What is one benefit of a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) on an Aruba AP?
A. It enables secure boot, which detects if hackers corrupt the OS with malware.
B. It deploys the AP with enhanced security, which includes disabling the password recovery mechanism.
C. It allows the AP to run in secure mode, which automatically enables CPsec and disables the console port.
D. It enables the AP to encrypt and decrypt 802.11 traffic locally, rather than at the MC.
Explanation: The TPM (Trusted Platform Module) is a hardware-based security feature that can provide various security functions, one of which includes secure boot. Secure boot is a process where the TPM ensures that the device boots using only software that is trusted by the manufacturer. If the OS has been tampered with or infected with malware, the secure boot process can detect this and prevent the system from loading the compromised OS.
What is a consideration for using MAC authentication (MAC-Auth) to secure a wired or wireless connection?
A. As a Layer 2 authentication method, MAC-Auth cannot be used to authenticate devices to an external authentication server.
B. It is very easy for hackers to spoof their MAC addresses and get around MAC authentication.
C. MAC-Auth can add a degree of security to an open WLAN by enabling the generation of a PMK to encrypt traffic.
D. Headless devices, such as Internet of Things (loT) devices, must be configured in advance to support MAC-Auth.
Explanation: MAC authentication, also known as MAC-Auth, is a method used to authenticate devices based on their Media Access Control (MAC) address. It is often employed in both wired and wireless networks to grant network access based solely on the MAC address of a device. While MAC-Auth is straightforward and doesn’t require complex configuration, it has significant security limitations primarily because MAC addresses can be easily spoofed. Attackers can change the MAC address of their device to match an authorized one, thereby gaining unauthorized access to the network. This susceptibility to MAC address spoofing makes MAC-Auth a weaker security mechanism compared to more robust authentication methods like 802.1X, which involves mutual authentication and encryption protocols.
You have been asked to send RADIUS debug messages from an ArubaOS-CX switch to a
central SIEM server at 10.5.15.6. The server is already defined on the switch with this
command: logging 10.5.6.12.
You enter this command: debug radius all.
What is the correct debug destination?
A. console
B. file
C. syslog
D. buffer
Explanation: When configuring an Aruba OS-CX switch to send RADIUS debug messages to a central SIEM server, it is important to correctly direct these debug outputs. The command debug radius all activates debugging for all RADIUS processes, capturing detailed logs about RADIUS operations. If the SIEM server is already defined on the switch for logging purposes (as indicated by the command logging 10.5.6.12), the correct destination for these debug messages to be sent to the SIEM server would be through the syslog. This ensures that all generated logs are forwarded to the centralized server specified for logging, enabling consistent log management and analysis. Using syslog as the destination leverages the existing logging setup and integrates seamlessly with the network's centralized monitoring systems.
A company has an ArubaOS controller-based solution with a WPA3-Enterprise WLAN. which authenticates wireless clients to Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM). The company has decided to use digital certificates for authentication A user's Windows domain computer has had certificates installed on it However, the Networks and Connections window shows that authentication has tailed for the user. The Mobility Controllers (MC's) RADIUS events show that it is receiving Access-Rejects for the authentication attempt. What is one place that you can you look for deeper insight into why this authentication attempt is failing?
A. the reports generated by Aruba ClearPass Insight
B. the RADIUS events within the CPPM Event Viewer
C. the Alerts tab in the authentication record in CPPM Access Tracker
D. the packets captured on the MC control plane destined to UDP 1812
Explanation: When an authentication attempt for a user's Windows domain computer is failing on a WPA3-Enterprise WLAN and the Mobility Controller is receiving Access- Rejects, one place to look for deeper insight is the RADIUS events within the CPPM Event Viewer. ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) logs all RADIUS authentication events, and the Event Viewer would show detailed information about why a particular authentication attempt was rejected. This could include reasons such as incorrect credentials, expired certificates, or policy mismatches. The CPPM Event Viewer is an essential troubleshooting tool within ClearPass to diagnose authentication issues, as indicated in the ClearPass Policy Manager documentation.
What is one way a noneypot can be used to launch a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack to wireless clients?
A. it uses a combination or software and hardware to jam the RF band and prevent the client from connecting to any wireless networks
B. it runs an NMap scan on the wireless client to And the clients MAC and IP address. The hacker then connects to another network and spoofs those addresses.
C. it examines wireless clients' probes and broadcasts the SSlDs in the probes, so that wireless clients will connect to it automatically.
D. it uses ARP poisoning to disconnect wireless clients from the legitimate wireless network and force clients to connect to the hacker's wireless network instead.
Explanation: A honeypot can be used to launch a Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack on wireless clients by examining wireless clients' probe requests and then broadcasting the SSIDs in those probes. Clients with those SSIDs in their preferred network list may then automatically connect to the honeypot, believing it to be a legitimate network. Once the client is connected to the attacker's honeypot, the attacker can intercept, monitor, or manipulate the client's traffic, effectively executing a MITM attack.
