What supply chain performance attributes are customer related?
A. Delivery reliability and supply chain management costs
B. Flexibility, delivery reliability, and responsiveness
C. Asset management efficiency and delivery reliability
D. Responsiveness, asset management efficiency, and flexibility
Explanation: According to the ASCM SCOR Digital Standard, supply chain performance attributes are the characteristics that define the performance of a supply chain. There are six performance attributes: reliability, responsiveness, agility, costs, asset management efficiency, and sustainability. Among these, flexibility, delivery reliability, and responsiveness are customer related, as they measure how well the supply chain meets the customer needs and expectations in terms of product availability, delivery time, and order fulfillment1. Flexibility is the ability to accommodate changes in demand or supply, delivery reliability is the ability to deliver products on time and in full, and responsiveness is the ability to react quickly to customer requests or market changes. The other options are not customer related, as they measure the internal efficiency or effectiveness of the supply chain.
A company has completed the responsive supply-demand matching (RDSM) phase of its digital transformation and has created a results tracking dashboard. Which of the following supply chain metrics should be included on this RDSM dashboard?
A. Inventory quality ratio
B. Customer backorder rate
C. Sell-through rate
D. On-time, in-full
Explanation: According to the CTSC Exam Content Manual1, one of the key enablers of digital supply chain transformation is “people and culture”. This includes developing the skills and capabilities of the workforce, aligning the organizational structure and culture with the transformation vision and goals, and fostering a collaborative and innovative environment. Therefore, employee talent development and organizational alignment are critical factors for high performance of digital supply chains, aside from investments in appropriate digital technologies. Option A, C and D are examples of metrics that can be used to measure digital supply chain performance, but they are not factors that enable or enhance it.
Implementing electronic data interchange (EDI) can provide benefit in establishing business relationships with suppliers by:
A. synchronizing.
B. building trust.
C. gainsharing.
D. reducing security risk.
Explanation: According to the CTSC exam content manual1, implementing electronic data interchange (EDI) can provide benefit in establishing business relationships with suppliers by building trust, which is one of the key elements of supplier relationship management. EDI can help to build trust by enabling faster, more accurate, and more secure data exchange, reducing errors and disputes, improving communication and collaboration, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
A supply chain manager wants to reduce waste and labor in their manufacturing process and is looking for a visual way to indicate the need for a component that is linked to consumer demand. Which lean manufacturing tool would be the best option?
A. Kanban
B. Just-in-time (JIT) purchasing
C. Kaizen
D. Theory of constraints (TOC)
Explanation: According to the CTSC Exam Content Manual1, Kanban is a lean manufacturing tool that uses visual signals to indicate the need for a component or material in a production process. Kanban is linked to consumer demand, as it triggers the replenishment of inventory only when there is actual consumption. Kanban helps to reduce waste and labor by minimizing overproduction, inventory, and waiting time. Option B, JIT purchasing, is a related concept that involves buying materials or components just before they are needed in the production process, but it does not necessarily use visual signals. Option C, Kaizen, is a lean manufacturing tool that involves continuous improvement of processes and activities, but it is not specific to reducing waste and labor in the manufacturing process. Option D, TOC, is a management philosophy that focuses on identifying and eliminating the constraints or bottlenecks that limit the performance of a system, but it does not use visual signals to indicate the need for a component.
Which of the following statements is an example of an external motivator for executing a supply chain transformation?
A. Employee turnover is expected to increase substantially over the next 3-5 years.
B. A national customer wants the company to sell to its international subsidiaries.
C. Forecasts show the current market expanding 25% over the next 2-3 years.
D. Suppliers will need to decrease their lead times by 50% over 18 months.
Explanation: An external motivator for executing a supply chain transformation is a factor that originates outside the organization and influences its decision to change its supply chain strategy, processes, or capabilities. Examples of external motivators include customer demands, market opportunities, competitive pressures, regulatory requirements, and environmental concerns1. In this case, the national customer’s request to sell to its international subsidiaries is an external motivator because it comes from a key stakeholder in the supply chain and requires the company to adapt to new markets, regulations, and logistics.
Which of the following performance measures describes the organization's ability to quickly adapt its strategic transformation response to demand and/or supply shocks?
