Topic 3: Exam Pool C
Based on the NIST 800-145 guide, which cloud architecture may be owned, managed, and operated by one or more of the organizations in the community, a third party, or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off premises?
A. hybrid cloud
B. private cloud
C. public cloud
D. community cloud
Explanation
The NIST Special Publication 800-145, "The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing," provides standardized definitions for the essential characteristics and service models of cloud computing. It specifically defines four deployment models: Public, Private, Community, and Hybrid.
Let's break down the definition in the question and compare it to the NIST definitions:
"owned, managed, and operated by one or more of the organizations in the community, a third party, or some combination of them":This is the key differentiator for a community cloud. The infrastructure is shared by several organizations that have a shared concern (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy, compliance considerations). This shared infrastructure can be managed by the organizations themselves or outsourced to a third party.
"may exist on or off premises":A community cloud is not defined by its physical location. It could be hosted on the premises of one of the community members or at a third-party data center.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. Hybrid Cloud:
A hybrid cloud is a composition of two or more distinct cloud infrastructures (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability. The question describes a single, shared infrastructure for a specific community, not a combination of multiple ones.
B. Private Cloud:
The private cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a single organization. It may be owned, managed, and operated by the organization, a third party, or some combination, but it is not shared with other organizations in a community.
C. Public Cloud:
The public cloud infrastructure is provisioned for open use by the general public. It is owned, managed, and operated by a business, academic, or government organization, and it exists on the premises of the cloud provider.
Reference
This definition is taken directly from the NIST Special Publication 800-145, "The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing."
The official NIST definition for a Community Cloud is:
"The cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a specific community of consumers from organizations that have shared concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations). It may be owned, managed, and operated by one or more of the organizations in the community, a third party, or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off premises."
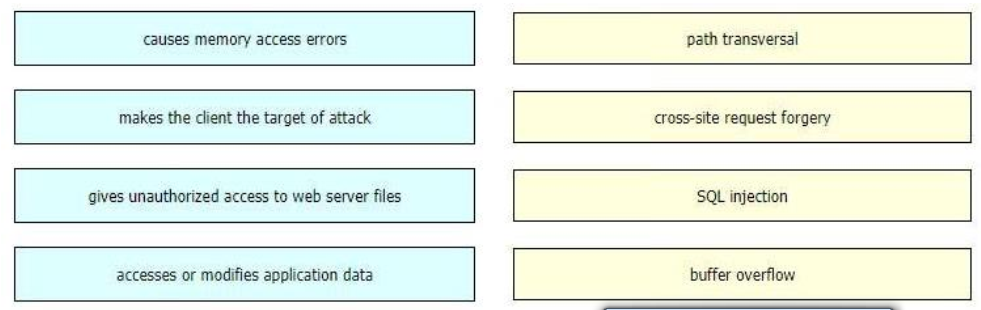
Drag and drop the exploits from the left onto the type of security vulnerability on the right.
What is a benefit of using Cisco Umbrella?
A.
DNS queries are resolved faster.
B.
Attacks can be mitigated before the application connection occurs
C.
Files are scanned for viruses before they are allowed to run
D.
It prevents malicious inbound traffic
Attacks can be mitigated before the application connection occurs
Which Cisco security solution determines if an endpoint has the latest OS updates and
patches installed on the system?
A.
Cisco Endpoint Security Analytics
B.
Cisco AMP for Endpoints
C.
Endpoint Compliance Scanner
D.
Security Posture Assessment Service
Security Posture Assessment Service
Refer to the exhibit. When creating an access rule for URL filtering, a network engineer adds certain categories and individual URLs to block. What is the result of the configuration?
A. Only URLs for botnets with reputation scores of 1-3 will be blocked.
B. Only URLs for botnets with a reputation score of 3 will be blocked
C. Only URLs for botnets with reputation scores of 3-5 will be blocked
D. Only URLs for botnets with a reputation score of 3 will be allowed while the rest will be blocked.
Explanation for Each Option:
A. Only URLs for botnets with reputation scores of 1-3 will be blocked (Incorrect):
The configuration likely specifies a single reputation score (e.g., 3) for botnet category blocking, as indicated by the question’s context of adding specific categories and URLs. Without evidence of a range (1-3), this option assumes a broader scope not supported by typical URL filtering rules, making it incorrect. (Reference: Cisco Umbrella Admin Guide, Reputation Scoring.)
