Topic 2: Exam Pool B
Drag and drop the threats from the left onto examples of that threat on the right
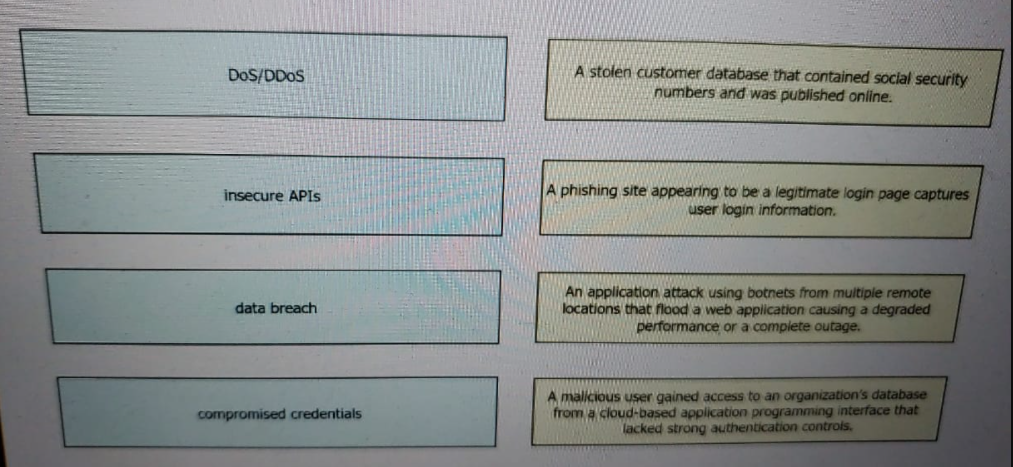
A data breach is the intentional or unintentional release of secure or
private/confidential information to anuntrusted environment.When your credentials have
been compromised, it means someone other than you may be in possession of your
account information, such as your username and/or password.
What is a difference between DMVPN and sVTI?
A.
DMVPN supports tunnel encryption, whereas sVTI does not.
B.
DMVPN supports dynamic tunnel establishment, whereas sVTI does not.
C.
DMVPN supports static tunnel establishment, whereas sVTI does not.
D.
DMVPN provides interoperability with other vendors, whereas sVTI does not.
DMVPN supports dynamic tunnel establishment, whereas sVTI does not.
What is the function of the Context Directory Agent?
A.
maintains users’ group memberships
B.
relays user authentication requests from Web Security Appliance to Active Directory
C.
reads the Active Directory logs to map IP addresses to usernames
D.
accepts user authentication requests on behalf of Web Security Appliance for user
identification
reads the Active Directory logs to map IP addresses to usernames
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/ibf/cda_10/Install_Config_guide/cda10/cda_oveviw.html
Why would a user choose an on-premises ESA versus the CES solution?
A.
Sensitive data must remain onsite
B.
Demand is unpredictable.
C.
The server team wants to outsource this service.
D.
ESA is deployed inline.
Sensitive data must remain onsite
What are two list types within AMP for Endpoints Outbreak Control? (Choose two)
A. blocked ports
B. simple custom detections
C. command and control
D. allowed applications
E. URL
Explanation
Cisco AMP for Endpoints' Outbreak Control feature is a proactive security mechanism that allows administrators to quickly enforce containment policies across their fleet in response to a new, high-severity global threat (an "outbreak"). It provides a set of pre-configured, draconian controls that can be activated with a single click.
Within Outbreak Control, you can create and manage specific lists to customize the lockdown behavior. The two list types are:
B. Simple Custom Detections:
This list allows you to define specific file hashes (SHA-256) that you want to either always block or always allow, regardless of the outbreak control state. This is useful for ensuring critical business applications are not blocked by a broad outbreak policy or for proactively blocking a malicious file specific to your environment.
D. Allowed Applications:
This is a crucial "safety net" list. When Outbreak Control is activated, it can be configured to block all unknown or unapproved applications. The Allowed Applications list is where you specify the trusted applications (by their file path, signer, or hash) that are exempt from this block policy. This prevents a company-wide outage by ensuring essential software like your corporate VPN client, accounting software, or other line-of-business applications continue to run.
Detailed Breakdown of Incorrect Options:
A. blocked ports:
Why it is incorrect:
Outbreak Control is focused on endpoint application and file execution control. It does not function as a host-based firewall that manages network traffic based on port numbers. Blocking ports is a separate function handled by the Windows Firewall or other network security products.
C. command and control:
Why it is incorrect:
While preventing command and control (C2) communication is a critical goal of endpoint security, it is not a specific list type within the Outbreak Control menu. C2 communication is typically blocked by the network-level security features of AMP (via the AMP cloud) or by the IPS/network sandboxing features integrated into the broader solution, not by a user-defined list in Outbreak Control.
