Topic 2: Volume B
What are the security advantages of virtualization, as described in the NIST Information Security and Privacy Advisory Board (ISPAB) paper "Perspectives on Cloud Computing and Standards"? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose three.
A.
It increases capabilities for fault tolerant computing.
B.
It adds a layer of security for defense-in-depth.
C.
It decreases exposure of weak software.
D.
It decreases configuration effort.
It increases capabilities for fault tolerant computing.
It adds a layer of security for defense-in-depth.
It decreases exposure of weak software.
Explanation: The security advantages of virtualization are as follows: It adds a layer of security for defense-in-depth. It provides strong encapsulation of errors. It increases intrusion detection through introspection. It decreases exposure of weak software. It increases the flexibility for discovery. It increases capabilities for fault tolerant computing using rollback and snapshot features. Answer: D is incorrect. Virtualization increases configuration effort because of complexity of the virtualization layer and composite system.
Mark works as a Network Administrator for NetTech Inc. The company has a Windows 2000 domain-based network. Users report that they are unable to log on to the network. Mark finds that accounts are locked out due to multiple incorrect log on attempts. What is the most likely cause of the account lockouts?
A.
Spoofing
B.
Brute force attack
C.
SYN attack
D.
PING attack
Brute force attack
Explanation: Brute force attack is the most likely cause of the account lockouts. In a brute force attack, unauthorized users attempt to log on to a network or a computer by using multiple possible user names and passwords. Windows 2000 and other network operating systems have a security feature that locks a user account if the number of failed logon attempts occur within a specified period of time, based on the security policy lockout settings. Answer: A is incorrect. Spoofing is a technique that makes a transmission appear to have come from an authentic source by forging the IP address, email address, caller ID, etc. In IP spoofing, a hacker modifies packet headers by using someone else's IP address to hide his identity. However, spoofing cannot be used while surfing the Internet, chatting on-line, etc. because forging the source IP address causes the responses to be misdirected. Answer: C is incorrect. A SYN attack affects computers running on the TCP/IP protocol. It is a protocol-level attack that can render a computer's network services unavailable. A SYN attack is also known as SYN flooding. Answer: D is incorrect. When a computer repeatedly sends ICMP echo requests to another computer, it is known as a PING attack.
Drag and drop the appropriate external constructs in front of their respective functions.
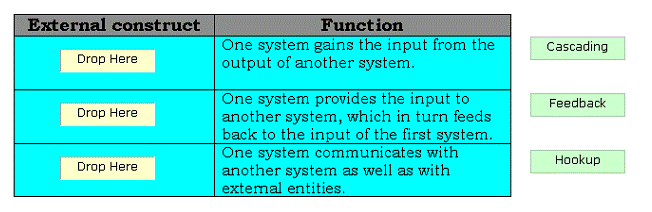
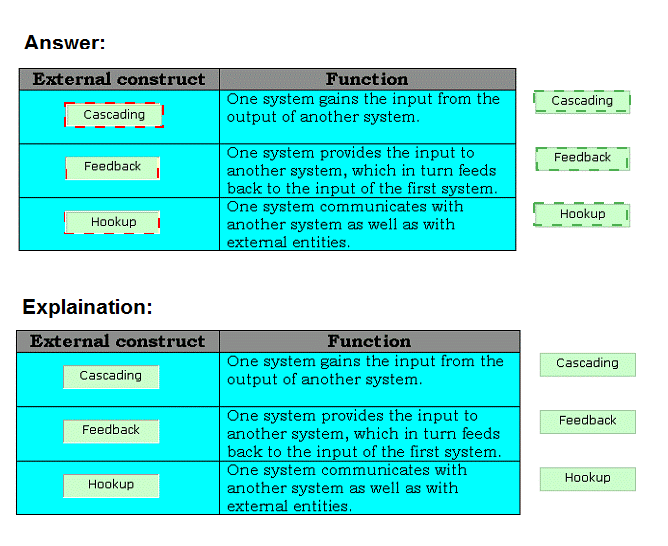
There are two types of compositional constructs: 1.External constructs: The various types of external constructs are as follows: Cascading: In this type of external construct, one system gains the input from the output of another system. Feedback: In this type of external construct, one system provides the input to another system, which in turn feeds back to the input of the first system. Hookup: In this type of external construct, one system communicates with another system as well as with external entities. 2.Internal constructs: The internal constructs include intersection, union, and difference.