A. The number of full-time employees needed to meet current demand
B. The sustained percentage increase in manufacturing and/or service orders
C. The number of days needed to meet a 25% unplanned change in demand
D. The amount of internal and external capacity needed for current demand throughput
Explanation: According to the CTSC Exam Content Manual, process harmonization is the degree to which an organization’s processes are standardized and aligned across its business units1.Documenting supply chain processes and maintaining updated documentation are used to achieve process harmonization, as they help to ensure consistency, transparency, and compliance of the processes across the organization2.Documenting supply chain processes also facilitates the identification of best practices, gaps, and improvement opportunities for the processes2.
What is the purpose of using value at risk (VAR) in supply chain risk management?
A. To establish a common language to quantify supply chain risk in terms of currency
B. To prioritize supply chain risks based on their likelihood of occurrence
C. To assess the financial impacts of supply chain risks
D. To measure the effectiveness of supply chain mitigation efforts
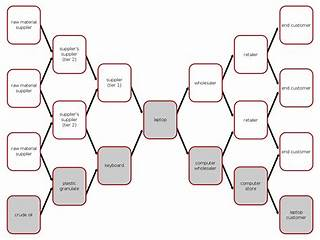
What is the process view of the geographic map that illustrates the material flow, material strategy, and the planning process relationship?
A. Value stream
B. Material flow analysis
C. Process map
D. Thread diagram
Explanation: According to the CTSC Enterprise and Supply Chain Management (ESCM) manual, a thread diagram is a process view of the geographic map that illustrates the material flow, material strategy, and the planning process relationship1.A thread diagram shows the sequence of activities and decisions that are involved in transforming raw materials into finished products and delivering them to customers1.It also shows the locations of the facilities, the transportation modes, the inventory policies, and the planning horizons1.A thread diagram helps to identify the key drivers and constraints of the supply chain performance, and to evaluate the trade-offs and synergies among different supply chain components1.
The most prominent characteristic of a digital supply chain is:
A. orientation towards perfect order fulfillment.
B. focus on demand simulation while managing costs.
C. optimal lot-sizing during replenishment.
D. access to latest point-of-sale (POS) data across the network.
Explanation: one of the most prominent characteristics of a digital supply chain is the access to latest point-of-sale (POS) data across the network.POS data refers to the information collected by retailers at the point of purchase, such as the product, quantity, price, date, time, and location of the transaction3.Access to this data enables digital supply chains to have realtime visibility of customer demand, inventory levels, and market trends, and to use advanced analytics and artificial intelligence to optimize planning, forecasting, replenishment, and delivery12.Access to POS data also helps digital supply chains to improve customer satisfaction, reduce costs, increase sales, and enhance collaboration among supply chain partners12.
A customer is purchasing a new cell phone, and the sales representative convinces the customer to buy a case to protect the phone. The customer representative has engaged in:
A. cross-selling.
B. suggestive selling.
C. ad-hoc selling.
D. up-selling.
Explanation: cross-selling is the practice of offering customers additional items that complement or enhance their main purchase12. In this case, the sales representative has engaged in cross-selling by offering the customer a case to protect the phone, which is a related and useful product for the customer’s main purchase of a new cell phone. Cross selling can help to increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue12.
The main objective of the ASCM Digital Capabilities Model (DCM) is to:
A. transform linear supply chains into a set of static networks.
B. prioritize areas that drive the lowest value in the supply network.
C. guide the development of digital supply networks.
D. help organizations understand their existing digitally-enabled capabilities.
A key component of a total quality management (TQM) program is:
A. statistical process control (SPC).
B. just-in-time (JIT) inventory.
C. autonomous maintenance.
D. supply chain optimization (SCO).
Explanation: According to the CTSC Exam Content Manual1, statistical process control (SPC) is a key component of a total quality management (TQM) program. SPC is a technique that uses statistical methods and tools to monitor and control the variation and performance of a process. SPC helps to ensure that the process is stable, capable, and predictable, and that the output meets the customer specifications and expectations. SPC also helps to identify and eliminate the causes of defects and errors, and to improve the quality and efficiency of the process. Option B, JIT inventory, is a component of lean manufacturing, not TQM. JIT inventory aims to reduce inventory levels and costs by delivering materials or components just before they are needed in the production process. Option C, autonomous maintenance, is a component of total productive maintenance (TPM), not TQM. Autonomous maintenance involves empowering the operators to perform basic maintenance tasks on their own equipment, such as cleaning, lubricating, inspecting, and adjusting. Option D, SCO, is a component of supply chain management, not TQM. SCO involves optimizing the flow of materials, information, and money across the supply chain network, from the suppliers to the customers.
| Page 3 out of 13 Pages |
| Previous |