A company implements Dynamics 36S Supply Chain Management.
You need to determine which feature to use to track inventory.
Which three types of information does the on-hand list provide? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. on order
B. physical reserved
C. last reserved
D. bin
E. physical inventory
Explanation:
The On-hand list in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management is a centralized inquiry page used to view current stock levels across various dimensions like site, warehouse, and batch. It provides a real-time snapshot of not just what is currently sitting on the shelf, but also what is committed to orders and what is expected to arrive. This visibility is crucial for warehouse managers and sales teams to prevent overpromising stock and to plan for upcoming replenishment needs across the organization.
Correct Option:
A. On order:
This field represents the total quantity that is expected to be delivered via purchase orders or other inbound journals but has not yet been received. It helps planners see future availability.
B. Physical reserved:
This shows the quantity that is physically present in the warehouse but has been locked or "reserved" for specific sales orders, production orders, or journals, making it unavailable for other uses.
E. Physical inventory:
This is the actual total quantity currently residing within the warehouse walls. It includes both available items and those that are physically reserved but not yet shipped.
Incorrect Option:
C. Last reserved:
This is not a standard transactional summary field in the on-hand list. While the system tracks reservation dates in the background, it is not one of the primary "bucket" totals shown in the on-hand overview.
D. Bin:
In Dynamics 365 SCM, a "Bin" is referred to as a Location. While you can filter the on-hand list by location, "Bin" itself is a dimension (where the item is) rather than a "type of information" or quantity (how much there is) provided by the list totals.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Inventory on-hand list - Supply Chain Management documentation.
Microsoft Learn: Check the availability of stock in Dynamics 365 SCM.
A company uses Dynamics 36S Supply Chain Management to manage production facility
assets.
A shop floor worker reports that a heating element in a hot water heater has stopped
working and needs to be replaced.
The shop floor manager recommends that all water heaters be checked for signs of failure.
You need to check and replace any failing heating elements in the facility.
What should you use? To answer, drag the appropriate concepts to the correct descriptions. Each concept may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation:
Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management uses the Asset Management module to manage the lifecycle and maintenance of production equipment. This system allows companies to track fixed assets like water heaters, manage their component parts through an Asset BOM, and schedule both reactive repairs and proactive inspections. By utilizing these tools, a facility can minimize downtime, accurately track the cost of repairs, and ensure that technicians have access to the specific technical details and parts required for each unique machine.
Correct Option:
Asset BOM (Bill of Materials):
This is used to track and manage the list of all spare parts and components, such as a specific heating element, that are used on an asset throughout its lifetime. It provides a complete record of item consumption for repairs.
Maintenance Round:
This is used to schedule a series of checks on multiple assets in a single sequence. This is the ideal tool for the manager’s recommendation to inspect all water heaters across the facility for signs of failure.
Asset Attribute:
This is used to define the technical specifications or properties of an asset, such as the wattage of a heating element or the capacity of a water tank. Attributes help uniquely describe assets without creating thousands of individual asset types.
Work Order:
This is used to manage the actual execution of the repair task, including recording the time spent and the specific parts replaced from the Asset BOM.
Incorrect Option:
Functional Location:
This is incorrect for tracking part lists or technical specs; it defines the physical "where" (e.g., Boiler Room 1) rather than the "what" of the asset's internal components or technical properties.
Maintenance Plan:
While similar to a round, a maintenance plan is typically used for time-based or counter-based preventive maintenance on a single asset, whereas a Round is specifically designed to group similar tasks for many assets together.
Maintenance Request:
This is used to report the initial fault (the worker reporting the failure) but does not provide the structure to track parts or manage the technical specifications of the water heater.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Asset BOMs in Supply Chain Management
Microsoft Learn: Maintenance rounds overview for Dynamics 365
Microsoft Learn: Asset attributes and types configuration
A company implements Dynamics 365 Project Operations.
Instructions: For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true.
Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation:
Dynamics 365 Project Operations is designed to manage the entire lifecycle of a project, from sales and resource management to financial reporting. It provides deep flexibility in how services are priced and how revenue is recognized to ensure compliance with international accounting standards. By integrating sales and project delivery, it allows organizations to create complex pricing models that reflect different resource skills, geographical locations, and customer-specific agreements, ensuring that project profitability is tracked accurately from the initial quote to final invoicing.
Correct Option:
Users can associate one or more price lists with a customer, an opportunity, or a quote (Yes):
Project Operations uses price lists to define the labor rates and expense costs for projects. You can have multiple price lists to account for different currencies, regions, or specific negotiated rates for a customer, allowing the system to automatically pull the correct pricing during the sales process.