B. Only URLs for botnets with a reputation score of 3 will be blocked (Correct):
In Cisco URL filtering solutions (e.g., Umbrella or Secure Web Gateway), reputation scores are assigned to categorize risk levels (e.g., 1-5, with 3 often indicating moderate risk like botnets). Adding a botnet category with a specific score (e.g., 3) blocks only those URLs matching that exact reputation score, aligning with the configuration intent. (Reference: Cisco Secure Web Gateway Configuration Guide, URL Filtering.)
C. Only URLs for botnets with reputation scores of 3-5 will be blocked (Incorrect):
A range like 3-5 would require explicit configuration to block multiple reputation levels, which is not implied by adding "certain categories and individual URLs." URL filtering typically applies to specific categories or scores unless a range is defined, making this assumption of a broader range incorrect. (Reference: Cisco Umbrella Policy Management Documentation.)
D. Only URLs for botnets with a reputation score of 3 will be allowed while the rest will be blocked (Incorrect):
The action of adding categories and URLs to block suggests a deny policy. Allowing only score 3 URLs while blocking others would require an explicit allow rule, which contradicts the intent of blocking specific categories. This misinterprets the configuration’s deny-focused purpose. (Reference: Cisco URL Filtering Best Practices.)
Additional Notes:
URL filtering configuration is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under content security. As of 10:10 AM PKT, October 02, 2025, reputation-based blocking remains a standard practice. Since the exhibit is unavailable, the answer assumes a typical Cisco URL filtering setup (e.g., Umbrella) with a specific reputation score. For details, refer to the Cisco Umbrella Admin Guide (umbrella.cisco.com) and the 350-701 Exam Blueprint (Section 3.0 Security Concepts).
Note:
The exhibit is not provided, so the explanation assumes a standard configuration where a specific reputation score (e.g., 3) is set for the botnet category, a common practice in Cisco URL filtering tools.
An engineer used a posture check on a Microsoft Windows endpoint and discovered that the MS17-010 patch
was not installed, which left the endpoint vulnerable to WannaCry ransomware. Which two solutions mitigate the risk of this ransom ware infection? (Choose two)
A.
Configure a posture policy in Cisco Identity Services Engine to install the MS17-010 patch before allowing access on the network.
B.
Set up a profiling policy in Cisco Identity Service Engine to check and endpoint patch level before allowing access on the network.
C.
Configure a posture policy in Cisco Identity Services Engine to check that an endpoint patch level is met before allowing access on the network.
D.
Configure endpoint firewall policies to stop the exploit traffic from being allowed to run and replicate throughout the network.
E.
Set up a well-defined endpoint patching strategy to ensure that endpoints have critical vulnerabilities patched in a timely fashion.
Configure a posture policy in Cisco Identity Services Engine to install the MS17-010 patch before allowing access on the network.
Configure a posture policy in Cisco Identity Services Engine to check that an endpoint patch level is met before allowing access on the network.
ExplanationA posture policy is a collection of posture requirements, which
are associated with one or more identity groups, and operating systems. We can configure ISE to check for the Windows patch at Work Centers > Posture > Posture Elements > Conditions > File.In this example, we are going to use the predefined file check to ensure that our Windows 10 clients have the critical security patch installed to prevent the Wanna Cry malware.
Which two key and block sizes are valid for AES? (Choose two)
A.
64-bit block size, 112-bit key length
B.
64-bit block size, 168-bit key length
C.
128-bit block size, 192-bit key length
D.
128-bit block size, 256-bit key length
E.
