Refer to the exhibit.
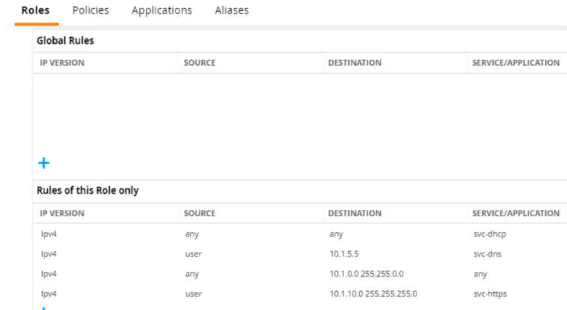
A diem is connected to an ArubaOS Mobility Controller. The exhibit snows all Tour firewall rules that apply to this diem
What correctly describes how the controller treats HTTPS packets to these two IP
addresses, both of which are on the other side of the firewall
10.1 10.10
203.0.13.5
A. It drops both of the packets
B. It permits the packet to 10.1.10.10 and drops the packet to 203 0.13.5
C. it permits both of the packets
D. It drops the packet to 10.1.10.10 and permits the packet to 203.0.13.5.
Explanation: Referring to the exhibit, the ArubaOS Mobility Controller treats HTTPS packets based on the firewall rules applied to the client. The rule that allows svc-https service for destination IP range 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 would permit an HTTPS packet to 10.1.10.10 since this IP address falls within the specified range. There are no rules shown that would allow traffic to the IP address 203.0.13.5; hence, the packet to this address would be dropped.
What is one difference between EAP-Tunneled Layer security (EAP-TLS) and Protected EAP (PEAP)?
A. EAP-TLS creates a TLS tunnel for transmitting user credentials, while PEAP authenticates the server and supplicant during a TLS handshake.
B. EAP-TLS requires the supplicant to authenticate with a certificate, hut PEAP allows the supplicant to use a username and password.
C. EAP-TLS begins with the establishment of a TLS tunnel, but PEAP does not use a TLS tunnel as part of Its process
D. EAP-TLS creates a TLS tunnel for transmitting user credentials securely while PEAP protects user credentials with TKIP encryption.
Which is a correct description of a stage in the Lockheed Martin kill chain?
A. In the delivery stage, malware collects valuable data and delivers or exfilltrated it to the hacker.
B. In the reconnaissance stage, the hacker assesses the impact of the attack and how much information was exfilltrated.
C. In the weaponization stage, which occurs after malware has been delivered to a system, the malware executes Its function.
D. In the exploitation and installation phases, malware creates a backdoor into the infected system for the hacker.
Explanation: The Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain model describes the stages of a cyber attack. In the exploitation phase, the attacker uses vulnerabilities to gain access to the system. Following this, in the installation phase, the attacker installs a backdoor or other malicious software to ensure persistent access to the compromised system. This backdoor can then be used to control the system, steal data, or execute additional attacks.
Your Aruba Mobility Master-based solution has detected a suspected rogue AP. Among
other information, the ArubaOS Detected Radios page lists this information for the AP:
SSID = PublicWiFi
BSSID = a8:bd:27:12:34:56
Match method = Plus one
Match method = Eth-Wired-Mac-Table
The security team asks you to explain why this AP is classified as a rogue. What should
you explain?
A. The AP has a BSSID that is close to your authorized APs' BSSIDs. This indicates that the AP might be spoofing the corporate SSID and attempting to lure clients to it, making the AP a suspected rogue.
B. The AP is probably connected to your LAN because it has a BSSID that is close to a MAC address that has been detected in your LAN. Because it does not belong to the company, it is a suspected rogue.
C. The AP has been detected using multiple MAC addresses. This indicates that the AP is spoofing its MAC address, which qualifies it as a suspected rogue.
D. The AP is an AP that belongs to your solution. However, the ArubaOS has detected that it is behaving suspiciously. It might have been compromised, so it is classified as a suspected rogue.
Explanation: The Match method 'Eth-Wired-Mac-Table' suggests that the BSSID of the rogue AP has been found in the Ethernet (wired) MAC address table of the network infrastructure. This means the AP is physically connected to the LAN. If the BSSID does not match the company's authorized APs, it implies the AP is unauthorized and hence classified as a rogue.
