Options?
A. Use RSA
Increases load (RSA is more resource-intensive than ECDSA).
B. Highest TLS version
TLS 1.3 improves security but doesn’t reduce decryption load (may even increase it).
D. SSL Forward Proxy
Irrelevant—this is for outbound decryption, not reducing resource usage.
Additional Optimization Tips:
Exclude low-risk traffic from decryption (e.g., public websites).
Use Session Timeouts to limit long-lived decrypted sessions.
Monitor Decryption Profiles to fine-tune policies.
Reference:
Palo Alto Networks Decryption Best Practices:
"ECDSA is recommended for reducing CPU load during decryption, particularly for non-critical traffic."
Which Panorama mode should be used so that all logs are sent to. and only stored in. Cortex Data Lake?
A. Log Collector
B. Panorama
C. Legacy
D. Management Only
Explanation:
Recall Panorama Deployment Modes
1.Panorama Mode
Full management + log collection.
Logs stored locally (Panorama / Dedicated Log Collectors).
2.Log Collector Mode
Panorama works only as a log collector.
Stores logs locally.
3.Legacy Mode
Pre–PAN-OS 8.0, combined mgmt + logging.
Deprecated.
4.Management Only Mode
Panorama manages devices (device-groups, templates, policies).
Does not store logs locally.
All logs can be forwarded to Cortex Data Lake (CDL).
✔ Exactly what the question requires.
Evaluate the options
A. Log Collector → Stores logs locally → ❌
B. Panorama → Stores logs locally → ❌
C. Legacy → Deprecated, still stores locally → ❌
D. Management Only → Sends logs only to Cortex Data Lake → ✅
Official Reference
Palo Alto Networks – Panorama Deployment Modes
“Use Management Only mode if you want Panorama to manage firewalls while all logs are forwarded to Cortex Data Lake, with no local log storage.”
An engineer is troubleshooting a traffic-routing issue. What is the correct packet-flow sequence?
A. PBF > Zone Protection Profiles > Packet Buffer Protection
B. BGP > PBF > NAT
C. PBF > Static route > Security policy enforcement
D. NAT > Security policy enforcement > OSPF
Explanation:
Why This Sequence?
1.Policy-Based Forwarding (PBF):
Evaluated first (before routing).
Overrides normal routing if a matching PBF rule exists.
2.Static Route (or Routing Table):
If no PBF match, the firewall checks the routing table (static/dynamic routes).
3.Security Policy Enforcement:
After routing is determined, traffic must pass security policies before egress.
Why Not Other Options?
AZone Protection and Packet Buffer Protection are security features, not routing steps.
BGP is a routing protocol (processed after PBF, but NAT happens before routing).
DOSPF is a routing protocol (evaluated after NAT and security policies).
Reference:
Palo Alto Packet Flow Order:
PBF → 2. Routing (Static/Dynamic) → 3. Security Policies → 4. Egress.
| Page 2 out of 27 Pages |
| Previous |