Monoclonal antibodies are monospecific antibodies that are the same because they are made by one type of immune cell which are all clones of a unique parent cell, also called a hybrid cell line, which usually arise from a hybridoma. The fusion of a specific antibodyproducing lymphocyte with a myeloma cell will multiply to become a source of pure monoclonal antibody. This is often used in the manufacturing process for monoclonal antibody reagents. Monoclonal antibodies are usually manufactured in vitro by using:
A. Cultured T cells
B. Human plasma cells
C. Hybridomas
D. Cytotoxic T cell
First, the RBC indices must be calculated. The MCV ((Hct/RBC) x 10) = 71 fL. Since the
reference range for the MCV is 80-100 fL, this anemia would be classified as microcytic.
The MCH ((Hgb/RBC) x 10) = 19.3 pg. Since the reference range for the MCH is 27-33 pg,
this would be considered hypochromic. Finally, the MCHC ((Hgb/Hct) X 100) = 27%. Since
the normal range for the MCHC is 33%-36%, this would indicate hypochromia which
correlates with the MCH findings. The correct answer is therefore microcytic, hypochromic
anemia.
A patient is admitted to the emergency room with lethargy and pallor. The CBC results are
as follows:
RBC = 4.1 x 1012/L
Hemoglobin = 7.9 g/cL
Hematocrit = 29%
How would you classify this anemia?
A. microcytic, hypochromic
B. normocytic, normochromic
C. macrocytic, normochromic
D. microcytic, hyperchromic
Provide the equivalent measurement for 1 decimeter
A. 1 microgram
B. 100 microns
C. 100 millimeters
D. 5 millimeters
Caffeine benzoate solution is used to split the unconjugated bilirubin protein complex releasing the bilirubin so that it can react with diazotised sulphanilic acid. The tartrate buffer creates an alkaline solution and converts the red acid bilirubin to a green coloured compound which can be measured spectrophotometrically. Which substance is used in the Jendrassik-Grof method to accelerate the reaction of unconjugated bilirubin with the diazo reagent?
A. NADH
B. N-butanol
C. caffeine
D. acetic acid
Which of these advancements in the clinical laboratory has led to concerns about patient privacy
A. high test volumes
B. staffing with several levels of lab professionals
C. computers
D. automated analyzers
Calculation:
Cells Counted (in this case the average of both sides) X dilution factor (in this case 100) / #
of squares counted (in this case 9) X area of each square (1mm2) X 0.1mm (depth factor)
So, in this problem:
158 x 100 / 9 x 1 x 0.1mm = 17555.55/mm3 (can be converted to 17.5 x 109/L*)
*There are 1,000,000 mm3 in a liter (L). So 17555.55 X 1,000,000 = 17.5 x 109/L
A manual white blood cell count was performed by the hematology technologist. The cell
counts for both sides were 152 and 164 respectively. All nine large squares were counted
on each side. The dilution for this kit was pre-measured at 1:100. What should the
technologist report as the white cell count?
A. 177.5 x 10^9/L
B. 17.5 x 10^9/L
C. 1.75 x 10^9/L
D. 175 x 10^9/L
Antibodies in the Rh system typically exhibit which one of the following characteristics?
A. Reacts best at 37ºC and AHG
B. Reacts best at room temperature
C. Shows hemolysis better than agglutination
The correct answer which best fits the characteristics in this question is Mycobacterium
kansasii.
The remaining Mycobacterium strains can be elimated as:
Mycobacterium marinum is considered a fast-grower.
Mycobacterium scrofulaceum produce deep-yellow to orange pigmented colonies when
grown in the either the light or dark.
Mycobacterium avium grows colonies which are nonpigmented in the light and dark which
do not intensify after light exposure.
What is the MOST likely identification of an acid-fast bacillus that demonstrates the
following characteristics?
Slow growth cream to tan colored colonies when grown in the dark
development of yellow pigment upon exposure to light.
A. Mycobacterium kansasii
B. Mycobacterium marinum
C. Mycobacterium avium
D. Mycobacterium scrofulaceum
Allergen-specific IgE, synthesized in response to allergens, becomes fixed to receptors on
cellular membranes, especially those of basophils. If these receptor-bound IgE molecules
are aggregated on re-exposure to specific allergen, both mast cells and basophils produce
mediators that result in the allergic response. IgE-antigen interaction at the cell surface
causes degranulation of cells and release of substances including: histamine, SRS-A,
platelet activator, a kallikrein, and an eosinophil chemotactic factor. Basophils are the
principal cells that bind IgE antibody while their number of receptor sites is proportional to
serum IgE levels. Eosinophils are drawn to the site by the basophil chemotaxis mechanism,
but are not the main cell which binds the IgE antibody.
Immunology
The mediator cells that bind MOST to IgE antibodies are:
A. Basophils
B. Eosinophils
C. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils
D. Macrophages
Micro - Matching
1. Upper left image
Multi-celled, rough walled macroconidia with a tapered terminal cell
2. Upper right image
Dense aggregates of echinulate, brown-black conidia
3. Lower left image
Loose clusters of elliptical conidia arranged in a "diphtheroid" pattern
4. Lower right image
Chains of large, lemon-shaped annelloconidia
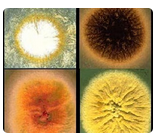
A. Aspergillus niger
B. Microsporum canis
C. Scopulariopsis species
D. Acremonium species
In DIC, or disseminated intravascular coagulation, the prothrombin time is increased due to
the consumption of the coagulation factors due to the tiny clots forming throughout the
vasculature. This is also the reason that the fibrinogen levels and platelet levels are
decreased. Finally FDP, or fibrin degredation products, are increased due to the formation
and subsequent dissolving of many tiny clots in the vasculature. The FDPs are the pieces
of fibrin that are left after the fibrinolytic processes take place.
Which of the following laboratory results would be seen in a patient with acute
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)?
A. prolonged PT, elevated platelet count, decreased FDP
B. normal PT, decreased fibrinogen, decreased platelet count, decreased FDP
C. prolonged PT, decreased fibrinogen, decreased platelet count, increased FDP
D. normal PT, decreased platelet count, decreased FDP
The term that is used to describe the color in these tubes of CSF is "xanthochromia."
Xanthochromia is an abnormal color, usually yellow, orange, or pink, in the supernatant of
the CSF sample. It may indicate that a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) has occurred.
Jaundice and icterus both describe a yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and eyes.
Blood plasma/serum that is deep yellow is also described as icteric.
What term is used to describe the color in these tubes of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
A. Jaundice
B. Xanthochromia
C. Icterus
| Page 3 out of 47 Pages |
| Previous |