You have an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC). for which you are already using Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) to authenticate access to the Web Ul with usernames and passwords You now want to enable managers to use certificates to log in to the Web Ul CPPM will continue to act as the external server to check the names in managers' certificates and tell the MC the managers' correct rote in addition to enabling certificate authentication. what is a step that you should complete on the MC?
A. Verify that the MC has the correct certificates, and add RadSec to the RADIUS server configuration for CPPM
B. install all of the managers' certificates on the MC as OCSP Responder certificates
C. Verify that the MC trusts CPPM's HTTPS certificate by uploading a trusted CA certificate Also, configure a CPPM username and password on the MC
D. Create a local admin account mat uses certificates in the account, specify the correct trusted CA certificate and external authentication
Explanation: To enable managers to use certificates to log into the Web UI of an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC), where Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) acts as the external server for authentication, it is essential to ensure that the MC trusts the HTTPS certificate used by CPPM. This involves uploading a trusted CA certificate to the MC that matches the one used by CPPM. Additionally, configuring a username and password for CPPM on the MC might be necessary to secure and facilitate communication between the MC and CPPM. This setup ensures that certificate-based authentication is securely validated, maintaining secure access control for the Web UI.
What is one way that WPA3-PerSonal enhances security when compared to WPA2- Personal?
A. WPA3-Perscn3i is more secure against password leaking Because all users nave their own username and password
B. WPA3-Personai prevents eavesdropping on other users' wireless traffic by a user who knows the passphrase for the WLAN.
C. WPA3-Personai is more resistant to passphrase cracking Because it requires passphrases to be at least 12 characters
D. WPA3-Personal is more complicated to deploy because it requires a backend authentication server
Explanation: WPA3-Personal enhances security over WPA2-Personal by implementing individualized data encryption. This feature, known as Wi-Fi Enhanced Open, provides each user's session with a unique encryption key, even if they are using the same network passphrase. This prevents an authenticated user from eavesdropping on the traffic of other users on the same network, thus enhancing privacy and security.
What is a consideration for implementing wireless containment in response to unauthorized devices discovered by ArubaOS Wireless Intrusion Detection (WIP)?
A. It is best practice to implement automatic containment of unauthorized devices to eliminate the need to locate and remove them.
B. Wireless containment only works against unauthorized wireless devices that connect to your corporate LAN, so it does not offer protection against Interfering APs.
C. Your company should consider legal implications before you enable automatic containment or implement manual containment.
D. Because wireless containment has a lower risk of targeting legitimate neighbors than wired containment, it is recommended in most use cases.
Explanation: When implementing wireless containment as a response to unauthorized devices, a company should consider the legal implications. Wireless containment might affect devices that are not part of the company's network and could be considered as a form of interference. This could have legal consequences, and therefore, such actions should be carefully reviewed and ideally should be performed in a targeted and controlled manner, reducing the risk of legal issues.
Refer to the exhibit.
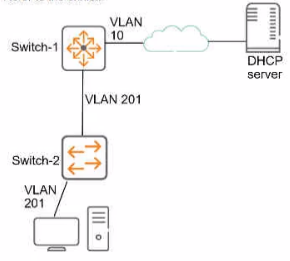
This company has ArubaOS-Switches. The exhibit shows one access layer switch, Swllcn-
2. as an example, but the campus actually has more switches. The company wants to slop
any internal users from exploiting ARP
What Is the proper way to configure the switches to meet these requirements?
A. On Switch-1, enable ARP protection globally, and enable ARP protection on ail VLANs.
B. On Switch-2, make ports connected to employee devices trusted ports for ARP protection
C. On Swltch-2, enable DHCP snooping globally and on VLAN 201 before enabling ARP protection
D. On Swltch-2, configure static PP-to-MAC bindings for all end-user devices on the network
Explanation: To prevent users from exploiting Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) on a
network with ArubaOS-Switches, the correct approach would be to enable DHCP snooping
globally and on VLAN 201 before enabling ARP protection, as stated in option C. DHCP
snooping acts as a foundation by tracking and securing the association of IP addresses to
MAC addresses. This allows ARP protection to function effectively by ensuring that only
valid ARP requests and responses are processed, thus preventing ARP spoofing attacks.
Trusting ports that connect to employee devices directly could lead to bypassing ARP
protection if those devices are compromised.
