Topic 6: Misc. Questions
A. Storage Blob Data Contributor
B. Reader
C. Storage Blob Data Reader
D. Contributor
E. Storage Account Contributor

A. a frontend IP address
B. a backend pool
C. a health probe
D. an inbound NAT rule
E. a virtual network
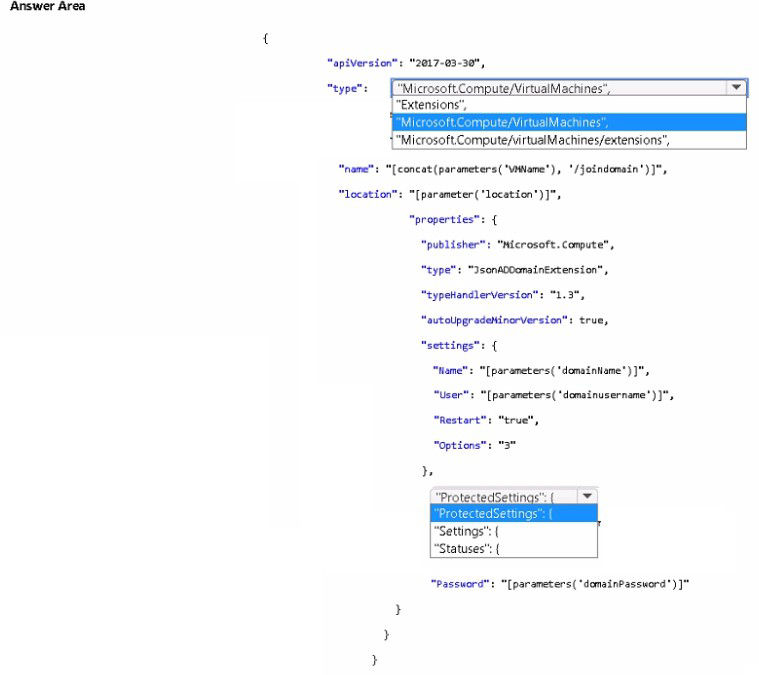
