Refer to the exhibit showing FortiGate configurations
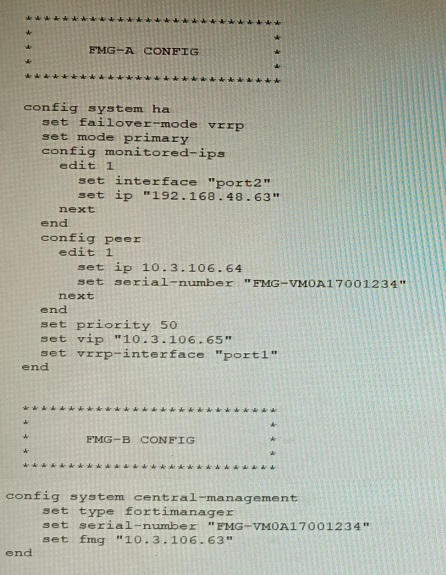
FortiManager VM high availability (HA) is not functioning as expected after being added to
an existing deployment.
The administrator finds that VRRP HA mode is selected, but primary and secondary roles
are greyed out in the GUI The managed devices never show online when FMG-B becomes
primary, but they will show online whenever the FMG-A becomes primary.
What change will correct HA functionality in this scenario?
A. Change the FortiManager IP address on the managed FortiGate to 10.3.106.65.
B. Make the monitored IP to match on both FortiManager devices.
C. Unset the primary and secondary roles in the FortiManager CLI configuration so VRRP will decide who is primary.
D. Change the priority of FMG-A to be numerically lower for higher preference
Explanation:
In VRRP HA mode, both FortiManager nodes must monitor the same interface/IP so failover occurs cleanly and FGFM traffic is routed to the active node via the shared VIP. A mismatch causes failover instability and devices appearing offline when the wrong node becomes primary.
Why other options are incorrect
A: Changing FortiGate’s FortiManager IP to 10.3.106.65 treats symptoms, not the cause. The issue is HA failover behavior due to monitored IP mismatch, not the manager address on devices. Correct the HA monitoring first to ensure consistent FGFM via the VIP.
C: Unsetting roles doesn’t fix a misconfigured monitored target. VRRP still needs consistent health checks; without matching monitored IPs, failover and FGFM routing remain unreliable, leading to devices offline when the secondary assumes primary.