The company’s goal is to prevent internal users from exploiting ARP within their ArubaOSSwitch
network. Let’s break down the options:
Option A (Incorrect): Enabling ARP protection globally on Switch-1 and all VLANs
is not the best approach. ARP protection should be selectively applied where needed, not globally. It’s also not clear why Switch-1 is mentioned when the exhibit
focuses on Switch-2.
Option B (Incorrect): Making ports connected to employee devices trusted for ARP
protection is a good practice, but it’s not sufficient by itself. Trusted ports allow
ARP traffic, but we need an additional layer of security.
Option C (Correct): This is the recommended approach. Here’s why:
Option D (Incorrect): While static ARP bindings can enhance security, they are
cumbersome to manage and don’t dynamically adapt to changes in the network.
What is a Key feature of me ArubaOS firewall?
A. The firewall is stateful which means that n can track client sessions and automatically allow return traffic for permitted sessions
B. The firewall Includes application layer gateways (ALGs). which it uses to filter Web traffic based on the reputation of the destination web site.
C. The firewall examines all traffic at Layer 2 through Layer 4 and uses source IP addresses as the primary way to determine how to control traffic.
D. The firewall is designed to fitter traffic primarily based on wireless 802.11 headers, making it ideal for mobility environments
Explanation: The ArubaOS firewall is a stateful firewall, meaning that it can track the state of active sessions and can make decisions based on the context of the traffic. This stateful inspection capability allows it to automatically allow return traffic for sessions that it has permitted, thereby enabling seamless two-way communication for authorized users while maintaining the security posture of the network.
What is the purpose of an Enrollment over Secure Transport (EST) server?
A. It acts as an intermediate Certification Authority (CA) that signs end-entity certificates.
B. It helps admins to avoid expired certificates with less management effort.
C. It provides a secure central repository for private keys associated with devices' digital certif-icates.
D. It provides a more secure alternative to private CAs at less cost than a public CA.
Explanation: EST (Enrollment over Secure Transport) is a protocol designed to streamline the certificate management process. It enables automated and secure enrollment, renewal, and revocation of digital certificates, which significantly reduces the management overhead typically associated with digital certificates. With EST, administrators can more easily manage certificates' lifecycle, ensuring that expired certificates are promptly replaced or renewed without significant manual intervention.
You need to deploy an Aruba instant AP where users can physically reach It. What are two recommended options for enhancing security for management access to the AP? (Select two )
A. Disable Its console ports
B. Place a Tamper Evident Label (TELS) over its console port
C. Disable the Web Ul.
D. Configure WPA3-Enterpnse security on the AP
E. install a CA-signed certificate
Explanation: When deploying an Aruba Instant AP in a location where users can
physically access it, enhancing security for management access could involve several
measures: C. Disabling the Web UI will prevent unauthorized access via the browserbased
management interface, which could be a security risk if the AP is within physical
reach of untrusted parties. E. Installing a CA-signed certificate helps ensure that any
communication with the AP's management interface is encrypted and authenticated,
preventing man-in-the-middle attacks and eavesdropping.
Reference: Aruba Instant AP deployment guides commonly include recommendations for
securing management access to prevent unauthorized configuration changes or data
breaches.
What is a guideline for deploying Aruba ClearPass Device Insight?
A. Deploy a Device Insight Collector at every site in the corporate WAN to reduce the impact on WAN links.
B. Make sure that Aruba devices trust the root CA certificate for the ClearPass Device Insight Analyzer's HTTPS certificate.
C. Configure remote mirroring on access layer Aruba switches, using Device Insight Analyzer as the destination IP.
D. For companies with multiple sites, deploy a pair of Device Insight Collectors at the HQ or the central data center.
Explanation: For deploying Aruba ClearPass Device Insight effectively, especially in environments with multiple sites, it is recommended to deploy a pair of Device Insight Collectors at the headquarters or the central data center. This deployment strategy helps in centralizing the data collection and analysis, which simplifies management and enhances performance by reducing the data load on the WAN links connecting different sites. Centralizing the collectors at a major site or data center allows for better scalability and reliability of the network management system. This configuration also aids in achieving a more consistent and comprehensive monitoring and analysis of the devices across the network, ensuring that the security and management policies are uniformly applied. This recommendation is based on best practices for network architecture design, particularly those discussed in Aruba’s deployment guides and network management strategies.
| Page 4 out of 14 Pages |
| Previous |