A customer has a large campus that requires 400 Aruba 335 APs to support a total of
20,000 wireless users and 12Gbps of traffic. Although the customer wants two controllers
for redundancy, each controller must be able to support all of the APs and users on its own.
Which Aruba Mobility Controller models meet the customer requirements and DO
NOT unnecessarily exceed them?
A.
Aruba 7024 controllers
B.
Aruba 7210 controllers
C.
Aruba 7240 controllers
D.
Aruba 7030 controllers
Aruba 7210 controllers
A company currently uses Instant APs (IAPs), all managed by a virtual controller. The
company expects to double in size without the next 18 months. The network manager
wants to purchase additional APs to service the increased traffic load. The network
manager also wants to deploy a Mobility Controller (MC) to manage all APs.
How should the network administrator adapt the current IAPs to a controlled architecture?
A.
Manage both the MCs and IAP clusters with Aruba Central.
B.
Configure the IAPs to establish CPSec tunnels to the new MCs.
C.
Manage both the MCs and IAP clusters with a Mobility Master (MM).
D.
Convert the IAPs to Campus APs controlled by the new MCs.
Convert the IAPs to Campus APs controlled by the new MCs.
A company plans to deploy a Mobility Master (MM). The MM will manage 50 Mobility
Controller (MC) appliances that will control a total of 700 APs, and 10 Virtual
Mobility Controllers (VMCs) that will control a total of 200 APs.
How many MM licenses does the company require?
A.
60
B.
210
C.
900
D.
960
960
Explanation:
Starting with ArubaOS 8.0.1, the MM license is required to terminate devices (controllers or
APs) on Mobility Master. If the Mobility Master does not have sufficient MM licenses and an
AP fails to obtain a license, that AP can get an IP address and connect to its controller, but
will not broadcast an SSID.
When an Aruba solution uses AirMatch, which device generates the channel and
power plan for an AP?
A.
the AirWave Management Platform
B.
the Mobility Master (MM)
C.
the Mobility Controller (MC) for the AP
D.
the AP itself
the Mobility Master (MM)
Refer to the exhibit.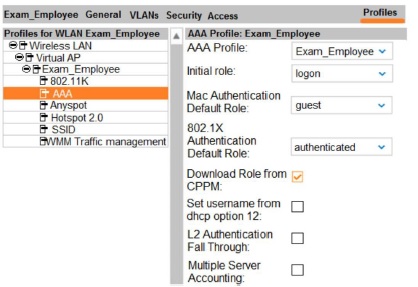
The exhibit shows the AAA profile for a WLAN on an Aruba solution. This WLAN uses
802.1X to authenticate users to a RADIUS server. A user successfully authenticates with
802.1X, but the RADIUS server does not send a role assignment.
How does the Aruba firewall handle the role assignment for this user?
A.
It does not assign a role.
B.
It applies the Aruba VSA role employee.
C.
It assigns the logon role.
D.
It assigns the authenticated role.
It assigns the authenticated role.
A company has an Aruba solution that is monitored by AirWave. Several users have
recurring connectivity and performance issues with their wireless clients.
How can network administrators use AirWave to minitor these clients more easily?
A.
Specify the clients as Watched Cliesnts and view the tables and graphs for these clients.
B.
Click the Down icon in the Airwave banner to quickly see a list of issues with client connections.
C.
Use the Client > Tags windows to tag the client for periodic checks and analysis.
D.
Run Device Summary reports and filter for the client MAC addresses within the report.
Click the Down icon in the Airwave banner to quickly see a list of issues with client connections.