Revenue recognition can be performed at set project milestones (Yes):
For fixed-price projects, the system allows you to define milestones. Revenue can be recognized as these milestones are achieved and billed, which aligns the financial reporting with the actual progress of the work performed rather than just the cash received.
A project task can have different prices for two different resources (Yes):
Pricing in Project Operations is highly granular. You can define different billable rates based on the "Role" or the specific "Resource" assigned to a task. For example, a Senior Consultant and a Junior Consultant working on the same task can be billed at different hourly rates.
Incorrect Option:
Single Price List Restriction:
Recommending that only one price list can be used globally is incorrect. This would prevent the system from handling multi-currency global operations or client-specific discounts, which are core features of the Project Operations sales module.
Cash-Basis Revenue Only:
Suggesting that revenue can only be recognized upon final payment is incorrect for an ERP context. Project Operations supports accrual-based accounting where revenue is recognized based on project completion percentages or specific milestones.
Uniform Resource Pricing:
It is incorrect to assume that a task must have a fixed price regardless of who performs it. The system's ability to differentiate pricing based on resource expertise is a key functional requirement for professional services automation (PSA).
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Project pricing and price lists overview
Microsoft Learn: Revenue recognition in Project Operations
Microsoft Learn: Manage project resources and roles pricing
A company plans to implement finance and operations apps.
You need to recommend a feature that allows users to edit Dynamics 365 data by using Microsoft Office. Changes that you make in Microsoft Office must update Dynamics 365.
What should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate option in the answer area.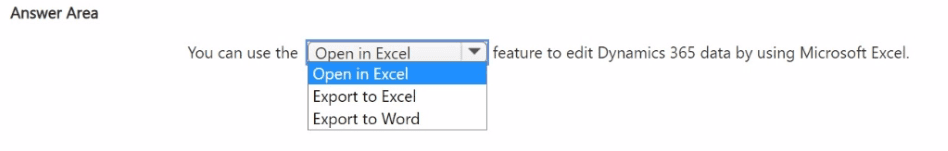
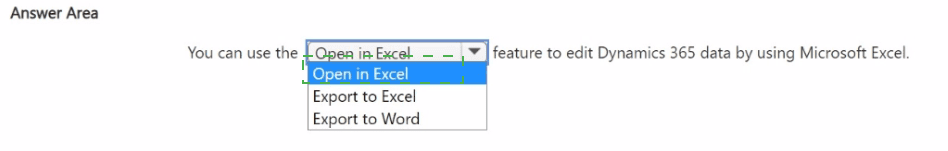
Explanation:
Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations apps provide seamless integration with the Microsoft Office suite to enhance user productivity. The system uses the Microsoft Dynamics Office Add-in to create a two-way data connection between the ERP environment and Excel spreadsheets. This allows users to leverage familiar Excel features—such as mass data entry, formulas, and data cleaning—while ensuring that the underlying business logic and security of Dynamics 365 are maintained during the synchronization process.
Correct Option:
Open in Excel:
This is the correct choice because it creates a live data connection. When you use "Open in Excel," the system generates a file that includes the Dynamics Office Add-in. This enables users to retrieve real-time data, make bulk edits within the spreadsheet, and then use the "Publish" button to push those changes directly back into the Dynamics 365 database.
Incorrect Option:
Export to Excel:
This option is incorrect for this requirement because it creates a static file. While it allows you to view and analyze Dynamics 365 data in Excel, any changes made to the resulting spreadsheet cannot be synced back to the system; it is a one-way data transfer only.
Export to Word:
This is incorrect because Microsoft Word is used primarily for document generation (like letters or invoices) via templates. It does not support the grid-based data editing or two-way synchronization required to update ERP records.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Office integration overview
Microsoft Learn: View and update entity data with Excel
A company plans to implement Dynamics 365 finance and operations apps. The company wants to integrate Microsoft Teams with these applications.
Which three platforms support Microsoft Teams integration? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. Dynamics 365 Commerce
B. Power BI
C. Microsoft Dataverse
D. Dynamics 365 Customer Engagement (on-premises)
E. SharePoint Online
Explanation:
Dynamics 365 finance and operations apps offer integrated collaboration by connecting with Microsoft Teams to streamline business processes. This integration allows users to share data, discuss tasks, and access critical business insights directly within the Teams interface without switching applications. For a company implementing these apps, leveraging existing platforms that already support native Teams integration ensures a unified experience for retail management, data analytics, and document storage, which are essential for modern ERP operations.