D: Lowering FMG-A’s priority forces it to be preferred but masks the problem. Proper HA requires identical monitored IP configuration so either node can become primary and maintain device connectivity via the shared VIP.
Reference
FortiManager HA best practices: VRRP failover uses a shared VIP; monitored interface/IP must be aligned across nodes for reliable failover and FGFM routing.
FortiManager HA setup and troubleshooting guidance emphasizes consistent HA settings across nodes for VRRP mode
Refer to the exhibits.
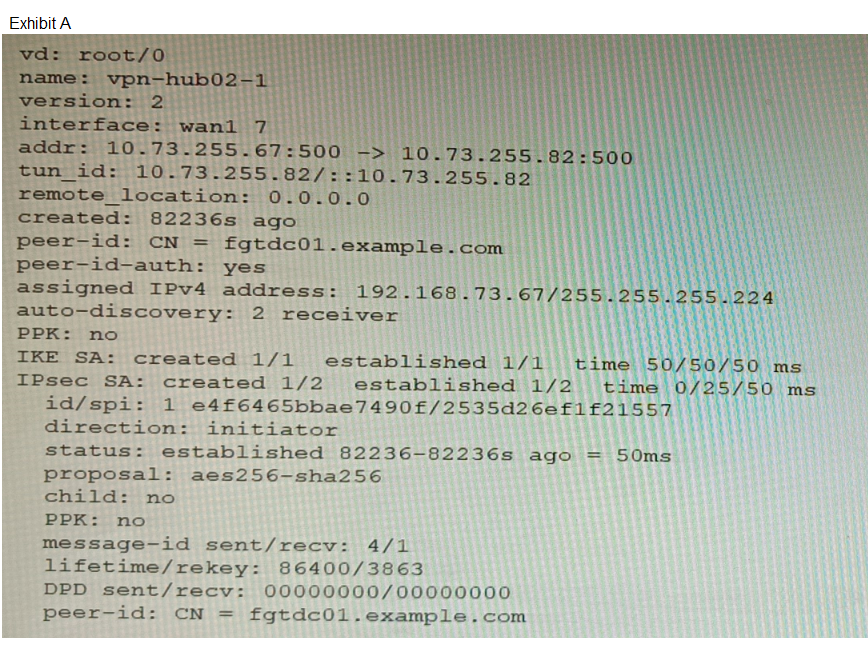
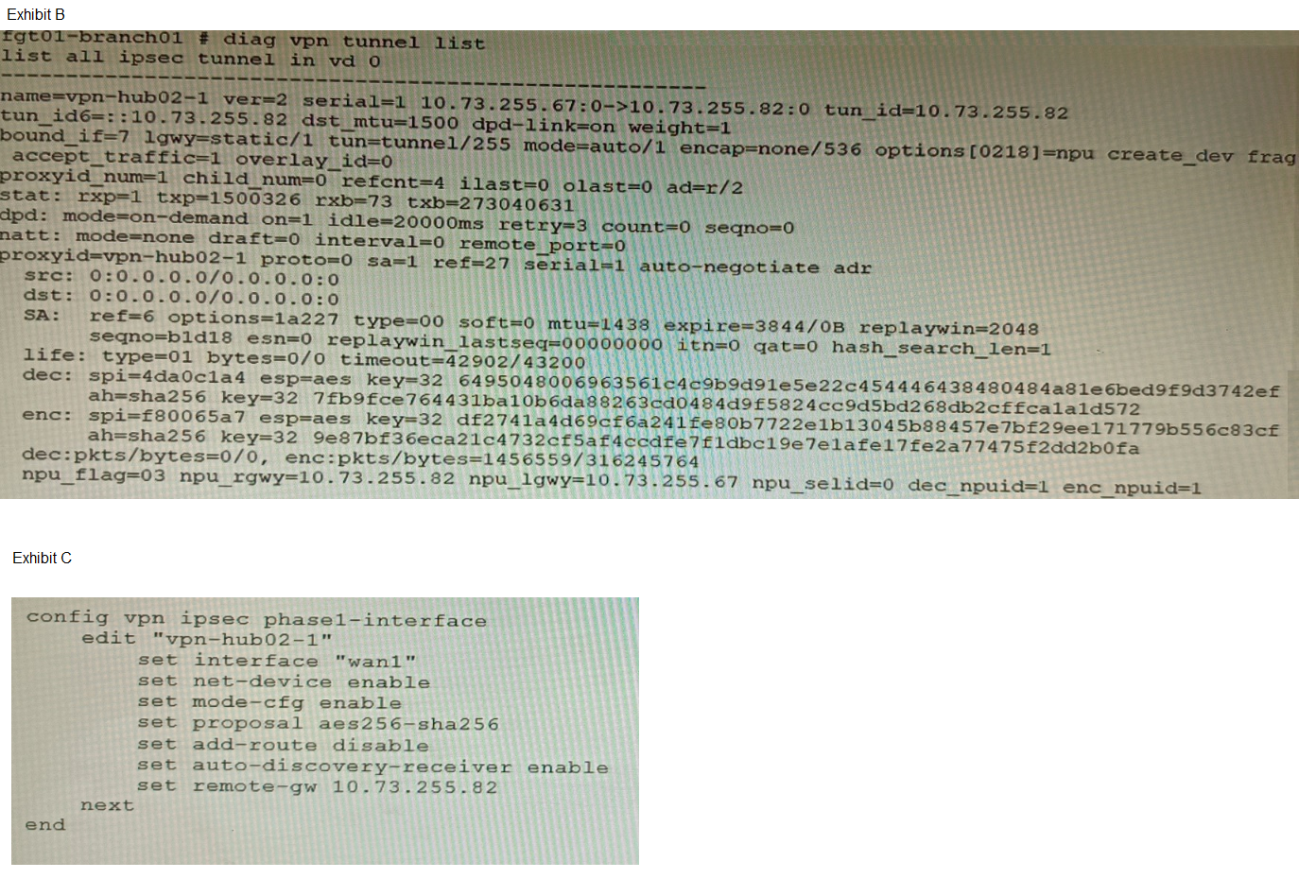
A customer is trying to set up a VPN with a FortiGate, but they do not have a backup of the
configuration. Output during a troubleshooting session is shown in the exhibits A and B and
a baseline VPN configuration is shown in Exhibit C Referring to the exhibits, which
configuration will restore VPN connectivity?
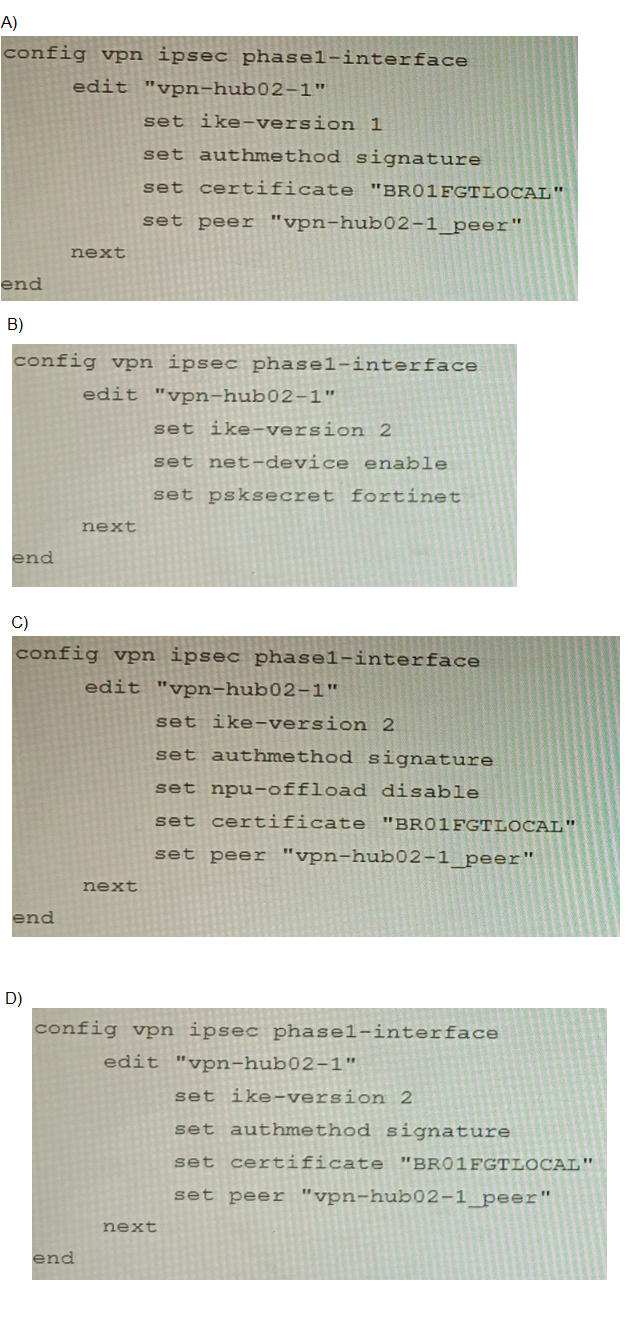
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation:
The diagnostic output (Exhibit A) shows the VPN is established with:
IKEv2 (ver=2)
Certificate authentication (peer-id: CN = fgtdc01.example.com and peer-id-auth: yes)
Signature authmethod (implied by certificate use)
NPU offloading active (npu_se1id=0 dec_npuid=1 enc_npuid=1)
Exhibit C (baseline configuration) confirms additional required settings: net-device enable and auto-discovery-receiver enable for ADVPN operation. Option C correctly matches all observed parameters: IKEv2, signature authmethod, certificate reference, and explicitly includes npu-offload disable to ensure software control matches the observed NPU session state. This comprehensive configuration restores connectivity by replicating all functional VPN attributes.
