Topic 3: Misc. Questions Set
You have a Fabric workspace that contains a warehouse named Warehouse1.
While monitoring Warehouse1, you discover that query performance has degraded during
the last 60 minutes.
You need to isolate all the queries that were run during the last 60 minutes. The results
must include the username of the users that submitted the queries and the query
statements. What should you use?
A. the Microsoft Fabric Capacity Metrics app
B. views from the queryinsights schema
C. Query activity
D. the sys.dm_exec_requests dynamic management view
Summary:
This question requires detailed, query-level diagnostics for a Fabric Warehouse to troubleshoot a specific performance degradation. You need to identify the exact queries, who ran them, and their text within a precise time window. This requires accessing historical query execution logs with rich metadata, not just high-level resource metrics.
Correct Option:
B. views from the queryinsights schema
The queryinsights schema in a Fabric Warehouse contains a set of dynamic management views (DMVs) designed specifically for this purpose. The queryinsights.exec_requests_history view stores a detailed history of executed queries, including columns like login_name (for the username), command (for the query statement), and submit_time/end_time. You can query this view with a WHERE filter (e.g., WHERE submit_time >= DATEADD(minute, -60, GETDATE())) to isolate all queries from the last 60 minutes, meeting all requirements precisely.
Incorrect Options:
A. the Microsoft Fabric Capacity Metrics app
This Power BI app provides high-level, capacity-wide metrics about resource consumption (e.g., CU/s usage, active operations). It is excellent for monitoring overall capacity health and spend but does not provide the granular, query-level details like the specific query text and the username of the person who submitted it.
C. Query activity
"Query activity" is a general term and not a specific tool within the Fabric admin portal. While there might be a monitoring section showing active or recent queries, the queryinsights DMVs offer a more powerful, flexible, and query-based approach to retrieve and filter the exact historical data needed for this investigation.
D. the sys.dm_exec_requests dynamic management view
The sys.dm_exec_requests DMV is used in SQL Server and Azure SQL Database to view currently executing requests. It does not show a history of queries that have already completed. Since the performance issue occurred over the last 60 minutes and many queries have likely finished, this DMV will not provide the necessary historical data.
Reference:
Microsoft Official Documentation: Query Insights dynamic management views (DMVs)
You have a Fabric warehouse named DW1 that loads data by using a data pipeline named
Pipeline1. Pipeline1 uses a Copy data activity with a dynamic SQL source. Pipeline1 is
scheduled to run every 15 minutes.
You discover that Pipeline1 keeps failing.
You need to identify which SQL query was executed when the pipeline failed.
What should you do?
A. From Monitoring hub, select the latest failed run of Pipeline1, and then view the output JSON.
B. From Monitoring hub, select the latest failed run of Pipeline1, and then view the input JSON.
C. From Real-time hub, select Fabric events, and then review the details of Microsoft.Fabric.ItemReadFailed.
D. From Real-time hub, select Fabric events, and then review the details of Microsoft. Fabric.ItemUpdateFailed.
Summary:
This question involves debugging a failing data pipeline in Fabric. The pipeline uses a dynamic SQL source, meaning the exact SQL query being executed is defined at runtime, likely via a parameter or expression. When a pipeline fails, the Monitoring hub provides detailed run history, including the specific input parameters and values passed to each activity, which is essential for replicating and diagnosing the failure.
Correct Option:
B. From Monitoring hub, select the latest failed run of Pipeline1, and then view the input JSON.
The Monitoring hub is the central place to inspect pipeline run history. For a failed run, you can drill into the details of the failed activity (in this case, the Copy data activity). The Input JSON shows the configuration of the activity at the time of the run. Since the source is dynamic SQL, the exact query that was executed—constructed from parameters and expressions—will be visible in this input payload. This allows you to see the problematic SQL command that caused the failure.
Incorrect Options:
A. From Monitoring hub, select the latest failed run of Pipeline1, and then view the output JSON.
The Output JSON of a failed activity typically contains error messages, codes, and stack traces. While this is crucial for understanding why the query failed (e.g., a syntax error or timeout), it usually does not contain the full, executed SQL command. The input is where the source definition, including the dynamic query, is stored.
C. From Real-time hub, select Fabric events, and then review the details of Microsoft.Fabric.ItemReadFailed.
D. From Real-time hub, select Fabric events, and then review the details of Microsoft. Fabric.ItemUpdateFailed.
The Real-time hub and Fabric events are used for event-driven architectures and auditing high-level workspace activities. Events like ItemReadFailed or ItemUpdateFailed are too granular and general for this task. They might indicate that a pipeline run failed but will not provide the detailed, activity-level input information (like the dynamic SQL query) needed to diagnose this specific data movement error.