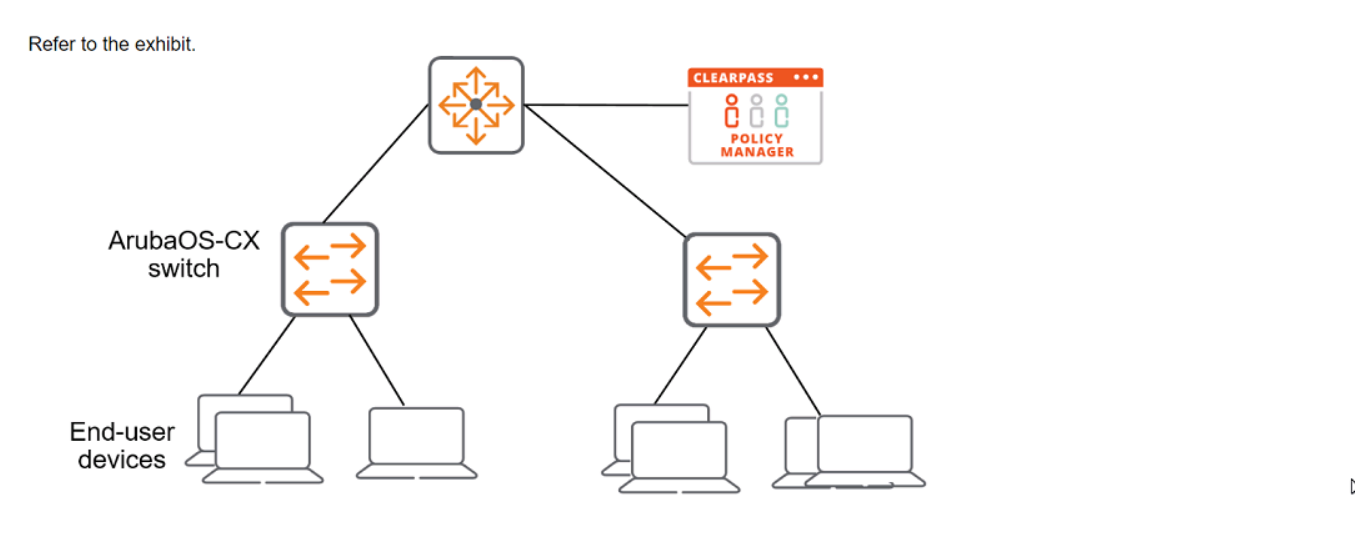
What is another setting that you must configure on the switch to meet these requirements?
A. Set the aaa authentication login method for SSH to the "radius" server-group (with local as backup).
B. Configure a CPPM username and password that match a CPPM admin account.
C. Create port-access roles with the same names of the roles that CPPM will send in Aruba-Admin-Role VSAs.
D. Disable SSH on the default VRF and enable it on the mgmt VRF instead.
Explanation:
To meet the requirements for configuring an ArubaOS-CX switch for integration with
ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM), it is necessary to set the AAA authentication login
method for SSH to use the “radius” server-group, with “local” as a backup. This ensures
that when an admin attempts to SSH into the switch, the authentication request is first sent
to CPPM via RADIUS. If CPPM is unavailable, the switch will fall back to using local
authentication12.
Here’s why the other options are not correct:
You have detected a Rogue AP using the Security Dashboard Which two actions should you take in responding to this event? (Select two)
A. There is no need to locale the AP If you manually contain It.
B. This is a serious security event, so you should always contain the AP immediately regardless of your company's specific policies.
C. You should receive permission before containing an AP. as this action could have legal Implications.
D. For forensic purposes, you should copy out logs with relevant information, such as the time mat the AP was detected and the AP's MAC address.
E. There is no need to locate the AP If the Aruba solution is properly configured to automatically contain it.
Explanation: When responding to the detection of a Rogue AP, it's important to consider
legal implications and to gather forensic evidence:
You should receive permission before containing an AP (Option C), as containing
it could disrupt service and may have legal implications, especially if the AP is on a
network that the organization does not own.
For forensic purposes, it is essential to document the event by copying out logs
with relevant information, such as the time the AP was detected and the AP's MAC
address (Option D). This information could be crucial if legal action is taken or if a
detailed analysis of the security breach is required.
Automatically containing an AP without consideration for the context (Options A and E) can
be problematic, as it might inadvertently interfere with neighboring networks and cause
legal issues. Immediate containment without consideration of company policy (Option B)
could also violate established incident response procedures.