Why other options are incorrect:
A fails because it uses IKEv1 (ike-version 1), while the diagnostic output clearly shows ver=2 (IKEv2). IKEv1 and IKEv2 are not interoperable.
B fails because it uses PSK authentication (psksecret fortinet), but the diagnostic shows certificate-based authentication (peer-id CN=...). PSK and certificate authentication are mutually exclusive.
D fails because it omits npu-offload disable. The diagnostic output shows NPU session IDs assigned (dec_npuid=1 enc_npuid=1), indicating hardware offloading is active. Without explicit control over NPU offloading, the VPN may not re-establish correctly if the original configuration managed offloading behavior. The baseline config in Exhibit C does not mention NPU offloading, but the presence of NPU IDs in the diagnostic suggests it was configured in the original setup.
Reference:
FortiOS 7.4 IPsec VPN Configuration Guide:
IKE version must match between peers (ike-version 2 for IKEv2).
Certificate authentication requires authmethod signature and a valid local certificate reference.
Refer to the exhibits.
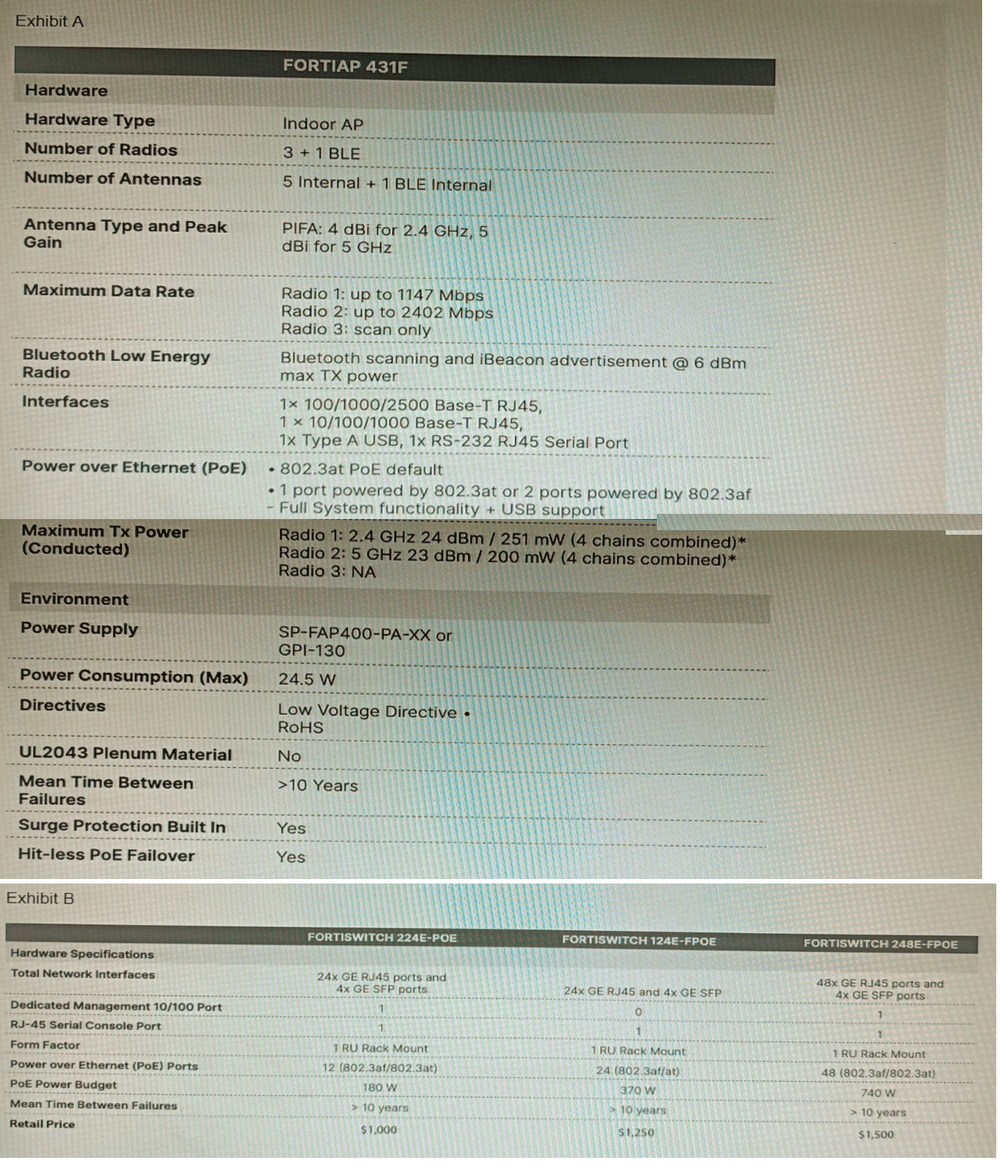
A customer wants to deploy 12 FortiAP 431F devices on high density conference center,
but they do not currently have any PoE switches to connect them to. They want to be able
to run them at full power while having network redundancy
From the FortiSwitch models and sample retail prices shown in the exhibit, which build of
materials would have the lowest cost, while fulfilling the customer's requirements?
