Albumin is a "negative" acute phase protein since it is found in decreased levels during acute phase response. Alpha-1-antitrypsin, fibrinogen, and ceruloplasmin are all "positive" acute phase proteins that are found in increased levels during acute phase response. Which one of the following usually shows a decrease during an acute phase response?
A. Albumin
B. Alpha-1 Antitrypsin
C. Fibrinogen
D. Ceruloplasmin
The A and B antigens are present on the red cells of an AB patient. H antigen is a precursor to the ABO antigens. An individual with type AB blood will demonstrate the complete absence of which of the following antigen sites?
A. A
B. B
C. H
D. None of the above
Failure to deliver glucose drawn in a serum separator tube (SST) to the laboratory within the recommended time will cause:
A. a falsely decreased glucose value
B. a falsely increased glucose value
C. glycolysis
D. both A and C
Yellow/gray or orange stopper tubes contain thrombin.
A. True
B. False
The hepatitis B vaccine is a series of immunizations consisting of three injections of the
hepatitis B antigen. The antigen causes the recipient of the injection to make antibodies
against the antigen, hence why this is an example of active immunity.
Immunology
The hepatitis B virus vaccine was administered to MLS students during Orientation. Which
type of immunity is expected to develop and provide long-term protection?
A. active
B. passive
C. adoptive
D. innate
E. inactive
Sterile yellow stopper tubes contain thixotropic gel and a clot activator.
A. True
B. False
The most common specimen analyzed in the hematology section is:
A. plasma.
B. whole blood.
C. urine.
D. serum.
A zone of inhibition is the area around an antibiotic-infused paper disk that does not show any bacterial growth. The antibiotic impregnated on the disk will diffuse into the agar in the area surrounding the disk. If the bacteria are sensitive to the antibiotic, they cannot grow near the disk. The size of the zone is proportional to how sensitive the organism is. If the organism is resistant to the antibiotic, it will grow very closely to the disk. The size of the zone of suppressed growth on a sensitivity plate using sensitivity disks is referred to as the zone of:
A. beta hemolysis
B. alpha hemolysis
C. gamma hemolysis
D. inhibition
E. susceptibility
1. B
2. C
3. A
Granular casts are composed of plasma protein aggregates and cellular remnants.
Granular casts appear as cylinders of coarse, or fine, highly refractive particles.
Broad casts or "renal failure' casts are formed in the collecting ducts as the result of urinary
stasis and are two to six times the size of other types of casts. Any type of cast can be a
broad cast. Broad casts are typically seen in patients with advanced renal failure.
Hyaline casts, the type most commonly seen in urine sediment, have a refractive index
similar to the urine in which they are suspended. For this reason, hyaline casts will appear
almost invisible under brightfield microscopy, but are easily of seen by phase-contrast
microscopy.
Match the following descriptions of casts with their appropriate name:
1. Casts with highly refractive particles
2. "Renal failure" cast
3. Low refractive index
A. Hyaline casts
B. Granular Casts
C. Broad
Assuming an alpha hemolytic reaction (not well seen in the image), viridans streptococcus
and S. pneumoniae are the two possible responses. However, these colonies are far too
mucoid for viridans streptococci; therefore, S. pneumoniae is the most likely choice. Also,
the colonies are much too large and the hemolytic reaction is wrong for S. pyogenes or S.
agalactiae.
A patient was admitted to the hospital recently with an obvious infection. A sputum
specimen was submitted and the microbiologist inoculated it to sheep blood agar. Based
on the colony morphology and the alpha hemolysis seen in the image to the right, the most
likely identification is:
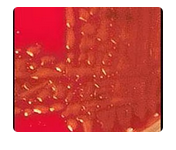
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. viridans streptococcus
C. Streptococcus pyogenes
D. Streptococcus agalactiae
All of the following have been an inspection deficiency for CLIA-approved laboratories except:
A. The laboratory needs to verify that written policies and procedures are established for patient testing.
B. The laboratory needs to verify the accuracy of any test or procedure it performs.
C. The laboratory needs to verify that the eyewash stations are properly functioning.
D. The laboratory needs to verify the proper storage for reagents and patient specimens.
In sickle cell anemia, rapid hemoglobin turnover may be present. HbA1C and other
glycated hemoglobin assays are not valid in rapid hemoglobin turnover and in abnormal
hemoglobin conditions. Fructosamine measurements can be used because of shorter half
life of albumin.
HbA1C measurements are NOT ordinarily used to monitor long-term diabetic control in a
diabetic with sickle cell anemia.
A. True
B. False
| Page 14 out of 47 Pages |
| Previous |