E. URL:
Why it is incorrect:
URL filtering is a function of web security gateways (like Cisco Secure Web Appliance) or DNS security layers (like Cisco Umbrella). AMP for Endpoints is a file-centric solution that focuses on what is executing on the endpoint, not on filtering web traffic based on URLs. While it can detect malicious files downloaded from URLs, you cannot create a list of blocked/allowed URLs within the Outbreak Control feature itself.
Reference and Key Context:
Cisco AMP for Endpoints Console:
Navigating to the Outbreak Control section of the AMP console will directly show the "Allowed Applications" and "Simple Custom Detections" as the primary configurable list types.
Cisco Documentation:
The official administration guide for AMP for Endpoints details these list types under the Outbreak Control configuration steps, explaining their purpose for creating exceptions and custom blocks during a security lockdown.
Summary:
Outbreak Control is a "break-glass" containment feature. Its associated lists are designed to manage exceptions and custom rules for application execution ("Allowed Applications") and specific files ("Simple Custom Detections") to balance security and operational continuity during a crisis.
What are two Trojan malware attacks? (Choose two)
A. Frontdoor
B. Rootkit
C. Smurf
D. Backdoor
E. Sync
Explanation for Each Option:
A. Frontdoor (Incorrect):
Frontdoor is not a widely recognized Trojan malware attack. It may refer to an outdated file transfer tool or a misnomer, but it is not classified as a specific Trojan variant. Trojans are defined by their stealthy delivery of malicious payloads, and Frontdoor does not fit this category, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Malware Taxonomy, Cisco Security Encyclopedia.)
B. Rootkit (Correct):
A rootkit is a type of Trojan malware that provides unauthorized access to a system by concealing its presence and granting attackers administrative (root) privileges. It is delivered covertly, often as a legitimate-looking file, aligning with Trojan characteristics, making it a valid example. (Reference: Cisco Secure Endpoint Rootkit Detection Guide.)
C. Smurf (Incorrect):
A Smurf attack is a type of Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack that floods a network with ICMP echo requests using spoofed IP addresses. It is not a Trojan, as it does not involve delivering a malicious payload disguised as legitimate software, rendering this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco DoS Mitigation Guide, Smurf Attacks.)
D. Backdoor (Correct):
A backdoor is a Trojan malware attack that creates a hidden entry point into a system, allowing attackers to bypass normal authentication and gain unauthorized access. It is typically disguised as legitimate software, fitting the Trojan definition, making it a valid example. (Reference: Cisco Malware Protection, Backdoor Threats.)
E. Sync (Incorrect):
"Sync" is not a recognized Trojan malware attack. It might be a typo or confusion with a SYN flood (a DoS attack type), which overwhelms a target with TCP SYN packets. As it does not represent a Trojan payload, this option is incorrect. (Reference: Cisco Security Threat Intelligence, SYN Floods.)
Additional Notes:
Identifying Trojan malware types is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under endpoint security. As of 02:09 PM PKT, October 02, 2025, rootkits and backdoors remain prevalent threats. For details, refer to the Cisco Secure Endpoint documentation (cisco.com) and the 350-701 Exam Blueprint (Section 2.0 Endpoint Security).
An organization has two systems in their DMZ that have an unencrypted link between them for communication.
The organization does not have a defined password policy and uses several default
accounts on the systems.
The application used on those systems also have not gone through stringent code reviews.
Which vulnerability would help an attacker brute force their way into the systems?
A. weak passwords
B. lack of input validation
C. missing encryption
D. lack of file permission
Explanation
The question is very specific:
it asks which vulnerability would help an attacker brute force their way into the systems.
Brute Force Attack:
This is a specific type of attack where an attacker systematically tries many password combinations until they find the correct one.
Weak Passwords:
This vulnerability directly enables successful brute force attacks. If passwords are short, common, predictable, or use default credentials (as mentioned in the scenario: "no defined password policy and uses several default accounts"), the number of guesses an attacker needs to make is dramatically reduced. This makes a brute-force attack practical and likely to succeed.
The unencrypted link (missing encryption) is a serious vulnerability, but it enables a different, more efficient type of attack.
Detailed Breakdown of Incorrect Options
B. lack of input validation:
Why it is incorrect:
Lack of input validation leads to vulnerabilities like SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), or buffer overflows. These are attacks that exploit logic flaws in the application code. An attacker using these methods is not "brute forcing their way in" by guessing passwords; they are exploiting a programming error to bypass authentication or execute commands directly.
C. missing encryption
Why it is incorrect:
A missing encryption (unencrypted link) enables eavesdropping or credential sniffing. An attacker on the network path could capture the authentication traffic and simply read the username and password as they are transmitted in clear text. If an attacker can sniff the credentials, they don't need to brute-force them. This is a more efficient attack that bypasses the need for brute-forcing entirely. Therefore, while a critical flaw, it does not "help" a brute-force attack; it provides a superior alternative.