A. 1x FortiSwitch 248EFPOE
B. 2x FortiSwitch 224E-POE
C. 2x FortiSwitch 248E-FPOE
D. 2x FortiSwitch 124E-FPOE
🔍Explanation:
Each FortiAP 431F requires up to 24.5 W. For 12 units, that’s ~294 W total. Only the 248E-FPOE provides enough PoE budget and port density to support all APs at full power with headroom. Two units ensure redundancy, and at $1500 each, this build is cost-effective for high-density deployment.
✅ Correct Option
C. 2x FortiSwitch 248E-FPOE
This setup provides 48 PoE ports per switch (total 96), with a combined PoE budget of 740 W × 2 = 1480 W. It supports full power for all 12 FortiAP 431F units (24.5 W max each) and offers redundancy with dual switches at the lowest cost per watt.
❌ Why Other Options Are Incorrect
A. 1x FortiSwitch 248E-FPOE
While it has 48 PoE ports and 740 W budget, using a single switch violates the redundancy requirement. If the switch fails, all APs go offline. The customer explicitly requires network redundancy, which this option does not provide.
B. 2x FortiSwitch 224E-POE
Each switch offers only 12 PoE ports and 180 W budget. Two switches provide 24 PoE ports and 360 W total, which barely meets the power requirement (294 W) but lacks port headroom and scalability. Also, 12 ports per switch is tight for cabling and future growth.
D. 2x FortiSwitch 124E-FPOE
Each offers 24 PoE ports and 370 W budget. Two switches give 48 ports and 740 W total, which meets the power requirement. However, at $1250 each, the total cost is $2500—more expensive than option C ($3000) with fewer ports and less scalability.
📚 Reference:
Fortinet Product Datasheets:
“FortiSwitch 248E-FPOE provides 48 PoE ports with 740 W budget, ideal for high-density AP deployments. Supports 802.3at for full power and redundancy when deployed in pairs.”
An administrator has configured a FortiGate device to authenticate SSL VPN users using
digital certificates. A FortiAuthenticator is the certificate authority (CA) and the Online
Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) server.
Part of the FortiGate configuration is shown below:
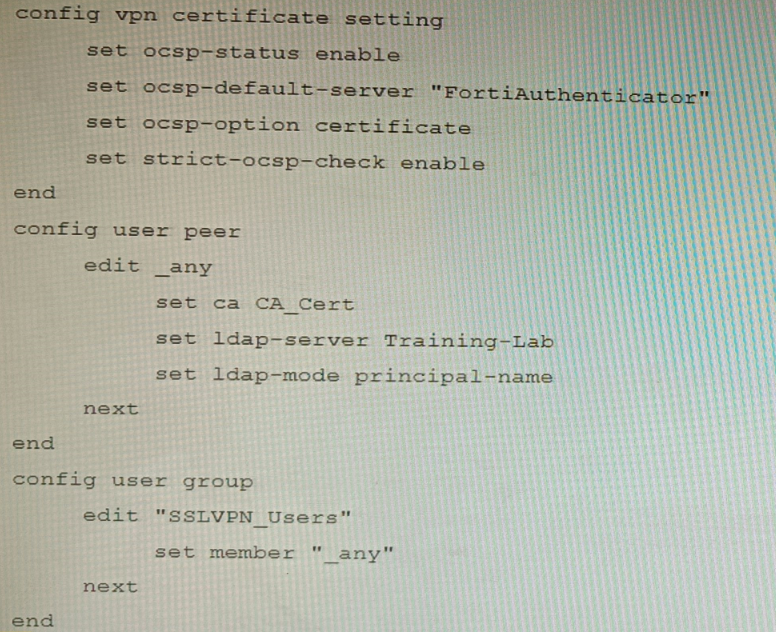
Based on this configuration, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
A. OCSP checks will always go to the configured FortiAuthenticator
B. The OCSP check of the certificate can be combined with a certificate revocation list.
C. OCSP certificate responses are never cached by the FortiGate.
D. If the OCSP server is unreachable, authentication will succeed if the certificate matches the CA.
Explanation:
B is correct because strict-ocsp-check enable requires OCSP validation, but FortiGate can also be configured to use both OCSP and CRL (Certificate Revocation List) checks simultaneously for comprehensive revocation verification.
D is correct because when strict-ocsp-check enable is set, if the OCSP server is unreachable, the FortiGate will fall back to checking the certificate's CRL Distribution Point (if available). If that also fails or isn’t configured, and the certificate is issued by a trusted CA, authentication can still succeed depending on the overall revocation-check settings. The question’s configuration does not have ocsp-option strict, so OCSP failure doesn’t necessarily block auth.
Why other options are incorrect:
A is false because ocsp-option certificate means the FortiGate first checks the certificate’s AIA (Authority Information Access) extension for an OCSP responder URL; it only uses the default server (FortiAuthenticator) if no URL is embedded in the certificate.
C is false because FortiGate does cache OCSP responses based on the nextUpdate field in the OCSP reply; cached responses are reused until they expire.
Reference:
FortiOS SSL‑VPN Administration Guide – OCSP settings:
ocsp-option certificate prioritizes the OCSP URL in the certificate’s AIA extension.
strict-ocsp-check enable enforces revocation checking but allows fallback to CRL if OCSP is unreachable (unless ocsp-option strict is set).