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1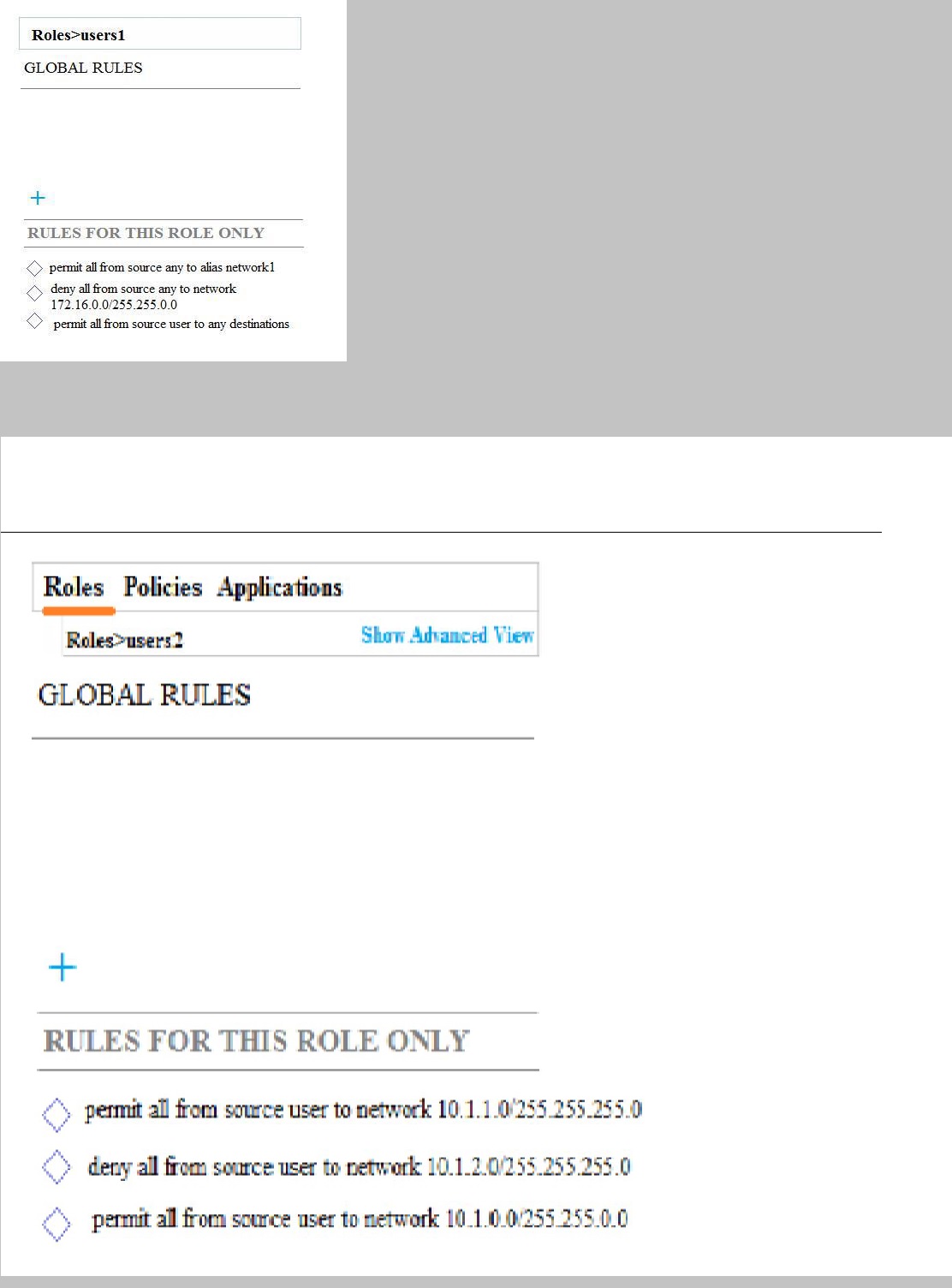
A company has an Aruba solution. Client 1 is assigned to the users1 role, and client 2
is assigned to the users2 role. The exhibits show current firewall rules for those roles.
The network1 alias used to be 10.1.1.0/24, but the network administrator now changes
the network1 alias to 172.16.1.0/24. Client 1 and Client 2 both send a packet destined
to 172.16.1.10.
How does the firewall handle these packets?
A.
It permits the packet from Client 1 and denies the packet from Client 2.
B.
It permits both packets.
C.
It denies the packet from Client 1 and permits the packet from Client 2.
D.
It denies both packets.
It permits the packet from Client 1 and denies the packet from Client 2.
A company has an Aruba solution and wants to provide guests with wireless access. The company wants to assign guests IP addresses in subnets that exist only within the Aruba
solution.
Which feature should network administrators set up so guests can send traffic on the
Internet without changes to the company routing solution?
A.
Enable NAT on the VLAN assigned to the guest WLAN.
B.
Set up a dynamic default gateway on the Mobility Controllers (MCs).
C.
Create destination NAT rules for the guest role.
D.
Enable policy-based routing for the guest traffic.
Enable NAT on the VLAN assigned to the guest WLAN.
A network manager wants to implement an Aruba wireless solution that
accommodates 802.1X with EAP-TLS. All wireless users will utilize Active Directory
(AD) accounts to authenticate.
Which device will the authenticator forward the authentication requests to in this type
of solution?
A.
APs
B.
RADIUS server
C.
Mobility Controller (MC)
D.
Mobility Master (MM)
RADIUS server
What is one setting that a network administrator can configure for user roles in an Aruba solution?
A.
DHCP pool
B.
ClientMatch rules
C.
source NAT
D.
Maximum session
Maximum session
What is one difference between an Aruba firewall access controle rule and an application
rule?
A.
An application rule cannot use the packet source and destination IP addresses as
part of its match criteria.
B.
An access rule can filter non-IP traffic, as well as IPv4 and IPv6 traffic.
C.
An access rule cannot apply different actions to different types of traffic sent to the same
destination.
D.
An application rule can filter traffic at a higher layer beyond the TCP or UDP port.
An application rule can filter traffic at a higher layer beyond the TCP or UDP port.
A Mobility Controller (MC) runs ArubaOS 8. What is a valid reason for an administrator
to set the MC to master-local mode?
A.
The company already has a partially hierarchical deployment based on the 6.x code and
wants to keep the current architecture.
B.
The company needs to manage third-party network infrastructure devices with the use of
the master controller interface.
C.
The company wants a deployment architecture that allows administrators to configure
all MC settings from a single location.
D.
The company requires a centralized licensing architecture that provides global
license pools.
The company already has a partially hierarchical deployment based on the 6.x code and
wants to keep the current architecture.
| Page 4 out of 11 Pages |
| Previous |