Section B (2 Mark)
An approved superannuation fund must have a minimum of _______ trustees
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. No restriction is applicable
Section A (1 Mark)
Mr. X’s minor daughter earned Rs. 50000 from his special talent. This income will be
clubbed with
A. It will not be clubbed
B. The income of Mrs. X
C. The income of Mr. X
D. Mr. X or Mrs. X, whoever’s income is higher
Section B (2 Mark)
Which of the following statement is correct w.r.t to the obligations of an Investment Advisor
Registered under SEBI Investment Advisor Regulations 2013.
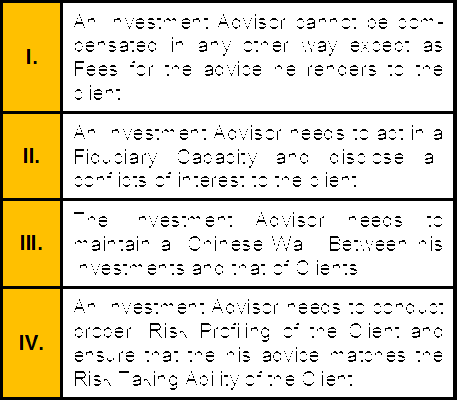
A. I, II and III
B. I, II, and IV
C. I, II, III and IV
D. II, III and IV
Section A (1 Mark)
Comprehensive Wealth Management addresses
A. Life Planning
B. Investment Planning
C. Estate Planning
D. All of the above
Section A (1 Mark)
____________means that people resist inequitable outcomes; i.e., they are willing to give
up some material payoff to move in the direction of more equitable outcomes.
A. In Equity Reversion
B. Money Illusion
C. Escalation of Commitment
D. Hindsight bias
Section A (1 Mark)
In reality, when risk and uncertainty or incomplete information about an alternative or high
degree of complexity is introduced, people or organizations may be have somewhat
different from rationality. This is called ___________.
A. Un Bound Rationality
B. Bounded Rationality
C. Optimization
D. None of the above
Section A (1 Mark)
The steps to establishing an investment policy are to state the
A. Minimum investment and maximum fees.
B. Regulatory guidelines for prudent man investing.
C. Objectives and constraints and preferences.
D. Asset allocation parameters and time horizons.
Section A (1 Mark)
A(n)______________________ loan is a short- or medium-term loan repayable in two or
more consecutive payments, usually monthly or quarterly.
A. Installment
B. Annuity
C. Deferred
D. Residential
Section A (1 Mark)
“Early accumulation” life stage is normally during ______
A. 12- 19 years
B. Our 20s
C. 30-40
D. Retirement years
Section C (4 Mark)
Read the senario and answer to the question.
Raman is considering the purchase of a office building and, as part of his analysis, from the
following given data calculate the appraised value of the property using the Income
Approach?
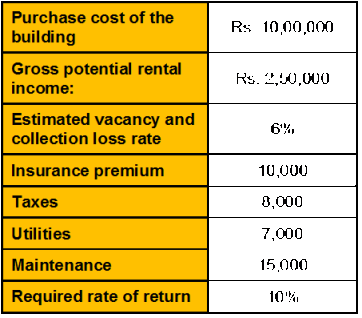
A. Rs. 19,50,000
B. Rs. 19,25,750
C. Rs. 19,15,500
D. Rs. 18,75,500
Section B (2 Mark) Mr. Rai has received a house under a will on death of his uncle in the financial year 1985- 86. His uncle purchased the house on 1-4-1968 for Rs.7 lakh. Mr. Rai has sold this during the financial year 2011-12 for Rs.62 lakh. Calculate the taxable amount of capital gain if the fair market value of house as on 1-4-1981 is Rs.20,00,000/- CII-12-13: 852,11-12: 785,10- 11:711]
A. 4820000
B. 4200000
C. 3600000
D. Nil
Section C (4 Mark)
The assumptions concerning the shape of utility functions of investors differ between
conventional theory and prospect theory. Conventional theory assumes that utility functions
are __________ whereas prospect theory assumes that utility functions are __________.
A. Concave and defined in terms of wealth; s-shaped (convex to losses and concave to gains) and defined in terms of loses relative to current wealth
B. Convex and defined loses relative to current wealth; s-shaped (convex to losses and concave to gains) and defined in terms of loses relative to current wealth
C. S-shaped (convex to losses and concave to gains) and defined in terms of loses relative to current wealth; concave and defined in terms of wealth
D. S-shaped (convex to losses and concave to gains) and defined in terms of wealth; concave and defined in terms of loses relative to current wealth
| Page 16 out of 103 Pages |
| Previous |