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a Branch1 configuration and routing table.
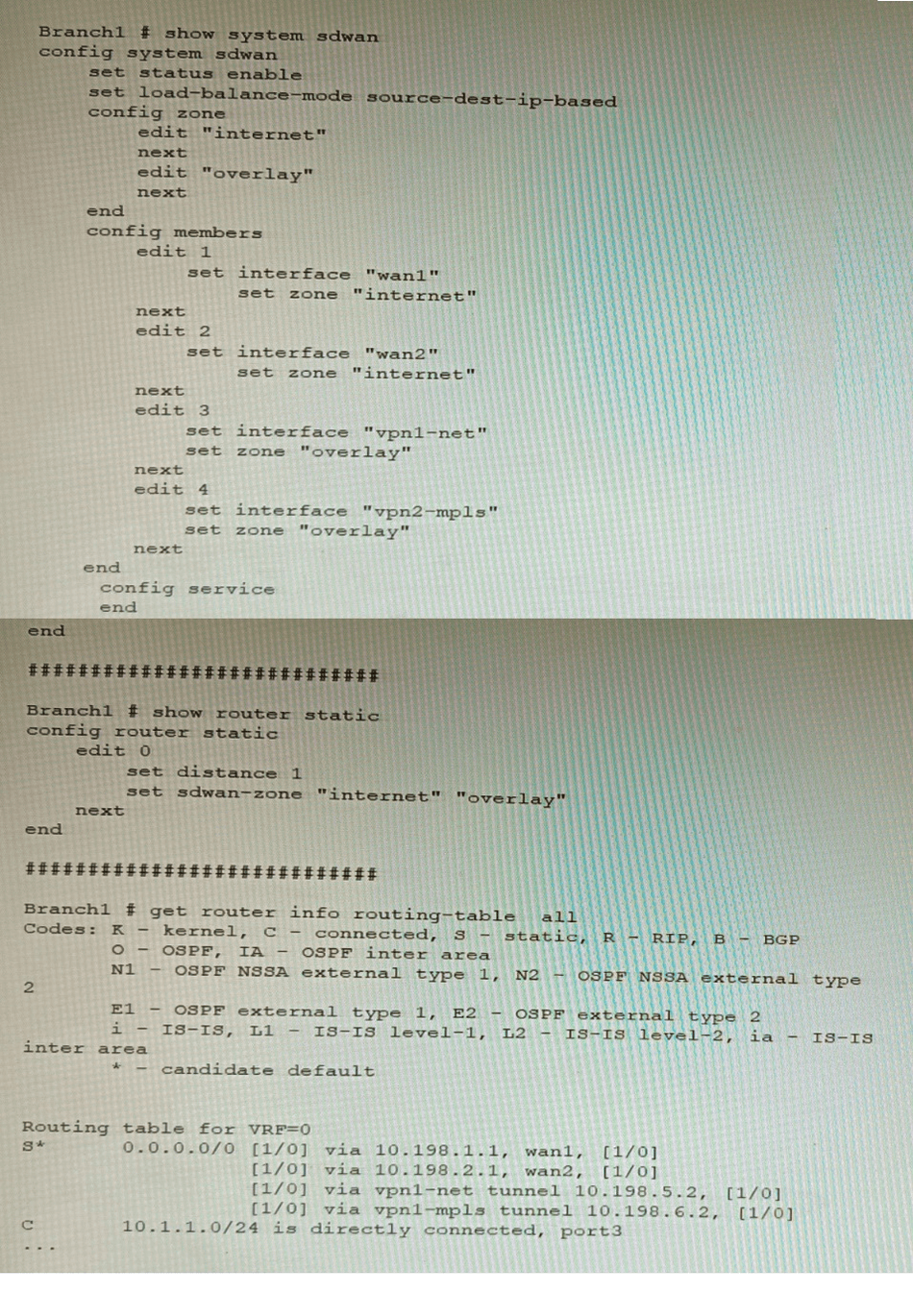
In the SD-WAN implicit rule, you do not want the traffic load balance for the overlay
interface when all members are available.
In this scenario, which configuration change will meet this requirement?
A. Change the load-balance-mode to source-ip-based.
B. Create a new static route with the internet sdwan-zone only
C. Configure the cost in each overlay member to 10.
D. Configure the priority in each overlay member to 10.
Explanation:
The default load balancing mode for the SD-WAN implicit rule is source IP
based. This means that traffic will be load balanced evenly between the overlay members,
regardless of the member's priority.
To prevent traffic from being load balanced, you can configure the priority of each overlay
member to 10. This will make the member ineligible for load balancing.
The other options are not correct. Changing the load balancing mode to source-IP based
will still result in traffic being load balanced. Creating a new static route with the internet
sdwan-zone only will not affect the load balancing of the overlay interface. Configuring the
cost in each overlay member to 10 will also not affect the load balancing, as the cost is only
used when the implicit rule cannot find a match for the destination IP address.

You want to use the MTA adapter feature on FortiSandbox in an HA-Cluster. Which statement about this solution is true?
A. The configuration of the MTA Adapter Local Interface is different than on port1.
B. The MTA adapter is only available in the primary node.
C. The MTA adapter mode is only detection mode.
D. The configuration is different than on a standalone device.
Explanation:
The MTA adapter in FortiSandbox allows SMTP-based email traffic to be relayed for sandboxing. In an HA cluster, only the primary node handles MTA adapter functions to avoid duplicate processing and ensure consistent policy enforcement. Secondary nodes do not process MTA traffic, maintaining HA integrity and load control.