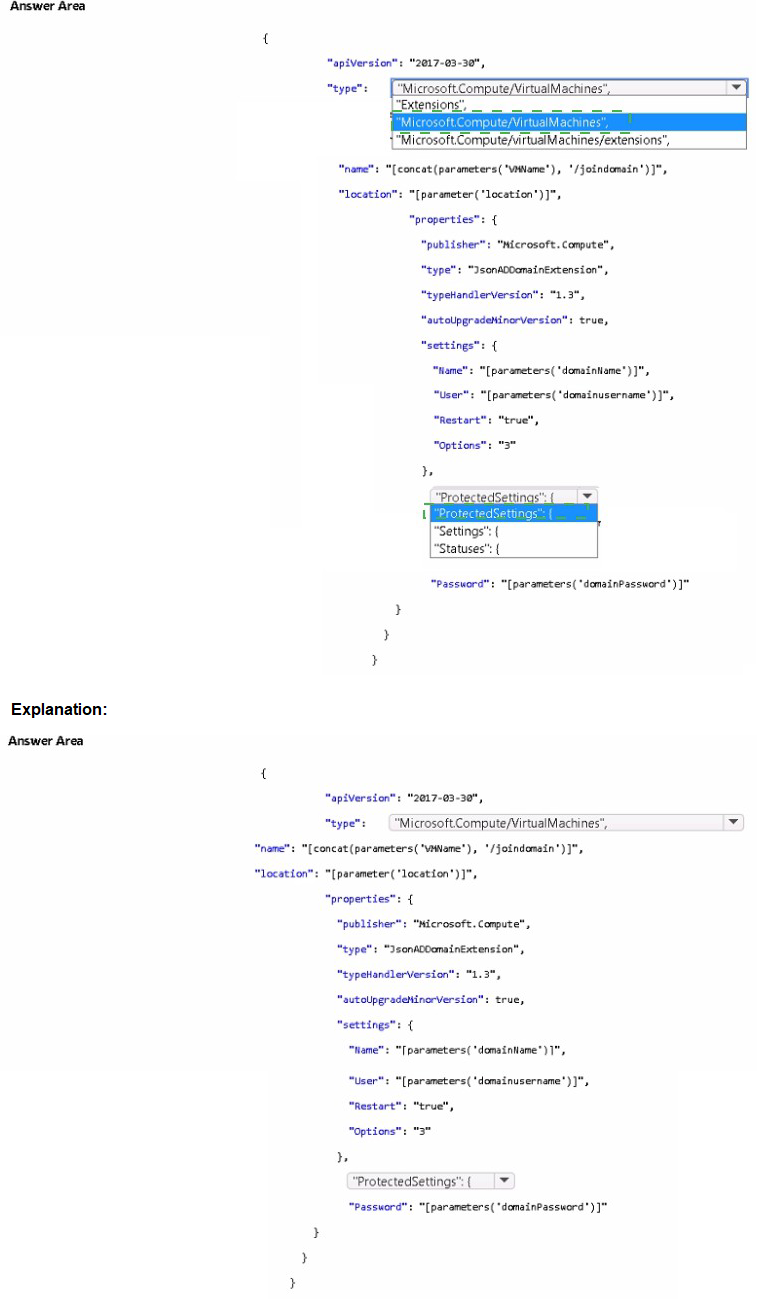
A. Add two load balancing rules that have HA Ports enabled and Floating IP disabled.
B. Deploy a basic load balancer.
C. Add a frontend IP configuration, a backend pool, and a health probe.
D. Add two load balancing rules that have HA Ports and Floating IP enabled.