Which of the following plans is designed to protect critical business processes from natural or man-made failures or disasters and the resultant loss of capital due to the unavailability of normal business processes?
A.
Contingency plan
B.
Business continuity plan
C.
Crisis communication plan
D.
Disaster recovery plan
Business continuity plan
Explanation: The business continuity plan is designed to protect critical business processes from natural or man-made failures or disasters and the resultant loss of capital due to the unavailability of normal business processes. Business Continuity Planning (BCP) is the creation and validation of a practiced logistical plan for how an organization will recover and restore partially or completely interrupted critical (urgent) functions within a predetermined time after a disaster or extended disruption. The logistical plan is called a business continuity plan. Answer: C is incorrect. The crisis communication plan can be broadly defined as the plan for the exchange of information before, during, or after a crisis event. It is considered as a sub-specialty of the public relations profession that is designed to protect and defend an individual, company, or organization facing a public challenge to its reputation. The aim of crisis communication plan is to assist organizations to achieve continuity of critical business processes and information flows under crisis, disaster or event driven circumstances. Answer: A is incorrect. A contingency plan is a plan devised for a specific situation when things could go wrong. Contingency plans are often devised by governments or businesses who want to be prepared for anything that could happen. Contingency plans include specific strategies and actions to deal with specific variances to assumptions resulting in a particular problem, emergency, or state of affairs. They also include a monitoring process and "triggers" for initiating planned actions. They are required to help governments, businesses, or individuals to recover from serious incidents in the minimum time with minimum cost and disruption. Answer: D is incorrect. A disaster recovery plan should contain data, hardware, and software that can be critical for a business. It should also include the plan for sudden loss such as hard disc crash. The business should use backup and data recovery utilities to limit the loss of data
Which of the following processes provides a standard set of activities, general tasks, and a management structure to certify and accredit systems, which maintain the information assurance and the security posture of a system or site?
A.
NSA-IAM
B.
NIACAP
C.
ASSET
D.
DITSCAP
NIACAP
Explanation: NIACAP is a process, which provides a standard set of activities, general tasks, and a management structure to certify and accredit systems that maintain the information assurance and the security posture of a system or site. Answer: D is incorrect. DITSCAP is a process, which establishes a standard process, a set of activities, general task descriptions, and a management structure to certify and accredit the IT systems that will maintain the required security posture. Answer: A is incorrect. The NSA-IAM evaluates information systems at a high level and uses a subset of the SSE-CMM process areas to measure the implementation of information security on these systems. Answer: C is incorrect. ASSET is a tool developed by NIST to automate the process of self-assessment through the use of the questionnaire in NIST.
Which of the following specifies access privileges to a collection of resources by using the URL mapping?
A.
Code Access Security
B.
Security constraint
C.
Configuration Management
D.
Access Management
Security constraint
Explanation: Security constraint is a type of declarative security, which specifies the protection of web content. It also specifies access privileges to a collection of resources by using the URL mapping. A deployment descriptor is used to define the security constraint. Security constraint includes the following elements: Web resource collection Authorization constraint User data constraint Answer: A is incorrect. Code Access Security (CAS), in the Microsoft .NET framework, is Microsoft's solution to prevent untrusted code from performing privileged actions. When the CLR (common language runtime) loads an assembly it will obtain evidence for the assembly and use this to identify the code group that the assembly belongs to. A code group contains a permission set (one or more permissions). Code that performs a privileged action will perform a code access demand, which will cause the CLR to walk up the call stack and examine the permission set granted to the assembly of each method in the call stack. The code groups and permission sets are determined by the administrator of the machine who defines the security policy. Answer: D is incorrect. Access Management is used to grant authorized users the right to use a service, while preventing access to non- authorized users. The Access Management process essentially executes policies defined in IT Security Management. It is sometimes also referred to as Rights Management or Identity Management. It is part of Service Operation and the owner of Access Management is the Access Manager. Access Management is added as a new process to ITIL V3. The sub-processes of Access Management are as follows: Maintain Catalogue of User Roles and Access Profiles Manage User Access Requests Answer: C is incorrect. Configuration Management (CM) is an Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) IT Service Management (ITSM) process. It tracks all of the individual Configuration Items (CI) in an IT system, which may be as simple as a single server, or as complex as the entire IT department. In large organizations a configuration manager may be appointed to oversee and manage the CM process.