❌ Why Other Options Are Incorrect
A. The configuration of the MTA Adapter Local Interface is different than on port1.
This is misleading. The MTA adapter can be bound to any interface, including port1, but the configuration syntax and behavior are consistent across interfaces. The key distinction in HA is not the interface used, but the node role (primary vs secondary).
C. The MTA adapter mode is only detection mode.
ncorrect. The MTA adapter supports both detection and inline blocking modes depending on policy configuration. Detection mode logs threats, while inline mode can quarantine or block malicious content. The adapter is not limited to detection-only.
D. The configuration is different than on a standalone device.
The configuration syntax and interface binding are the same. What differs is operational behavior in HA: only the primary node processes MTA traffic. This ensures centralized control and avoids redundant scanning across nodes.
📚 Reference:
Fortinet Documentation – FortiSandbox MTA Adapter:
“In HA clusters, the MTA adapter is only active on the primary node. Secondary nodes do not process email traffic.”
Refer to the exhibit.
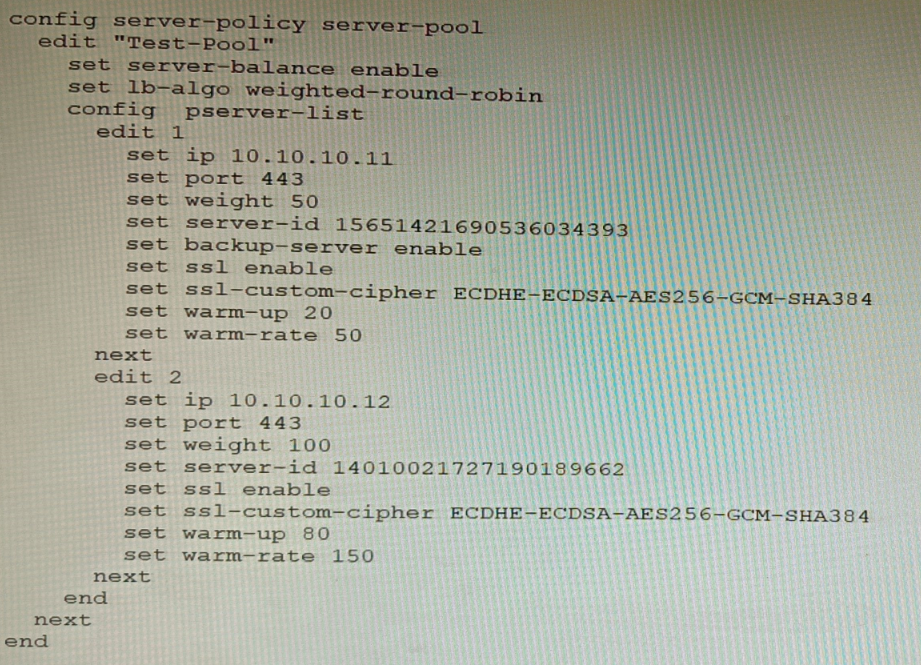
A FortiWeb appliance is configured for load balancing web sessions to internal web
servers. The Server Pool is configured as shown in the exhibit.
How will the sessions be load balanced between server 1 and server 2 during normal
operation?
A. Server 1 will receive 25% of the sessions, Server 2 will receive 75% of the sessions
B. Server 1 will receive 20% of the sessions, Server 2 will receive 66.6% of the sessions
C. Server 1 will receive 33.3% of the sessions, Server 2 will receive 66 6% of the sessions
D. Server 1 will receive 0% of the sessions Server 2 will receive 100% of the sessions
Explanation:
The FortiWeb server pool uses weighted-round-robin load balancing. Server 1 has a weight of 50, and Server 2 has a weight of 100. The total weight is 150. Therefore, Server 1 receives
50
150
=
33.3
%
of sessions, and Server 2 receives
100
150
=
66.6
%
.
❌ Why Other Options Are Incorrect
A. Server 1 will receive 25%, Server 2 75%
This implies a 1:3 weight ratio, which would require weights of 50 and 150 respectively. The actual weights are 50 and 100, so the ratio is 1:2, not 1:3. This makes the percentage split incorrect.
B. Server 1 will receive 20%, Server 2 66.6%
These percentages don’t align with any valid weight ratio. 20% would imply Server 1 has a weight of 30 compared to Server 2’s 120, which is not the case. Also, the total doesn’t sum to 100%, making this option invalid.
D. Server 1 will receive 0%, Server 2 100% Server 1
is marked as a backup server, but FortiWeb still includes it in the weighted-round-robin unless the primary (Server 2) fails. During normal operation, both servers participate based on their weights. So Server 1 does receive traffic unless failover is triggered.
📚 Reference
Fortinet FortiWeb Admin Guide:
“Weighted-round-robin distributes sessions proportionally based on server weights. Backup servers participate unless failover conditions are met.”
A customer's cybersecurity department needs to implement security for the traffic between
two VPCs in AWS, but these belong to different departments within the company. The
company uses a single region for all their VPCs.
Which two actions will achieve this requirement while keeping separate management of
each department's VPC? (Choose two.)
A. Create a transit VPC with a FortiGate HA cluster, connect to the other two using VPC peering, and use routing tables to force traffic through the FortiGate cluster.
B. Create an 1AM account for the cybersecurity department to manage both existing VPC, create a FortiGate HA Cluster on each VPC and IPSEC VPN to force traffic between the VPCs through the FortiGate clusters
C. Migrate all the instances to the same VPC and create 1AM accounts for each department, then implement a new subnet for a FortiGate auto-scaling group and use routing tables to force the traffic through the FortiGate cluster.
