Confirmed cases of H1N1 virus have been reported more often in children and younger
adults than in any other age group.
Micro
The age groups that have been most affected by the H1N1 virus are children and younger
adults.
A. true
B. false
One agency that accredits education programs for clinical laboratory personnel is the:
A. North Central Association (NCA)
B. American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science (ASCLS)
C. National Accrediting Agency for Clinical Laboratory Sciences (NAACLS)
D. American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP)
Donor and recipient blood samples (samples utilized for pre-transfusion compatibility testing) must be kept for at least 7 days after transfusion. Blood samples must be available to investigate a transfusion reaction, if necessary. Donor and recipient blood samples must be kept for at least how long after transfusion?
A. 10 days
B. 7 days
C. 3 days
D. Not a requirement
Refrigerated temperatures, those close to 4 ºC, are recommended for the preservation of enzyme activity in a patient sample.
Chemistry
The recommended storage temperature for the preservation of activity for MOST enzymes
is:
A. 0 ºC
B. 4 ºC
C. 25 ºC
D. 37 ºC
The clue to the identification of the colony seen in the upper frame is the gram stain in the
lower frame, in which are seen short, rounded, gram positive bacilli, many of which
possess distinct spores. As the colonies grew aerobically, the presence of spores indicates
Bacillus species. The colonies are spreading, smooth, yellow-white and non-hemolytic. The
lack of hemolysis and the small size of the bacterial cells suggests a species other than
Bacillus cereus, the species causing most human infections. The isolate was identified as
Bacillus circulans, which is consistent with the gram stain morphology. Clostridium
septicum also produces spores; however, this species is an anaerobe and would grow
poorly if at all and not produce spores aerobically. Listeria monocytogenes and
Lactobacillus species are gram positive bacilli; however, neither of these produce spores.
The colonies seen in the upper frame, grown after 48 hours incubation aerobically at 35°C,
and the accompanying gram stain in the lower frame are uncommonly associated with
human disease, but have been associated with septicemia, bronchopneumonia,
osteomyelitis and other infections, particularly in intravenous drug users. The most likely
identification is:
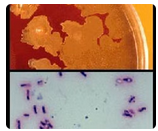
A. Clostridium septicum
B. Bacillus circulans
C. Listeria monocytogenes
D. Lactobacillus species
"Universal donor", (a misnomer) is usually applied to group O, Rh negative blood. Although it may be necessary to use group O, Rh negative blood in an extreme emergency, it is preferable to use type specific blood for emergencies. In an extreme emergency , if the ABO and Rh type are unknown which of the following should be given to the patient?
A. Group O, Rh positive blood
B. Group AB, Rh negative blood
C. Group O, Rh negative blood
D. Any blood type is OK
hs-CRP is a recent marker of chronic inflammation. New measurements of CRP in lower levels (hs-CRP) are now measured to monitor risk of cardiovascular disease. Select the statement that best describes hs-CRP?
A. hs-CRP is a measurement of acute inflammation and is used to monitor these conditions
B. hs-CRP is an anti-inflammatory adipokine synthesized by adipocytes
C. hs-CRP is a marker of chronic inflammation and measured to predict the risk of cardiovascular disease
D. hs-CRP is decreased in inflammatory conditions and measured to predict a return of inflammation
Measures Light scatter by particles - Nephelometer
Measures change in vapor pressure - Osmometer
Measures amount of electricity passing between two electrodes - Coulometry
Measures absorbance of light at a specific wavelength - Spectrophotometer
Lab operations
Matching
1. Measures Light scatter by particles
2. Measures change in vapor pressure
3. Measures amount of electricity passing between two electrodes
4. Measures absorbance of light at a specific wavelength
A. Coulometry
B. Nephelometer
C. Spectrophotometer
D. Osmometer
Unconjugated bilirubin is a byproduct of RBC breakdown, or hemolysis. It would be
expected to see an increase in unconjugated bilirubin when hemolysis is occuring at an
increased rate. The liver enzymes would not remain at normal levels if there were a viral
infection of the liver, chemical damage to the liver, or obstruction of bile ducts.
Chemistry
A patient presents with an elevation of unconjugated bilirubin, normal serum alkaline
phosphatase, normal liver enzymes, and no bilirubin in the urine. This combination would
suggest:
A. Viral infection of the liver.
B. Chemical damage to the liver.
C. Increased rate of hemolysis
D. Obstruction of common bile duct
HLA-DR is a class II MHC.
HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C are all class I MHC.
Which of the following antigens is classified as a Major Histocompatibility Complex
Class II antigen (MHCII)?
A. HLA-A
B. HLA-B
C. HLA-C
D. HLA-DR
Rapid vascular constriction, not dilation, immediately occurs when there is vascular injury in
order to constrict the amount of blood that escapes the vessels; ultimately preventing
massive loss of blood.
Primary hemostatic processes resulting from vascular damage include all of the following
EXCEPT:
A. collagen activates glycoprotein IIb/IIIa during platelet activation
B. von Willebrand factor mediates platelet adhesion
C. platelet granule release and fibrinogen mediate platelet aggregation
D. rapid and immediate vascular dilation occurs
E. b & c
Francisella is slow growing on primary isolation culture media and produces poorly-staining coccobacilli on Gram stain. Because Francisella tularensis is included on the list of bioterrorism agents, suspicious isolates should be referred immediately to a public health laboratory in lieu of attempting an in-laboratory identification. One of the BIGGEST problems with isolating Francisella is that these organisms:
A. produce wide zones of hemolysis
B. grow so slowly
C. overgrow other organisms
D. produce greenish colonies like E. coli
| Page 6 out of 47 Pages |
| Previous |