Correct Option:
A. Dynamics 365 Commerce:
This platform supports integration by allowing retail workers and managers to communicate and manage tasks within Teams. It enables the synchronization of task management between Commerce and Teams, improving store operations and staff collaboration.
B. Power BI:
Power BI has a native app for Microsoft Teams, allowing users to embed interactive reports and dashboards directly into Teams channels. This ensures that data-driven insights are easily accessible to the entire project team during discussions.
E. SharePoint Online:
SharePoint is the primary document management system for Microsoft 365 and is deeply integrated into Teams. Every Teams channel has a corresponding SharePoint folder, allowing finance and operations documents to be stored, shared, and co-authored seamlessly.
Incorrect Option:
C. Microsoft Dataverse:
While Dataverse is the underlying data platform for many Dynamics apps, it is a data storage layer rather than a "user-facing platform" that supports a complete Teams integration solution in the context of this specific functional question.
D. Dynamics 365 Customer Engagement (on-premises):
On-premises versions typically do not support the modern, cloud-native integration features required for Microsoft Teams. Teams integration is primarily designed for cloud-based (Online) environments to ensure real-time data flow.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Integrate Dynamics 365 finance and operations apps with Microsoft Teams
Microsoft Learn: Power BI and Microsoft Teams integration overview
Microsoft Learn: Dynamics 365 Commerce and Microsoft Teams integration
A company uses Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management. The company wants to use
SharePoint to manage documents from Supply Chain Management.
Instructions: For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true.
Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation:
Dynamics 365 finance and operations apps offer robust document management capabilities by integrating with Microsoft SharePoint. This allows organizations to move away from storing attachments directly in the ERP database, which can lead to excessive storage costs and performance issues. By using SharePoint, companies can leverage advanced document features such as versioning, external sharing, and advanced security. The integration is flexible, supporting various SharePoint environments to ensure that businesses can maintain their existing document workflows regardless of their specific infrastructure.
Correct Option:
Integrate with Online and On-premises (Yes):
Dynamics 365 supports integration with both SharePoint Online and SharePoint on-premises. For on-premises versions, the SharePoint server must be accessible to the finance and operations apps, often requiring specific authentication configurations like S2S (Server-to-Server) or a gateway. This ensures businesses with hybrid cloud strategies can still manage documents centrally.
Modern experience support (No):
While the modern experience is the current standard and offers a better user interface, Dynamics 365 document management integration also supports SharePoint classic sites. The core functionality relies on the underlying SharePoint API rather than the visual layout of the site, meaning older site collections can still be utilized for document storage.
Incorrect Option:
Database-only storage:
Recommending that documents only be stored in the Dynamics 365 database is incorrect. While possible for small files, it is not scalable and lacks the document lifecycle management tools provided by SharePoint, such as check-in/check-out and deep search capabilities.
Exclusive Modern Experience:
Suggesting that only "Modern" sites work is a common misconception. Restricting the system to only modern sites would prevent many legacy enterprises from integrating their existing SharePoint repositories with their new ERP implementation.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Configure document management for finance and operations apps
Microsoft Learn: SharePoint storage overview for Dynamics 365
A company implements Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management.
The company needs to use inventory journals to post different types of physical inventory
transactions.
Match each type of inventory journal to its use case. To answer, drag the appropriate type of inventory journal from the column on the left to its use case on the right. Each type of inventory journal may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
NOTE: Each correct match is worth one point.

Explanation:
Inventory journals in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management are essential tools for managing physical stock levels and their corresponding financial values. They allow warehouse managers and accountants to record changes in inventory that occur outside of standard sales or purchase processes, such as internal transfers, breakage, or annual stocktakes. Each journal type is purpose-built to handle specific accounting requirements, ensuring that every physical change in the warehouse is accurately reflected in the company's general ledger and financial statements.
Correct Option:
Movement Journal:
This is used when you need to specify a specific offset account for a transaction. This allows you to bypass default posting profiles and direct the financial impact of an inventory issue to a specific cost center or department, such as charging "Office Supplies" directly to the HR budget.
Transfer Journal:
This type is designed to move items between different physical or logical locations, such as moving stock from Warehouse A to Warehouse B. It updates the on-hand quantity at both sites without impacting the overall value of inventory in the general ledger.
Inventory Adjustment Journal:
This is used to add or remove stock while automatically using the default posting profiles. It allows users to add costs to items during the receipt process, ensuring the ledger transaction reflects the correct value of the newly added inventory.
Counting Journal:
This is the standard tool for physical stocktaking. It allows users to enter the "actual" quantity found in the warehouse; the system then calculates the difference from the "on-hand" record and posts the necessary adjustments to synchronize the two.