D. Create a VPC with a FortiGate auto-scaling group with a Transit Gateway attached to the three VPC to force routing through the FortiGate cluster
Explanation:
Transit VPC with FortiGate HA (A):
Centralizes inspection between departmental VPCs while keeping their management separate. Spoke VPCs peer to the transit VPC, and routing forces east–west traffic through FortiGate for L3–L7 security.
Transit Gateway with FortiGate auto-scaling (D):
Scales and centralizes security via TGW attachments from each VPC to a FortiGate security VPC, preserving departmental autonomy while enforcing inspection on inter-VPC flows.
Why the other options are incorrect
B: Grants the cybersecurity IAM account management over both VPCs, violating separate VPC management. Per-VPC FortiGate HA clusters plus IPsec between them can secure traffic, but central control over both VPCs breaks the requirement of separate management domains.
C: Migrating all instances into a single VPC consolidates departments, eliminating separate VPC management. It also introduces major re-architecture risk. AWS and Fortinet recommend centralized security using Transit VPC or TGW to keep VPCs separate while inspecting inter-VPC traffic.
References:
Fortinet Deployment Guide: AWS Transit VPC with FortiGate NGFW – hub-and-spoke security for inter-VPC traffic.
AWS Whitepaper: Centralized network security for VPC-to-VPC traffic using Transit VPC, TGW, GWLB.
Which two statements are correct on a FortiGate using the FortiGuard Outbreak Protection Service (VOS)? (Choose two.)
A. The FortiGuard VOS can be used only with proxy-base policy inspections.
B. If third-party AV database returns a match the scanned file is deemed to be malicious.
C. The antivirus database queries FortiGuard with the hash of a scanned file
D. The AV engine scan must be enabled to use the FortiGuard VOS feature
E. The hash signatures are obtained from the FortiGuard Global Threat Intelligence database.
Explanation:
FortiGuard Outbreak Protection Service (VOS) enhances FortiGate antivirus by querying FortiGuard with file hashes. When a file is scanned, its hash is checked against FortiGuard’s Global Threat Intelligence database. If a match is found, the file is flagged as malicious, providing rapid outbreak detection without full signature downloads.
❌ Why Other Options Are Incorrect
A. The FortiGuard VOS can be used only with proxy-based policy inspections. Incorrect.
VOS is not limited to proxy-based inspection. It works with both flow-based and proxy-based AV policies, as long as the FortiGate can generate file hashes and query FortiGuard. Restricting it to proxy-only would reduce flexibility, which is not the case in FortiOS design.
B. If third-party AV database returns a match the scanned file is deemed to be malicious. Incorrect.
VOS relies on FortiGuard’s own Global Threat Intelligence database, not third-party AV databases. Fortinet maintains its own intelligence network and outbreak detection system. Third-party AV databases are not queried by FortiGate in this context.
D. The AV engine scan must be enabled to use the FortiGuard VOS feature. Incorrect.
VOS can operate independently of full AV scanning. It specifically uses file hashes to query FortiGuard, which means even if full signature-based AV scanning is not enabled, VOS can still provide outbreak detection. AV scanning enhances detection but is not a prerequisite for VOS.
📚 Reference:
Fortinet Documentation – FortiGuard Outbreak Protection Service:
“Outbreak Prevention queries FortiGuard with file hashes against the Global Threat Intelligence database to detect emerging threats.”
Fortinet Docs –
Outbreak Prevention Service
You must analyze an event that happened at 20:37 UTC. One log relevant to the event is
extracted from FortiGate logs:
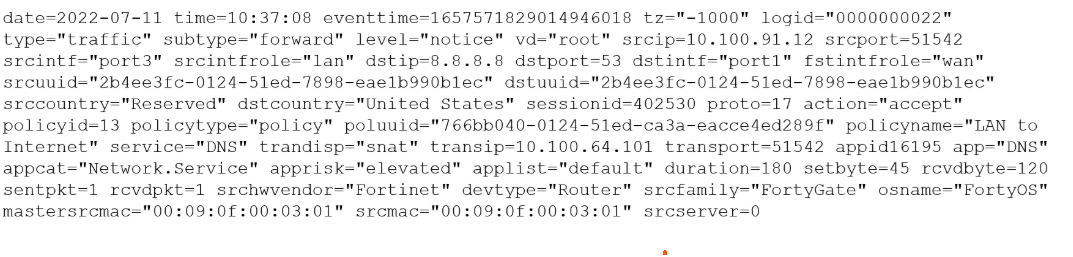
The devices and the administrator are all located in different time zones Daylight savings
time (DST) is disabled
• The FortiGate is at GMT-1000.
• The FortiAnalyzer is at GMT-0800
• Your browser local time zone is at GMT-03.00
You want to review this log on FortiAnalyzer GUI, what time should you use as a filter?
A. 20:37:08
B. 10:37:08
C. 17:37:08
D. 12.37:08
Explanation:
You must convert the event's known UTC time to the FortiAnalyzer's local time zone for accurate filtering in its GUI. FortiGate logs store timestamps based on the device's local time, but all logs in FortiAnalyzer are normalized and indexed in UTC in the database. The FortiAnalyzer GUI automatically converts your local filter input from its configured time zone back to UTC for searching.
Known Event Time: The event occurred at 20:37:08 UTC.
FortiAnalyzer Time Zone: The FortiAnalyzer appliance is configured for GMT-08:00 (8 hours behind UTC).
Conversion: To find the local time on the FortiAnalyzer, subtract its offset from UTC:
FortiAnalyzer Local Time = 20:37:08 (UTC) - 8 hours = 12:37:08.