Refer to the exhibit.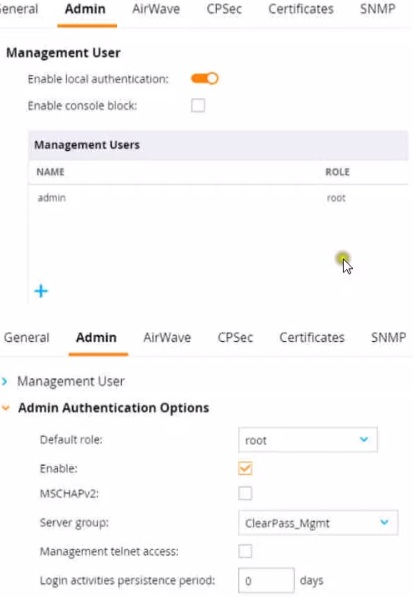
This Aruba Mobility Controller (MC) should authenticate managers who access the Web Ul
to ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) ClearPass admins have asked you to use RADIUS
and explained that the MC should accept managers' roles in Aruba-Admin-Role VSAs.
Which setting should you change to follow Aruba best security practices?
A. Change the local user role to read-only
B. Clear the MSCHAP check box
C. Disable local authentication
D. Change the default role to "guest-provisioning"
Explanation: For following Aruba best security practices, the setting you should change is to disable local authentication. When integrating with an external RADIUS server like ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) for authenticating administrative access to the Mobility Controller (MC), it is a best practice to rely on the external server rather than the local user database. This practice not only centralizes the management of user roles and access but also enhances security by leveraging CPPM's advanced authentication mechanisms.
What is symmetric encryption?
A. It simultaneously creates ciphertext and a same-size MAC.
B. It any form of encryption mat ensures that thee ciphertext Is the same length as the plaintext.
C. It uses the same key to encrypt plaintext as to decrypt ciphertext.
D. It uses a Key that is double the size of the message which it encrypts.
Explanation: Symmetric encryption is a type of encryption where the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the message. It's called "symmetric" because the key used for encryption is identical to the key used for decryption. The data, or plaintext, is transformed into ciphertext during encryption, and then the same key is used to revert the ciphertext back to plaintext during decryption. It is a straightforward method but requires secure handling and exchange of the encryption key.
What role does the Aruba ClearPass Device Insight Analyzer play in the Device Insight architecture?
A. It resides in the cloud and manages licensing and configuration for Collectors
B. It resides on-prem and provides the span port to which traffic is mirrored for deep analytics.
C. It resides on-prem and is responsible for running active SNMP and Nmap scans
D. It resides In the cloud and applies machine learning and supervised crowdsourcing to metadata sent by Collectors
Explanation: The Aruba ClearPass Device Insight Analyzer plays a crucial role within the Device Insight architecture by residing in the cloud and applying machine learning and supervised crowdsourcing to the metadata sent by Collectors. This component of the architecture is responsible for analyzing vast amounts of data collected from the network to identify and classify devices accurately. By utilizing machine learning algorithms and crowdsourced input, the Device Insight Analyzer enhances the accuracy of device detection and classification, thereby improving the overall security and management of the network.
What is a benefit of deploying Aruba ClearPass Device insight?
A. Highly accurate endpoint classification for environments with many devices types, including Internet of Things (loT)
B. visibility into devices' 802.1X supplicant settings and automated certificate deployment
C. Agent-based analysts of devices' security settings and health status, with the ability to implement quarantining
D. Simpler troubleshooting of ClearPass solutions across an environment with multiple ClearPass Policy Managers
Explanation: Aruba ClearPass Device Insight offers a significant benefit by providing
highly accurate endpoint classification. This feature is particularly useful in complex
environments with a wide variety of device types, including IoT devices. Accurate device
classification allows network administrators to better understand the nature and behavior of
devices on their network, which is crucial for implementing appropriate security policies and
ensuring network performance and security.
Reference: This feature is highlighted in Aruba ClearPass Device Insight literature and is a
major selling point of the product as it addresses the challenges posed by diverse and
growing device environments in modern networks.
What is a guideline for managing local certificates on an ArubaOS-Switch?
A. Before installing the local certificate, create a trust anchor (TA) profile with the root CA certificate for the certificate that you will install
B. Install an Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) certificate to simplify the process of enrolling and re-enrolling for certificate
C. Generate the certificate signing request (CSR) with a program offline, then, install both the certificate and the private key on the switch in a single file.
D. Create a self-signed certificate online on the switch because ArubaOS-Switches do not support CA-signed certificates.
Explanation: When managing local certificates on an ArubaOS-Switch, a recommended guideline is to create a trust anchor (TA) profile with the root CA certificate before installing the local certificate. This step ensures that the switch can verify the authenticity of the certificate chain during SSL/TLS communications. The trust anchor profile establishes a basis of trust by containing the root CA certificate, which helps validate the authenticity of any subordinate certificates, including the local certificate installed on the switch. This process is essential for enhancing security on the network, as it ensures that encrypted communications involving the switch are based on a verified certificate hierarchy.
| Page 5 out of 14 Pages |
| Previous |