Reference:
Microsoft Official Documentation: Monitor pipeline runs in Microsoft Fabric
You have a Fabric workspace that contains a lakehouse named Lakehouse1. Data is
ingested into Lakehouse1 as one flat table. The table contains the following columns.
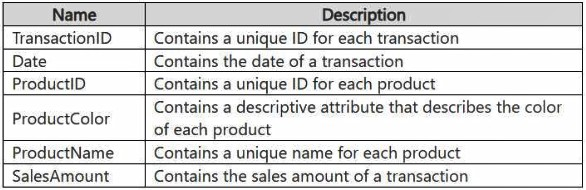
You plan to load the data into a dimensional model and implement a star schema. From the
original flat table, you create two tables named FactSales and DimProduct. You will track
changes in DimProduct.
You need to prepare the data.
Which three columns should you include in the DimProduct table? Each correct answer
presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. Date
B. ProductName
C. ProductColor
D. TransactionID
E. SalesAmount
F. ProductID
Summary:
This question tests your understanding of the star schema dimensional model. A star schema consists of fact tables (containing business measurements and foreign keys) and dimension tables (containing descriptive context). The DimProduct table is a dimension table, so it must contain the descriptive attributes about products. It must also include the business key (ProductID) to uniquely identify a product and to serve as the join key for the FactSales table.
Correct Options:
B. ProductName
This is a descriptive attribute of a product. In a dimension table, you include all the descriptive fields that users will want to filter by or group by when analyzing the facts. ProductName is a core descriptive property of a product entity.
C. ProductColor
Similar to ProductName, ProductColor is a descriptive attribute that provides context about the product. It belongs in the dimension table so analysts can slice sales data by product color.
F. ProductID
This is the primary key for the DimProduct dimension table. It uniquely identifies each product. This same ProductID will appear as a foreign key in the FactSales table to create the relationship between facts and the product dimension. It is essential for both the table's structure and for joining the tables.
Incorrect Options:
A. Date
Date is a key business context, but it belongs in its own dimension table, DimDate. It would be a foreign key in the FactSales table, not in the DimProduct table.
D. TransactionID
TransactionID is a unique identifier for a sales transaction. This is a measure or event identifier and is the natural primary key for the FactSales table. It does not describe a product and has no place in the DimProduct dimension.
E. SalesAmount
SalesAmount is a numerical measurement of a business event (a sale). This is a classic fact or measure and must be stored in the FactSales table. Placing it in a dimension table would violate the principles of a star schema.
Reference:
Microsoft Official Documentation: Dimensional modeling - While this link is for Power BI, the concepts of star schema and dimensional modeling are universal across data warehousing, including Fabric.
You have three users named User1, User2, and User3.
You have the Fabric workspaces shown in the following table.
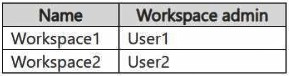
You have a security group named Group1 that contains User1 and User3.
The Fabric admin creates the domains shown in the following table.

User1 creates a new workspace named Workspace3.
You add Group1 to the default domain of Domain1.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select
No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Summary
This question tests the interaction between Fabric domains and workspace permissions. A domain is a security and governance boundary that contains workspaces. Permissions can be assigned at the domain level, which are then inherited by the workspaces within that domain. The default domain is the specific domain where new workspaces are automatically placed if no other is specified. The key is to track who creates the workspace (becoming the Admin) and how domain-level permissions assigned to a group propagate to the workspaces within that domain.
Correct Option Explanations
1. User3 has Viewer role access to Workspace3.
Answer: Yes
User1 created Workspace3, making them its admin. Because no other domain was specified, Workspace3 is placed in the default domain of Domain1.
Group1 (containing User1 and User3) was added to the default domain of Domain1. When a group is added to a domain, its members inherit a specific role across all workspaces in that domain.
The question does not specify the role, but the most logical default inheritance that would give User3 access is the Viewer role. Therefore, through domain inheritance, User3 gains Viewer access to Workspace3. User1, as the creator, is the Admin.
2. User3 has Domain contributor access to Domain1.
Answer: No
The scenario states that "You add Group1 to the default domain of Domain1." It does not specify which domain role (like Domain Contributor) was assigned to the group. Merely being added to a domain does not automatically grant a specific administrative role like Domain Contributor. Domain Contributor is a high-level permission for managing the domain itself. Without an explicit assignment of this role, we must assume User3 does not have it.