Which of the following agencies is responsible for funding the development of many technologies such as computer networking, as well as NLS?
A.
DIAP
B.
DTIC
C.
DARPA
D.
DISA
DARPA
Explanation: The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is an agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of new technology for use by the military. DARPA has been responsible for funding the development of many technologies which have had a major effect on the world, including computer networking, as well as NLS, which was both the first hypertext system, and an important precursor to the contemporary ubiquitous graphical user interface. DARPA supplies technological options for the entire Department, and is designed to be the "technological engine" for transforming DoD. Answer: D is incorrect. The Defense Information Systems Agency is a United States Department of Defense combat support agency with the goal of providing real-time information technology (IT) and communications support to the President, Vice President, Secretary of Defense, the military Services, and the Combatant Commands. DISA, a Combat Support Agency, engineers and provides command and control capabilities and enterprise infrastructure to continuously operate and assure a global net-centric enterprise in direct support to joint warfighters, National level leaders, and other mission and coalition partners across the full spectrum of operations. Answer: B is incorrect. The Defense Technical Information Center (DTIC) is a repository of scientific and technical documents for the United States Department of Defense. DTIC serves the DoD community as the largest central resource for DoD and government-funded scientific, technical, engineering, and business related information available today. DTIC's documents are available to DoD personnel and defense contractors, with unclassified documents also available to the public. DTIC's aim is to serve a vital link in the transfer of information among DoD personnel, DoD contractors, and potential contractors and other U.S. Government agency personnel and their contractors. Answer: A is incorrect. The Defense-wide Information Assurance Program (DIAP) protects and supports DoD information, information systems, and information networks, which is important to the Department and the armed forces throughout the day-to-day operations, and in the time of crisis. The DIAP uses the OSD method to plan, observe, organize, and incorporate IA activities. The role of DIAP is to act as a facilitator for program execution by the combatant commanders, Military Services, and Defense Agencies. The DIAP staff combines functional and programmatic skills for a comprehensive Defense-wide approach to IA. The DIAP's main objective is to ensure that the DoD's vital information resources are secured and protected by incorporating IA activities to get a secure net-centric GIG operation enablement and information supremacy by applying a Defense-in-Depth methodology that integrates the capabilities of people, operations, and technology to establish a multi-layer, multidimensional protection.
In which of the following architecture styles does a device receive input from connectors and generate transformed outputs?
A.
N-tiered
B.
Heterogeneous
C.
Pipes and filters
D.
Layered
Pipes and filters
Explanation: In the pipes and filters architecture style, a device receives input from connectors and generates transformed outputs. A pipeline has a series of processing elements in which the output of each element works as an input of the next element. A little amount of buffering is provided between the two successive elements.
Which of the following is used by attackers to record everything a person types, including usernames, passwords, and account information?
A.
Packet sniffing
B.
Keystroke logging
C.
Spoofing
D.
Wiretapping
Keystroke logging
Explanation: Keystroke logging is used by attackers to record everything a person types, including usernames, passwords, and account information. Keystroke logging is a method of logging and recording user keystrokes. It can be performed with software or hardware devices. Keystroke logging devices can record everything a person types using his keyboard, such as to measure employee's productivity on certain clerical tasks. These types of devices can also be used to get usernames, passwords, etc. Answer: D is incorrect. Wiretapping is used to eavesdrop on voice calls. Eavesdropping is the process of listening in on private conversations. It also includes attackers listening in on network traffic. Answer: C is incorrect. Spoofing is a technique that makes a transmission appear to have come from an authentic source by forging the IP address, email address, caller ID, etc. In IP spoofing, a hacker modifies packet headers by using someone else's IP address to hide his identity. However, spoofing cannot be used while surfing the Internet, chatting on-line, etc. because forging the source IP address causes the responses to be misdirected. Answer: A is incorrect. Packet sniffing is a process of monitoring data packets that travel across a network. The software used for packet sniffing is known as sniffers. There are many packet-sniffing programs that are available on the Internet. Some of these are unauthorized, which can be harmful for a network's security.