Incorrect Option:
BOM (Bill of Materials) Journal:
While listed as an option, this is incorrect for these use cases. A BOM journal is specifically used to post the finished product and consume its components in a single step, which is a manufacturing process rather than a simple inventory adjustment or move.
Tag Counting Journal:
This is incorrect for a standard counting use case as it is a specialized tool for high-volume environments where physical "tags" are used to track every item counted before the final reconciliation is posted to the ledger.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Inventory journals overview in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
Microsoft Learn: Use inventory journals to manage physical inventory transactions
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation:
Dynamics 365 Human Resources provides a comprehensive framework for managing employee compensation and benefits. To maintain internal equity and market competitiveness, the system uses a structured approach to pay. This involves creating "grids" or matrices that define exactly how much an employee should be paid based on their specific job level and performance. Additionally, the system supports modern benefit offerings like "Flex Credits," which empower employees to customize their benefits package—such as choosing between extra vacation time or higher health insurance coverage—within a set credit budget provided by the employer.
Correct Option:
Compensation structure matrix (Yes):
This is correct because compensation structures in Dynamics 365 HR are designed as matrices. These matrices map job levels (grades) to specific pay ranges (minimum, midpoint, and maximum), ensuring that pay is standardized across the organization for similar roles.
Fixed compensation grids (Yes):
Fixed compensation refers to an employee's regular base pay. These plans rely on compensation grids to maintain the pay rates. When a grid is updated (for example, due to inflation), the system can automatically suggest updates for all employees linked to that specific grid.
Flex credit programs (Yes):
Flex credit programs allow organizations to give employees a "budget" of credits. Employees then "spend" these credits on various benefit options during open enrollment. This feature is a core part of the Benefits Management module in Dynamics 365 Human Resources.
Incorrect Option:
Variable Compensation (Context):
It would be incorrect to use a compensation grid for variable pay like one-time bonuses or stock options. Variable pay is typically handled through separate "Variable Compensation Plans" that do not rely on fixed matrix ranges.
Manual Benefit Assignment:
Recommending that benefits must be assigned manually to every employee is incorrect. The system is designed to use "Eligibility Rules" and "Flex Credit Programs" to automate the distribution and selection process for the workforce.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Compensation plans overview in Dynamics 365 Human Resources
Microsoft Learn: Set up compensation grids
Microsoft Learn: Benefits management overview and flex credits
A company plans to implement Dynamics 365 Customer Insights and use the audience insights capability. Instructions: For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation:
Dynamics 365 Customer Insights is a Customer Data Platform (CDP) designed to unify fragmented data to provide a holistic "360-degree" view of customers.
End-to-end visibility:
The audience insights capability allows businesses to connect data from various touchpoints—such as transactional systems (ERP), behavioral data from websites, and observational data from social media. This creates a unified profile that tracks buying habits and interactions throughout the entire customer journey.
Cleanse and analyze data:
A core function of the platform is its Data Unification process. It allows you to ingest data from multiple disparate sources (using Power Query connectors) and then perform "Map, Match, and Merge" activities. This process cleanses the data by resolving duplicates and standardizing formats before analyzing it to generate predictive insights, such as churn risk or lifetime value.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: What is Dynamics 365 Customer Insights?
Microsoft Learn: Data unification overview in Customer Insights
Exam MB-900 Study Guide: Describe Dynamics 365 Customer Insights – Audience insights and engagement insights capabilities
A company implements the performance management feature in Dynamics 365 Human Resources.
Which performance management component can employees create by using the Employee Self-Service workspace?
A. Goals
B. Workflows
C. Performance reviews
D. Performance Journal
Explanation:
In Dynamics 365 Human Resources, the Performance Management module is designed to foster a culture of continuous feedback and development. The Employee Self-Service (ESS) workspace acts as a personal hub for workers to manage their professional growth without needing administrative intervention for every task. While formal structures like reviews and workflows are typically managed by HR or Managers, the Performance Journal is specifically intended for the employee's day-to-day use.
Correct Option:
D. Performance Journal:
This is the correct recommendation because employees use the Performance Journal to record their achievements, progress on tasks, or specific feedback as it happens throughout the year. Entries in the journal can later be linked to formal performance reviews or goals to provide evidence of work performed.
Incorrect Options:
A. Goals:
While employees can often view or update progress on goals, the creation and final approval of formal business goals are typically part of a structured process involving managers to ensure alignment with company objectives.
B. Workflows:
Workflows are system-level configurations created by administrators or HR professionals to define how data (like a review) moves through the approval process.