Therefore, to find this specific log entry, you must set the time filter in the FortiAnalyzer GUI to 12:37:08.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
A (20:37:08):
This is the event time in UTC, not the FortiAnalyzer's local time. The GUI expects input in the appliance's configured time zone.
B (10:37:08):
This is the FortiGate's local time (GMT-10). Using this in the FortiAnalyzer (GMT-8) would search for logs from a different UTC moment, yielding no results.
C (17:37:08):
This would correspond to the FortiAnalyzer being at GMT-3, which is the administrator's browser time zone, not the appliance's configured time zone. The GUI uses the appliance's time zone setting for filter input unless explicitly overridden, which is not indicated here.
Reference
Fortinet documentation on log timestamps and FortiAnalyzer time zone handling states that logs are stored in UTC and that the FortiAnalyzer GUI displays and accepts filter times based on the appliance's own configured system time zone.
A customer wants to use the FortiAuthenticator REST API to retrieve an SSO group called
SalesGroup. The following API call is being made with the 'curl' utility:

Which two statements correctly describe the expected behavior of the FortiAuthenticator
REST API? (Choose two.)
A. Only users with the "Full permission" role can access the REST API
B. This API call will fail because it requires that API version 2
C. If the REST API web service access key is lost, it cannot be retrieved and must be changed.
D. The syntax is incorrect because the API calls needs the get method.
Explanation:
The provided curl command attempts to update (-X PUT) an SSO group. Let's analyze the options based on standard FortiAuthenticator REST API behavior and the flawed command syntax.
D. The syntax is incorrect because the API calls needs the get method.
This is correct. The customer's goal is to retrieve an SSO group ("SalesGroup"). The command uses -X PUT, which is the HTTP method for updating or creating a resource. To retrieve information, the correct HTTP method is GET. Using PUT with a GET operation will cause a method mismatch error. Furthermore, the URL path and JSON data format are malformed for a simple retrieval.
B. This API call will fail because it requires that API version 2
This is correct. For operations on SSO groups (like api/v1/ssogroup/100/), FortiAuthenticator's REST API requires version 2 (v2) of the API. Using v1 in the endpoint path will result in failure because the ssogroup resource is not available or fully functional under the older API version. The correct endpoint should be /api/v2/ssogroup/.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
A. Only users with the "Full permission" role can access the REST API
Incorrect. REST API access is controlled by a specific API web service access key, not by the admin user's GUI role permissions. A dedicated key must be generated in the FortiAuthenticator GUI under System > Admin > Administrators > REST API Admin. Any administrator with privileges to generate this key can use it for API calls.
C. If the REST API web service access key is lost, it cannot be retrieved and must be changed.
Incorrect. The FortiAuthenticator GUI does not display the API key in plain text after creation for security reasons. If lost, you cannot retrieve the original key. However, you do not necessarily "change" the existing one; you must generate a new key, which automatically invalidates the old one. The statement is misleading because it implies a change procedure rather than regeneration.
Reference
FortiAuthenticator Administration Guide, REST API chapter, specifies:
The API endpoint for SSO group management is /api/v2/ssogroup/
HTTP methods: GET (retrieve), POST (create), PUT (update), DELETE (remove)
Access requires a valid API key, not a user role.
You must configure an environment with dual-homed servers connected to a pair of
FortiSwitch units using an MCLAG.
Multicast traffic is expected in this environment, and you should ensure unnecessary traffic
is pruned from links that do not have a multicast listener.
In which two ways must you configure the igmps-f lood-traffic and igmps-flood-report
settings? (Choose two.)
A. disable on ICL trunks
B. enable on ICL trunks
C. disable on the ISL and FortiLink trunks
D. enable on the ISL and FortiLink trunks
Explanation:
In a FortiSwitch MCLAG (Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation Group) environment with multicast traffic, the goal is to efficiently forward multicast streams only to switch ports that have interested listeners (IGMP snooping), preventing unnecessary flooding. This requires precise control over the igmps-flood-traffic and igmps-flood-report settings on different trunk types.
D. enable on the ISL and FortiLink trunks
This is correct for ISL (Inter-Switch Link) and FortiLink trunks (connecting the FortiSwitch units to the FortiGate). Enabling flooding on these uplink trunks ensures that:
IGMP Reports are flooded upstream so the FortiGate/querier is aware of all listeners.
Unknown multicast traffic is flooded upstream to reach the multicast source or router.
This ensures proper multicast group membership learning and delivery across the network.
A. disable on ICL trunks
This is correct for the ICL (Inter-Chassis Link) trunk connecting the two MCLAG peers. Disabling flooding on the ICL prevents:
Duplicate multicast traffic being sent between the two switches unnecessarily.
IGMP reports being looped between the peers.
Since MCLAG peers synchronize IGMP snooping tables via the ICL, flooding is not required and would waste bandwidth.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
B. enable on ICL trunks
Incorrect. Enabling on the ICL would cause unnecessary multicast traffic and IGMP report flooding between the two MCLAG peers, creating duplicates and wasting ICL bandwidth.
C. disable on the ISL and FortiLink trunks
Incorrect. Disabling on these uplink trunks would break multicast routing. IGMP reports would not reach the querier (FortiGate), and multicast data would not reach upstream sources/routers, causing multicast streams to fail.
Reference:
FortiSwitch OS Administration Guide, “IGMP snooping” chapter, specifically the sections on igmps-flood-traffic and igmps-flood-report in MCLAG topologies. The guide explains that these settings should be configured to optimize multicast forwarding and avoid unnecessary traffic on the ICL.
| Page 3 out of 9 Pages |
| Previous |