Which of the following federal agencies has the objective to develop and promote measurement, standards, and technology to enhance productivity, facilitate trade, and improve the quality of life?
A.
National Security Agency (NSA)
B.
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
C.
United States Congress
D.
Committee on National Security Systems (CNSS)
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
Explanation: The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), known between 1901 and 1988 as the National Bureau of Standards (NBS), is a measurement standards laboratory which is a non-regulatory agency of the United States Department of Commerce. The institute's official mission is to promote U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology in ways that enhance economic security and improve quality of life. Answer: D is incorrect. The Committee on National Security Systems (CNSS) is a United States intergovernmental organization that sets policy for the security of the US security systems. The CNSS holds discussions of policy issues, sets national policy, directions, operational procedures, and guidance for the information systems operated by the U.S. Government, its contractors, or agents that contain classified information, involve intelligence activities, involve cryptographic activities related to national security, etc. Answer: A is incorrect. The National Security Agency/Central Security Service (NSA/CSS) is a crypto-logic intelligence agency of the United States government. It is administered as part of the United States Department of Defense. NSA is responsible for the collection and analysis of foreign communications and foreign signals intelligence, which involves cryptanalysis. NSA is also responsible for protecting U.S. government communications and information systems from similar agencies elsewhere, which involves cryptography. NSA is a key component of the U.S. Intelligence Community, which is headed by the Director of National Intelligence. The Central Security Service is a co-located agency created to coordinate intelligence activities and co-operation between NSA and U.S. military cryptanalysis agencies. NSA's work is limited to communications intelligence. It does not perform field or human intelligence activities. Answer: C is incorrect. The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States of America. It consists of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. Both senators and representatives are chosen through direct election. Each of the 435 members of the House of Representatives represents a district and serves a two-year term. House seats are apportioned among the states by population. The 100 Senators serve staggered six-year terms. Each state has two senators, regardless of population. Every two years, approximately one-third of the Senate is elected at a time. The United States Congress main function is to make laws. The Office of the Law Revision Counsel organizes and publishes the United States Code (USC). It is a consolidation and codification by subject matter of the general and permanent laws of the United States.
Which of the following policies can explain how the company interacts with partners, the company's goals and mission, and a general reporting structure in different situations?
A.
Informative
B.
Advisory
C.
Selective
D.
Regulatory
Informative
Explanation: An informative policy informs employees about certain topics. It is not an enforceable policy, but rather one to teach individuals about specific issues relevant to the company. The informative policy can explain how the company interacts with partners, the company's goals and mission, and a general reporting structure in different situations. Answer: D is incorrect. A regulatory policy ensures that an organization follows the standards set by specific industry regulations. This type of policy is very detailed and specific to a type of industry. The regulatory policy is used in financial institutions, health care facilities, public utilities, and other government-regulated industries, e.g., TRAI. Answer: B is incorrect. An advisory policy strongly advises employees regarding which types of behaviors and activities should and should not take place within the organization. It also outlines possible ramifications if employees do not comply with the established behaviors and activities. The advisory policy can be used to describe how to handle medical information, handle financial transactions, and process confidential information. Answer: C is incorrect. It is not a valid type of policy.
Which of the following SDLC phases consists of the given security controls: Misuse Case Modeling Security Design and Architecture Review Threat and Risk Modeling Security Requirements and Test Cases Generation?
A.
Deployment
B.
Requirements Gathering
C.
Maintenance
D.
Design
Design
Explanation: The various security controls in the SDLC design phase are as follows: Misuse Case Modeling: It is important that the inverse of the misuse cases be modeled to understand and address the security aspects of the software. The requirements traceability matrix can be used to track the misuse cases to the functionality of the software. Security Design and Architecture Review: This control can be introduced when the teams are engaged in the "functional" design and architecture review of the software. Threat and Risk Modeling: Threat modeling determines the attack surface of the software by examining its functionality for trust boundaries, data flow, entry points, and exit points. Risk modeling is performed by ranking the threats as they pertain to the users organization's business objectives, compliance and regulatory requirements and security exposures. Security Requirements and Test Cases Generation: All the above three security controls, i.e., Misuse Case Modeling, Security Design and Architecture Review, and Threat and Risk Modeling are used to produce the security requirements.
| Page 11 out of 29 Pages |
| Previous |