3. User2 has Contributor role access to Workspace3.
Answer: No
User2 is not in Group1. User2 has no direct assignment to Workspace3 and is not the workspace admin. Furthermore, User2 is not a Domain Admin for Domain1 (User1 is the Domain1 admin). Therefore, User2 has no inherited or direct permissions to Workspace3 and does not have the Contributor role.
Reference:
Microsoft Official Documentation: Domains in Microsoft Fabric
Microsoft Official Documentation: How domain roles work
You have a Fabric workspace that contains a warehouse named Warehouse1. Data is
loaded daily into Warehouse1 by using data pipelines and stored procedures.
You discover that the daily data load takes longer than expected.
You need to monitor Warehouse1 to identify the names of users that are actively running
queries.
Which view should you use?
A. sys.dm_exec_connections
B. sys.dm_exec_requests
C. queryinsights.long_running_queries
D. queryinsights.frequently_run_queries
E. sys.dm_exec_sessions
Summary:
This question requires real-time monitoring to see which users are actively running queries right now in the Fabric Warehouse. The solution needs to provide a live view of current sessions and the users associated with them. This is distinct from looking at historical query performance or aggregated patterns.
Correct Option:
E. sys.dm_exec_sessions
This Dynamic Management View (DMV) returns one row per authenticated session in the Fabric Warehouse. It includes columns like login_name which directly shows the username of the user connected to that session. By querying this view, you can get a list of all users who are currently connected and have active sessions, which is the precise requirement for identifying users who are actively running queries.
Incorrect Options:
A. sys.dm_exec_connections
This DMV shows information about the network connections established to the database. While it can provide connection-level details, it is less directly tied to the user context and the specific session running queries compared to sys.dm_exec_sessions. The session view is more appropriate for identifying users.
B. sys.dm_exec_requests
This DMV shows information about each currently executing request within the Warehouse. While it can show the user for active queries, it will not show users who are connected (have a session) but are not currently running a query (e.g., their query has finished or they are idle). sys.dm_exec_sessions gives the broader view of all active users.
C. queryinsights.long_running_queries
This is a pre-aggregated view designed for analyzing historical performance of queries that are typically slow. It is not for real-time monitoring and does not provide a simple list of currently active users.
D. queryinsights.frequently_run_queries
Similar to the long-running queries view, this is an aggregated view for identifying queries that run often over a period of time. It is used for performance tuning, not for real-time monitoring of active user sessions.
Reference:
Microsoft Official Documentation: sys.dm_exec_sessions (Azure SQL Database and Microsoft Fabric)
You have a Fabric warehouse named DW1. DW1 contains a table that stores sales data
and is used by multiple sales representatives.
You plan to implement row-level security (RLS).
You need to ensure that the sales representatives can see only their respective data.
Which warehouse object do you require to implement RLS?
A. ISTORED PROCEDURE
B. CONSTRAINT
C. SCHEMA
D. FUNCTION
Summary:
This question focuses on the technical components required to implement Row-Level Security (RLS) in a Fabric Warehouse. RLS works by automatically applying a filter predicate to queries on a table. This filter is defined within a security policy, and the core logic that determines which rows a user can access is encapsulated in a specific type of database object.
Correct Option:
D. FUNCTION
Specifically, an inline table-valued function is required to implement RLS. This function contains the security logic (the predicate), such as WHERE SalesRepName = USER_NAME(). The CREATE SECURITY POLICY statement then ADDs a FILTER PREDICATE that references this function. The function is the essential component that defines the row-access rules.
Incorrect Options:
A. STORED PROCEDURE
Stored procedures are used to encapsulate and execute batches of T-SQL code. They cannot be used as the filter predicate within a CREATE SECURITY POLICY statement. The RLS predicate must be defined within an inline table-valued function.
B. CONSTRAINT
Constraints (like CHECK, FOREIGN KEY) are used to enforce data integrity rules, not to dynamically filter data based on the user executing a query. They are not involved in the implementation of RLS.
C. SCHEMA
A schema is a container used to organize and group database objects (tables, views, functions) for manageability and security. While the function and table involved in RLS reside within schemas, the schema itself is not the object that implements the security logic.
Reference:
Microsoft Official Documentation: Row-Level Security - This documentation explicitly states: "Row-Level Security... uses the CREATE SECURITY POLICY statement, and inline table-valued functions created with the CREATE FUNCTION statement."
You have a Fabric workspace that contains a lakehouse named Lakehouse1.
In an external data source, you have data files that are 500 GB each. A new file is added
every day.
You need to ingest the data into Lakehouse1 without applying any transformations. The
solution must meet the following requirements
Trigger the process when a new file is added.
Provide the highest throughput.
