The indole (modified Kovacs' reagent) is used to assess the ability of certain bacteria to
produce indole by the deamination of tryptophan. Indole reacts with aldehyde in the
Kovac's reagent to produce a red color. An alcoholic layer holds the red color as a ring at
the top of the tube used for the idole test.
If a bacteria produces the enzyme tryptophanase to break down the amino acid tryptophan,
which of the following tests will be positive with Kovac's reagent?
A. oxidase test
B. esculin test
C. catalase test
D. citrate test
E. indole test
Iron deficiency anemia, or IDA, is associated with an increased TIBC as there is less iron to bind to transferrin. Microcytic, hypochromic red cell morphology, a decreased serum iron level, a decreased serum ferritin level, and a decreased hemoglobin level are all characteristics associated with IDA. All of the following are characteristic findings in patients with iron deficiency anemia EXCEPT:
A. microcytic, hypochromic red cell morphology
B. decreased serum iron level
C. decreased total iron-binding capacity (TIBC)
D. decreased ferritin
E. decreased hemoglobin
Which of the following cardiac biomarkers rises within 30 minutes - 4 hours after chest pain, peaks in 2 - 12 hours, and is usually normal within 24 - 36 hours.
A. Cardiac troponins
B. CK-MB
C. Myoglobin
Howell-Jolly bodies are composed of DNA and appear as small round ball-like inclusions
inside the red cells. Usually only one Howell-Jolly body will be present in each red cell.
Single erythrocyte inclusions which are large, round, smooth and purplish-blue staining are
most likely: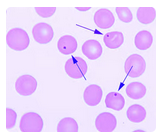
A. Howell-Jolly bodies
B. Heinz bodies
C. Basophilic stippling
D. Cabot rings
Pluripotential stem cells are ultimately capable of differentiating into all types of leukocytes.
Hematology
Pluripotential stem cells are capable of producing which of the following:
A. Only T-lymphocyte and B-lymphocyte subsets
B. Erythropoietin, thrombopoietin and leukopoietin
C. Lymphoid and myeloid stem cells
D. Daughter cells from only a single cell line
Which of the following fields is NOT an aspect of clinical microbiology?
A. virology
B. bacteriology
C. pathology
D. parasitology
The Bethesda assay is used to measure the titer and activity of the antibody present in a
patient's sample. Prothrombin time is an initial screening procedure for bleeding disorders
and a test used for monitoring anticoagulant therapy. A thrombin time is used to detect
heparin interference in an aPTT mixing study. A mixing study is performed to detect the
presence of a factor deficiency or coagulation inhibitor, but does not quantify the result.
Hematology
Which of the following tests is used to quantify a coagulation inhibitor?
A. Prothrombin time
B. Thrombin time
C. Mixing study
D. Bethesda assay
Anything that can cause significant turbidity in a blood sample, such as high leukocyte
count or lipemia can potentially interfere with the accuracy of a spectrophotometric
hemoglobin assay.
Hematology
Which of the following may interfere with the accurate measurement of hemoglobin:
A. Leukocytosis
B. EDTA
C. Heparin
D. Leukocytosis and lipemia
Secondary granules, also known as specific granules first appear in the myelocyte stage
next to the nucleus. In neutrophils this is termed the "dawn of neutrophilia".
What is one of the main characteristics of secondary granules in the neutrophilic
granulocyte cytoplasm?
A. Appear first at the myelocyte stage
B. Dissolve in mature granulocytes
C. Are formed on the mitochondria
D. Are derived from azurophil (primary) granules
Patients with antibody to the following antigen are immune to Hepatitis B:
A. Core antigen
B. Surface antigen
C. antigen
D. Delta antigen
Provide the equivalent measurement for 1000 milligrams.
A. 1 microgram
B. 5 grams
C. 100 microns
D. 1 gram
Protein in urine can be confirmed using sulfosalicylic acid (SSA) precipitation. The SSA reagent is added to a small volume of urine. Acidification causes precipitation of protein in the sample, which is subjectively graded as trace, 1+, 2+, 3+ or 4+. SSA reaction will detect albumin, globulins, and Bence-Jones proteins. Which of the following would be the most appropriate method to confirm a positive protein from a urine dipstick:
A. Immunoelectropheresis
B. Heat precipitation
C. Sulfosalicylic acid precipitation
D. Protein electrophoresis
| Page 18 out of 47 Pages |
| Previous |