E. Deploy a standard load balancer.
F. Add a frontend IP configuration, two backend pools, and a health probe.
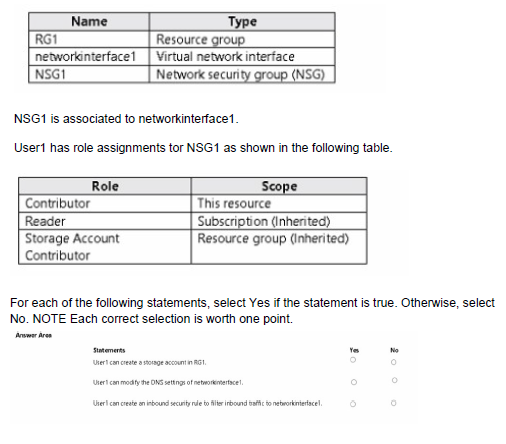
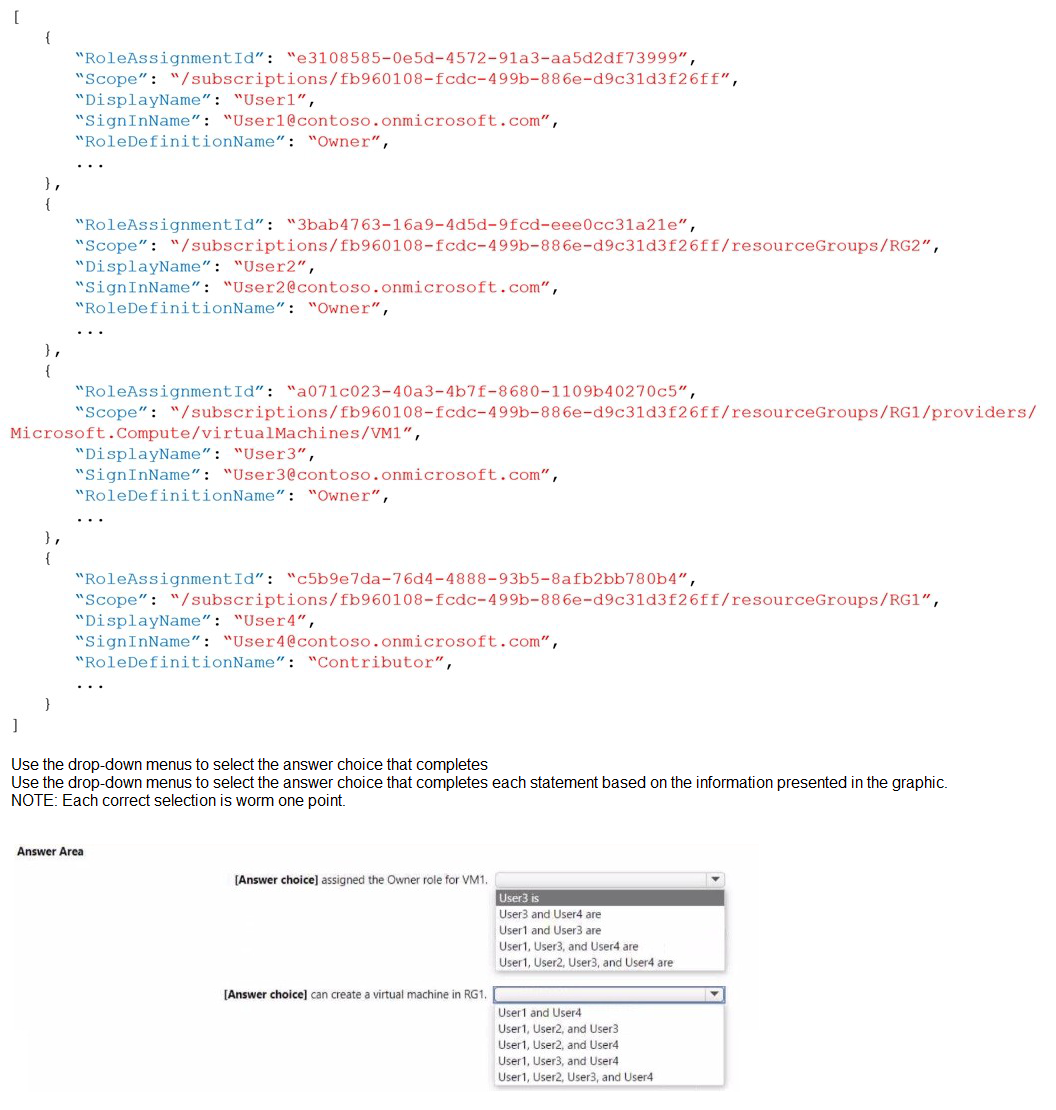
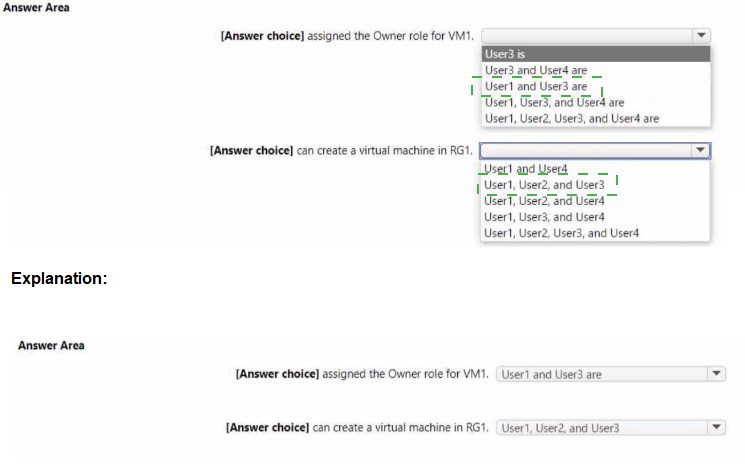
You have the role assignment file shown in the following exhibit.