C. Performance reviews:
Formal reviews are generally "initiated" by HR or a Manager at set intervals (e.g., annually or quarterly). While employees complete their section of the review, they do not typically "create" the review component itself in the system.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn: Performance management overview in Dynamics 365 Human Resources
Microsoft Learn: Employee self-service overview
Microsoft Learn: Create a performance journal entry
A company is evaluating Dynamics 365 Finance capabilities. The company requires the ability to create the following:
• Debit and credit register
• Depreciation entries
• Employee charges
You need to recommend which modules the company should use to provide these capabilities. Which three modules should you recommend? Each correct answer presents a part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. product management
B. fixed assets
C. expense management
D. general ledger
E. inventory management
Recommended Modules
D. General ledger (Debit and credit register):
This is the foundational module where all financial transactions are ultimately recorded. It provides the Debit and Credit register through the use of main accounts and journals, ensuring that the company's financial statements remain balanced and compliant with accounting standards.
B. Fixed assets (Depreciation entries):
This module is used to track the value of a company’s long-term assets over time. It automates depreciation entries based on various methods (such as straight-line or reducing balance), ensuring that the wear and tear of equipment or property is accurately reflected as an expense in the financial records.
C. Expense management (Employee charges):
This module allows the company to manage employee charges, such as travel and entertainment expenses. It facilitates the submission, approval, and reimbursement of employee-related costs, which are then posted back to the general ledger.
Explanation of Components
The integration of these modules ensures a seamless flow of data across the organization. For instance, when a depreciation entry is generated in the Fixed assets module, it automatically posts a debit to a depreciation expense account and a credit to an accumulated depreciation account within the General ledger. Similarly, when employee charges are finalized in Expense management, the system automatically creates the necessary ledger entries to recognize the business expense and the liability to the employee.
Incorrect Options
A. Product management:
This is primarily used in Supply Chain Management to define item master data (like names and dimensions) and does not handle financial accounting or employee expenses.
E. Inventory management:
While this module tracks physical stock and its value, it is not the primary location for managing depreciation of non-stock assets or general debit/credit registers.
Reference
Microsoft Learn: General ledger overview in Dynamics 365 Finance
Microsoft Learn: Fixed assets overview and depreciation methods
Microsoft Learn: Expense management overview in Dynamics 365
A company plans to modernize its enterprise resource planning (ERP) system The company identities the following issues with the current ERP system:
• Departments are isolated without knowledge of cross-departmental data Departmental data must remain isolated for compliance reasons.
• The company system is outdated, slow, and does not automatically update Vou need to address the current ERP system issues.
Which Dynamics 365 capability should you use? To answer, drag the appropriate Dynamics 365 capability to the correct issue. Each Dynamics 365 capability may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation:
This question asks you to match identified business problems with the foundational capabilities of the Dynamics 365 platform itself. The issues are classic pain points of legacy, on-premises systems: departmental data silos and outdated, static software. The solutions map directly to core architectural and deployment benefits of Dynamics 365.
Correct Option:
Issue: Isolated departments → Capability: Dynamics 365 Reporting
This addresses the data silo problem. Dynamics 365 provides unified reporting tools (primarily Power BI integrated with the Entity Store) that can pull compliant, secured data from multiple departments and modules into a single, holistic view. Security roles and data isolation rules ensure departmental data remains protected for compliance, while authorized users can gain cross-departmental insights through reports and dashboards, breaking down informational barriers.
Issue: Outdated and slow system... → Capability: Dynamics 365 cloud deployment
This directly solves the technical debt. Opting for a cloud deployment means Microsoft manages the infrastructure, performance, and, critically, automatic, regular updates. This eliminates the cycle of costly, disruptive upgrades, ensures the company is always on a current, fast, and secure version with the latest features, and provides scalable performance that legacy on-premises systems lack.
Why "Dynamics 365 on-premises deployment" is Incorrect Here:
Selecting on-premises deployment would perpetuate the second issue, not solve it. An on-premises deployment requires the company to manage its own servers, performance tuning, and manual application of updates/upgrades. This would maintain the "outdated and slow system that lacks automatic feature updates" problem. The cloud deployment model is specifically the answer to modernizing away from that outdated model.
Reference:
Microsoft Learn - "Explore Dynamics 365 deployment options" and "Introduction to analytics and reporting." The cloud deployment model is defined by its service-based updates and scalability. The reporting and analytics tools are highlighted as key to gaining unified business insights across applications while maintaining security and compliance.
| Page 3 out of 13 Pages |
| Previous |