Which type of item should you use to ingest the data?
A. Event stream
B. Dataflow Gen2
C. Streaming dataset
D. Data pipeline
Summary:
This question involves ingesting very large (500 GB) raw data files into a lakehouse. The key requirements are high-throughput data movement, no transformation, and a trigger based on the arrival of a new file. This scenario describes a classic bulk data ingestion pattern that requires orchestration and scheduling capabilities, which is the primary purpose of a data pipeline.
Correct Option:
D. Data pipeline
A data pipeline in Fabric is the correct tool for orchestrating and executing high-volume data copy operations. It can be triggered by a schedule or, crucially, by an event (such as a new file arriving in cloud storage). The Copy Data activity within a pipeline is specifically optimized for moving large amounts of data with high throughput from a source to a destination without transformation. This directly meets all the requirements.
Incorrect Options:
A. Event stream
An eventstream is designed for processing high-velocity, low-latency streaming data from sources like Azure Event Hubs or IoT Hub. It is not built for efficiently copying massive 500 GB batch files. Its throughput and use case are geared towards real-time event processing, not scheduled or event-triggered bulk file ingestion.
B. Dataflow Gen2
A Dataflow Gen2 is a powerful transformation tool that uses a Power Query engine. While it can copy data, its primary strength is in applying complex data shaping logic. Using it for a simple "no transformations" copy of a 500 GB file is inefficient and would not provide the highest possible throughput compared to the dedicated Copy Data activity in a pipeline.
C. Streaming dataset
A streaming dataset is a destination for data that will be visualized in a Power BI real-time dashboard. It is not a data ingestion or orchestration tool for landing large raw files in a lakehouse. It is an endpoint for small, frequently updated data, not a 500 GB daily file.
Reference:
Microsoft Official Documentation: Copy data using the Copy Data activity
Microsoft Official Documentation: Event-based triggers in Azure Data Factory
You have a Fabric workspace named Workspacel that contains the following items:
• A Microsoft Power Bl report named Reportl
• A Power Bl dashboard named Dashboardl
• A semantic model named Modell
• A lakehouse name Lakehouse1
Your company requires that specific governance processes be implemented for the items.
Which items can you endorse in Fabric?
A. Lakehouse1, Modell, and Dashboard1 only
B. Lakehouse1, Modell, Report1 and Dashboard1
C. Report1 and Dashboard1 only
D. Model1, Report1, and Dashboard1 only
E. Lakehouse1, Model1, and Report1 only
Summary:
This question tests your knowledge of the Endorsement governance feature in Microsoft Fabric. Endorsement allows admins and experts to promote high-quality, trusted items to other users in the organization. It's a way to signal that an item is reliable and approved for use. However, not all item types within a workspace are eligible for this specific governance action.
Correct Option:
D. Model1, Report1, and Dashboard1 only
In Microsoft Fabric, the endorsement feature is available for specific Power BI artifacts and semantic models. You can endorse:
Semantic Models (Model1):
Promoting a trusted data model for building reports.
Power BI Reports (Report1):
Marking a report as certified or promoted.
Power BI Dashboards (Dashboard1):
Endorsing a dashboard as a trusted source of information.
Lakehouses and other data engineering items are not subject to the Power BI-centric "endorsement" governance process.
Incorrect Options:
A. Lakehouse1, Modell, and Dashboard1 only:
Incorrect because it includes the lakehouse, which cannot be endorsed, and excludes the report, which can be.
B. Lakehouse1, Modell, Report1 and Dashboard1:
Incorrect because it includes the lakehouse, which cannot be endorsed.
C. Report1 and Dashboard1 only:
Incorrect because it excludes the semantic model (Modell), which is a primary item for endorsement.
E. Lakehouse1, Model1, and Report1 only:
Incorrect because it includes the lakehouse and excludes the dashboard.
Reference:
Microsoft Official Documentation: Endorsement in Power BI - While this documentation is from the Power BI perspective, it defines the scope of endorsable items (datasets/reports/dashboards), which correspond to Semantic Models, Reports, and Dashboards in Fabric.
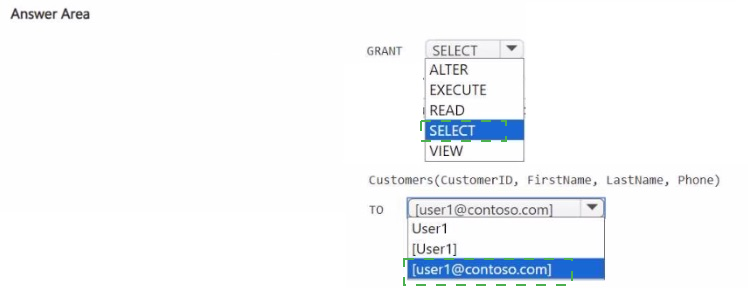
You have a Fabric workspace that contains a warehouse named Warehouse1. Warehouse!
contains a table named Customer. Customer contains the following data.