D. lack of file permission
Why it is incorrect:
Improper file permissions could allow an attacker who already has some access to a system to read sensitive files (like password hashes). However, this is typically a post-exploitation step or a separate attack vector. It does not directly facilitate a brute-force attack against a live login service.
Key Takeaway:
The question is very specific: "Which vulnerability would help an attacker brute force their way in?"
Brute Force is guessing passwords. Weak passwords make guessing easy and practical.
Sniffing (enabled by missing encryption) is stealing passwords, which is a different and often superior attack method.
An administrator is trying to determine which applications are being used in the network but does not want the network devices to send metadata to Cisco Firepower. Which feature should be used to accomplish this?
A. NetFlow
B. Packet Tracer
C. Network Discovery
D. Access Control
Explanation
The key requirement in the question is that the administrator wants to identify applications on the network without having the network devices send metadata to Cisco Firepower. This excludes features that rely on Firepower's own deep packet inspection or metadata collection.
A. NetFlow:
This is the correct answer. NetFlow (and its variants like IPFIX and Flexible NetFlow) is a standard protocol for network traffic monitoring and statistics collection. Network devices (routers, switches) can be configured to export NetFlow records to a collector. These records contain information about traffic flows, including source/destination IPs, ports, and protocols. A NetFlow analysis tool can then interpret this data to infer and report on the applications in use, all without sending any proprietary metadata to the Firepower Management Center. It is a separate, standards-based data source.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. Packet Tracer:
This is a troubleshooting tool within Firepower and ASA devices used to simulate how a packet would be processed by the configuration (ACLs, NAT, etc.). It does not provide a network-wide view of application usage.
C. Network Discovery:
This is a specific feature within Cisco Firepower that relies on metadata sent to it. Firepower uses various methods, including its own deep packet inspection and the analysis of metadata from sensors, to build a map of hosts, services, and applications on the network. This is explicitly what the administrator is trying to avoid.
D. Access Control:
This is the core policy enforcement feature of Firepower. While Access Control policies can be used to see traffic that they block or allow, the visibility they provide is a byproduct of the Firepower platform inspecting the traffic itself. It requires the network device (Firepower Threat Defense appliance, etc.) to send data to the Firepower Management Center, which is against the stated requirement.
Reference:
This distinction is covered in the architecture of network visibility tools. The fundamental difference is:
Firepower Network Discovery & Application Detectors: These are proprietary, deep-packet inspection based technologies that require the sensor to process and send data to the FMC.
NetFlow: An industry-standard flow export protocol. The data is collected and analyzed independently of the Firepower application identification engine.
In summary, if the goal is to identify applications without using Firepower's native metadata-based discovery, the administrator must use an external source of traffic data, and NetFlow is the standard method for achieving this.
Which two features are used to configure Cisco ESA with a multilayer approach to fight viruses and malware?(Choose two)
A. Sophos engine
B. white list
C. RAT
D. outbreak filters
E. DLP
Explanation for Each Option:
A. Sophos engine (Correct):
The Sophos engine is an integrated antivirus scanning component in Cisco ESA that performs multilayer malware detection using signature-based analysis and heuristic scanning. It examines email attachments and content at multiple stages to identify and block viruses, contributing to a comprehensive defense approach. (Reference: Cisco ESA Antivirus Configuration Guide, Sophos Engine.)
B. white list (Incorrect):
A white list allows known safe senders or content to bypass scanning, which is a filtering mechanism but not a multilayer approach to fight viruses and malware. It focuses on allowing rather than detecting threats, making it unsuitable for proactive virus defense. (Reference: Cisco ESA Mail Policies Guide, White Listing.)
C. RAT (Incorrect):
RAT (Remote Access Trojan) is a type of malware that provides unauthorized access, not a configuration feature in Cisco ESA. It is a threat to detect, not a tool for multilayer virus protection, rendering this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco ESA Threat Detection Overview.)
D. outbreak filters (Correct):
Outbreak filters, powered by Cisco Talos threat intelligence, provide multilayer protection by scanning emails for emerging malware and viruses not yet in signature databases. They use reputation-based analysis and real-time updates to block suspicious content, enhancing the ESA's virus-fighting capabilities. (Reference: Cisco ESA Outbreak Filters Guide.)
E. DLP (Incorrect):
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) focuses on preventing sensitive data exfiltration, not on detecting or fighting viruses and malware. While it adds security, it is not part of the multilayer antivirus approach, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco ESA DLP Configuration.)
Additional Notes:
Configuring multilayer protection in Cisco ESA is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under content security. As of 5:00 PM PKT, October 03, 2025, Sophos and outbreak filters are essential.