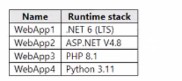
You plan to create the Azure web apps shown in the following Table.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4


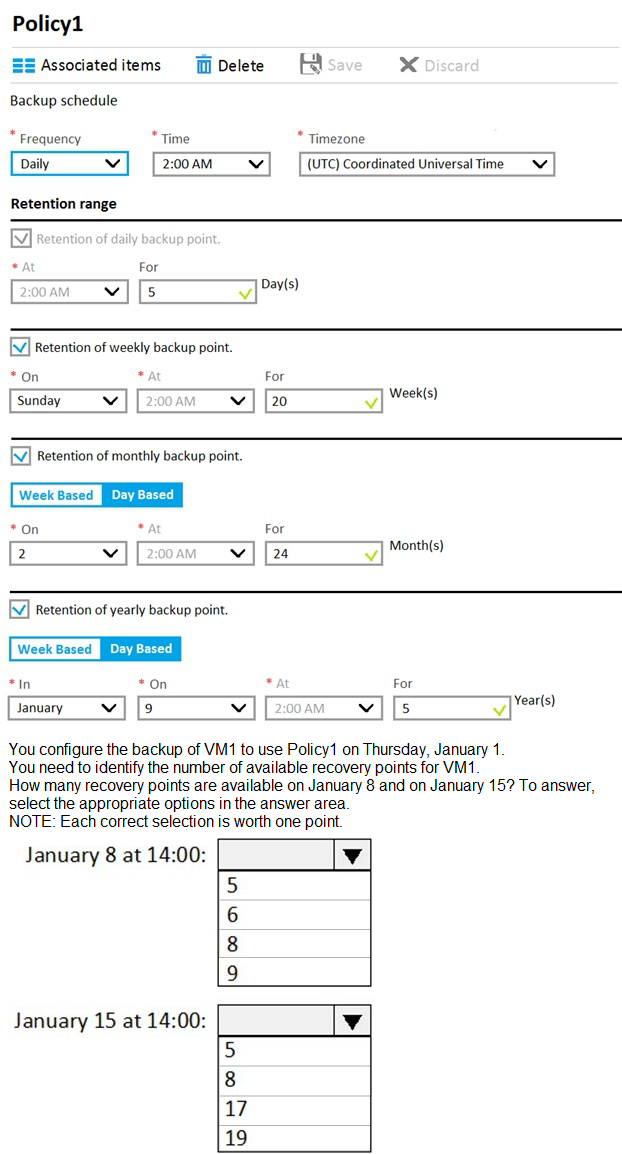
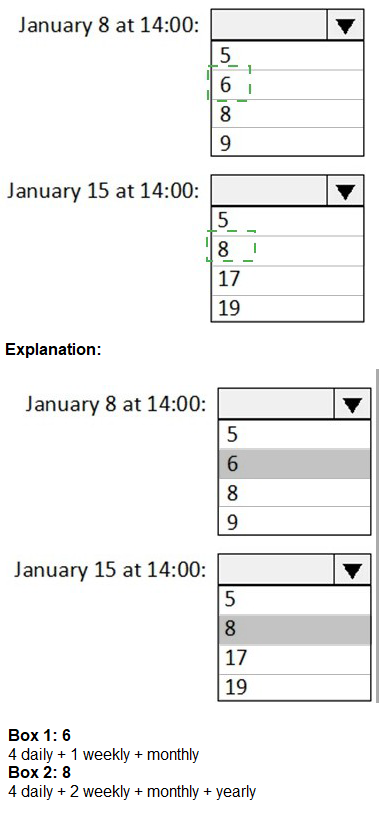
You have an Azure policy as shown in the following exhibit.
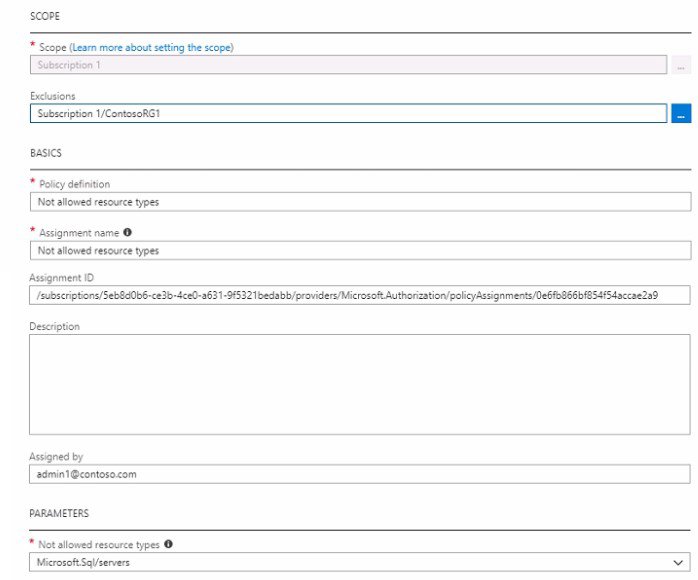
A. You are prevented from creating Azure SQL servers anywhere in Subscnption1.
B. You can create Azure SQL servers in ContosoRG1 only.
C. You can create Azure SQL servers in any resource group within Subscnption1.
D. You are prevented from creating Azure SQL Servers in ContosoRG1 only.
A. Yes
B. No
A. Diagnostic settings for VM1
B. Insights for VM1
C. NSG flow logs for NSG1
D. Diagnostic settings for NSG1
| Page 14 out of 38 Pages |
| Previous |