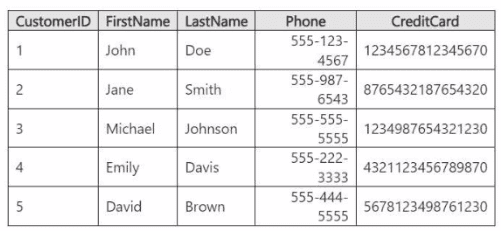
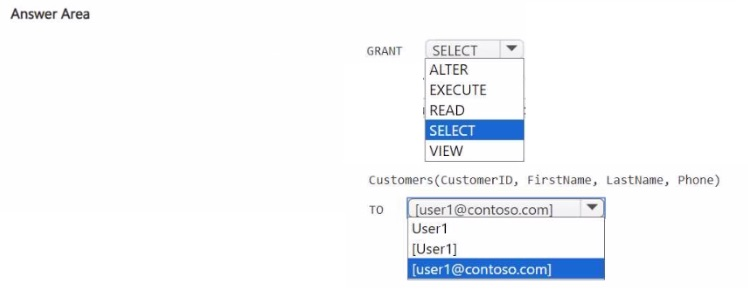
You have an internal Microsoft Entra user named User1 that has an email address of
user1@contoso.com.
You need to provide User1 with access to the Customer table. The solution must prevent
User1 from accessing the CreditCard column.
How should you complete the statement? To answer, select the appropriate options in the
answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
You have a Fabric workspace that contains an eventhouse and a KQL database named
Database1. Database1 has the following:
A table named Table1
A table named Table2
An update policy named Policy1
Policy1 sends data from Table1 to Table2.
The following is a sample of the data in Table2.

Recently, the following actions were performed on Table1:
An additional element named temperature was added to the StreamData column.
The data type of the Timestamp column was changed to date.
The data type of the DeviceId column was changed to string.
You plan to load additional records to Table2.
Which two records will load from Table1 to Table2? Each correct answer presents a
complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation:
Changes to Table1 Structure:
StreamData column: An additional temperature element was added.
Timestamp column: Data type changed from datetime to date.
DeviceId column: Data type changed from guid to string.
Impact of Changes:
Only records that comply with Table2’s structure will load.
Records that deviate from Table2’s column data types or structure will be rejected.
Record B:
Timestamp: Matches Table2 (datetime format).
DeviceId: Matches Table2 (guid format).
StreamData: Contains only the index and eventid, which matches Table2.
Accepted because it fully matches Table2’s structure and data types.
Record D:
Timestamp: Matches Table2 (datetime format).
DeviceId: Matches Table2 (guid format).
StreamData: Matches Table2’s structure.
Accepted because it fully matches Table2’s structure and data types.
You have a Fabric workspace named Workspace1 that contains a warehouse named
Warehouse1.
You plan to deploy Warehouse1 to a new workspace named Workspace2.
As part of the deployment process, you need to verify whether Warehouse1 contains
invalid references. The solution must minimize development effort.
What should you use?
A. a database project
B. a deployment pipeline
C. a Python script
D. a T-SQL script
Explanation: A deployment pipeline in Fabric allows you to deploy assets like warehouses, datasets, and reports between different workspaces (such as from Workspace1 to Workspace2). One of the key features of a deployment pipeline is the ability to check for invalid references before deployment. This can help identify issues with assets, such as broken links or dependencies, ensuring the deployment is successful without introducing errors. This is the most efficient way to verify references and manage the deployment with minimal development effort.
You have a Fabric workspace that contains a Real-Time Intelligence solution and an
eventhouse.
Users report that from OneLake file explorer, they cannot see the data from the
eventhouse.
You enable OneLake availability for the eventhouse.
What will be copied to OneLake?
A. only data added to new databases that are added to the eventhouse
B. only the existing data in the eventhouse
C. no data
D. both new data and existing data in the eventhouse
E. only new data added to the eventhouse
Explanation: When you enable OneLake availability for an eventhouse, both new and existing data in the eventhouse will be copied to OneLake. This feature ensures that data, whether newly ingested or already present, becomes available for access through OneLake, making it easier for users to interact with and explore the data directly from OneLake file explorer.
| Page 2 out of 8 Pages |
| Previous |