Which Cisco platform ensures that machines that connect to organizational networks have the recommended antivirus definitions and patches to help prevent an organizational malware outbreak?
A. Cisco WiSM
B. Cisco ESA
C. Cisco ISE
D. Cisco Prime Infrastructure
Explanation:
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) is the central policy engine that enables Network Access Control (NAC). A core component of its functionality is Posture Assessment.
Let's break down why ISE is the correct answer and the role of the other platforms:
C) Cisco ISE is CORRECT.
Cisco ISE's Posture Service is specifically designed to check the state (or "health") of an endpoint before allowing it onto the network. It can verify:
The presence, version, and status of antivirus/antimalware software.
Whether the latest antivirus signatures are installed.
The presence of specific operating system security patches and hotfixes.
The status of the host firewall.
Based on this check, ISE can enforce a policy. For example, it can grant full access to compliant devices, but place non-compliant devices into a quarantined VLAN where they can only access patch servers until they meet the security requirements. This directly prevents vulnerable machines from connecting and causing a malware outbreak.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A) Cisco WiSM is INCORRECT.
Cisco WiSM (Wireless Services Module) was a hardware module for Catalyst switches that hosted wireless controllers. It is an obsolete product related to wireless LAN management, not endpoint compliance.
B) Cisco ESA is INCORRECT.
Cisco ESA (Email Security Appliance) is a gateway that scans incoming and outgoing emails for spam, malware, and phishing attacks. It protects the email vector but does not check the compliance state of endpoints already inside the network.
D) Cisco Prime Infrastructure is INCORRECT.
Cisco Prime Infrastructure is a network management tool. It is used for provisioning, monitoring, and troubleshooting network devices (routers, switches, WLCs). While it can provide visibility into what devices are connected, it does not have the capability to perform a posture check on an endpoint to verify its antivirus status or patch level.
Reference:
Cisco ISE Administrator Guide, "About Posture Service": The official documentation defines the Posture service as the component that "assesses the state of an endpoint to determine whether it is compliant with the policies that you define," explicitly listing checks for antivirus and patch levels.
Cisco SCOR 350-701 Exam Objectives: The blueprint covers Secure Network Access using Cisco ISE, with posture being a key technology for ensuring endpoint compliance.
In which two ways does a system administrator send web traffic transparently to the Web Security Appliance? (Choose two)
A. configure Active Directory Group Policies to push proxy settings
B. configure policy-based routing on the network infrastructure
C. reference a Proxy Auto Config file
D. configure the proxy IP address in the web-browser settings
E. use Web Cache Communication Protocol
Explanation:
"Transparent" redirection means that end-users do not need to configure any proxy settings in their web browsers. The redirection happens at the network level, invisible to the user.
B) configure policy-based routing on the network infrastructure is CORRECT.
Policy-Based Routing (PBR) allows a network administrator to define routing policies that override the normal routing table. A router or layer 3 switch can be configured with a PBR rule that matches web traffic (e.g., TCP port 80/443) and forwards it to the WSA's IP address instead of sending it directly to its destination.
E) use Web Cache Communication Protocol is CORRECT.
WCCP (Web Cache Communication Protocol) is a Cisco-developed protocol specifically designed for transparently redirecting traffic. A network device (like a router) running WCCP (the "client") forms a relationship with the WSA (the "server"). The network device then intercepts web traffic and transparently forwards it to the WSA for filtering and scanning.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A) configure Active Directory Group Policies to push proxy settings is INCORRECT.
This is an explicit proxy deployment method, not a transparent one. The client is explicitly told to send its web traffic to the proxy (WSA) by its configuration.
C) reference a Proxy Auto Config file is INCORRECT.
A PAC file is also a form of explicit proxy configuration. The browser is given a script (the PAC file) that tells it when to use a proxy and when to connect directly.
D) configure the proxy IP address in the web-browser settings is INCORRECT.
This is the most basic form of explicit proxy configuration. The user or administrator manually enters the proxy server's details into the browser's connection settings.
Summary:
Transparent Redirection: WCCP, PBR. The user is unaware.
Explicit Proxy: Browser settings, PAC files, Group Policy. The client is configured to use the proxy.
Reference:
Cisco WSA Deployment Guide, "Transparent Redirection": The official documentation details both WCCP and PBR as the primary methods for deploying the WSA in a transparent mode.
What is a benefit of conducting device compliance checks?
A.
It indicates what type of operating system is connecting to the network.
B.
It validates if anti-virus software is installed
C.
It scans endpoints to determine if malicious activity is taking place
D.
It detects email phishing attacks.
It validates if anti-virus software is installed
| Page 7 out of 61 Pages |
| 12345678910111213141516171819 |
| 350-701 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our 350-701 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies (SCOR 350-701) exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive 350-701 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.