192-bit block size, 256-bit key length
128-bit block size, 192-bit key length
128-bit block size, 256-bit key length
The AES encryption algorithm encrypts and decrypts data in
blocks of 128 bits (block size). It can do this using 128-bit, 192-bit, or 256-bit keys
When choosing an algorithm to us, what should be considered about Diffie Hellman and RSA for key establishment?
A. RSA is an asymmetric key establishment algorithm intended to output symmetric keys
B. RSA is a symmetric key establishment algorithm intended to output asymmetric keys
C. DH is a symmetric key establishment algorithm intended to output asymmetric keys
D. DH is on asymmetric key establishment algorithm intended to output symmetric keys
Explanation for Each Option:
A. RSA is an asymmetric key establishment algorithm intended to output symmetric keys (Incorrect):
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) is an asymmetric algorithm used for encryption, digital signatures, and key exchange, but it does not inherently output symmetric keys. It is typically used to securely exchange a symmetric key, not to generate one directly, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco NGE Cryptographic Algorithms, RSA Usage.)
B. RSA is a symmetric key establishment algorithm intended to output asymmetric keys (Incorrect):
RSA is an asymmetric algorithm, not symmetric, and it does not output asymmetric keys. It generates a public-private key pair for asymmetric cryptography, not a key establishment process for symmetric keys, rendering this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco RSA Configuration Guide.)
C. DH is a symmetric key establishment algorithm intended to output asymmetric keys (Incorrect):
Diffie-Hellman (DH) is an asymmetric key establishment protocol that enables two parties to establish a shared secret (symmetric key) over an insecure channel. It does not output asymmetric keys, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco DH Key Exchange Overview.)
D. DH is an asymmetric key establishment algorithm intended to output symmetric keys (Correct):
Diffie-Hellman (DH) is an asymmetric key establishment algorithm that allows two parties to derive a shared symmetric key (e.g., for use in AES) without exchanging the key directly. This aligns with its purpose in secure key exchange, making it the correct choice. (Reference: Cisco NGE Diffie-Hellman Guide.)
Additional Notes:
Choosing key establishment algorithms is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under network security. As of 5:06 PM PKT, October 03, 2025, DH’s role in symmetric key generation is critical.
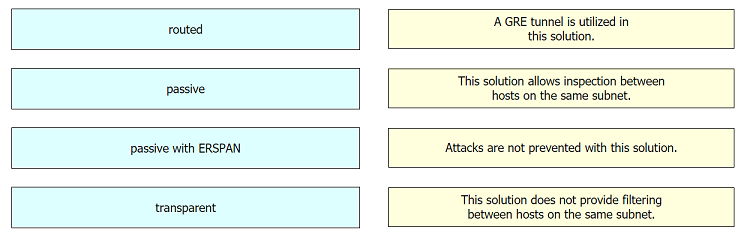
Drag and drop the deployment models from the left onto the explanations on the right.
Which ID store requires that a shadow user be created on Cisco ISE for the admin login to work?
A.
RSA SecureID
B.
Internal Database
C.
Active Directory
D.
LDAP
Active Directory
What is the term for when an endpoint is associated to a provisioning WLAN that is shared with guest access, and the same guest portal is used as the BYOD portal?
A. single-SSID BYOD
B. multichannel GUI
C. dual-SSID BYOD
D. streamlined access
Explanation for Each Option:
A. single-SSID BYOD (Incorrect):
Single-SSID BYOD refers to a configuration where a single wireless network (SSID) is used for both employee and BYOD onboarding, typically with separate authentication and provisioning processes. It does not involve sharing a guest access WLAN or portal, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco BYOD Design Guide, Single-SSID.)
B. multichannel GUI (Incorrect):
Multichannel GUI is not a recognized term in the context of Cisco wireless or BYOD deployments. It suggests a user interface concept, not a specific endpoint association or portal-sharing configuration, rendering this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco Wireless Controller GUI Overview.)
C. dual-SSID BYOD (Correct):
Dual-SSID BYOD involves associating endpoints to a provisioning WLAN that is shared with guest access, using the same guest portal for both BYOD onboarding and guest access. This configuration leverages two SSIDs (e.g., one for provisioning/guest, another for corporate) with a unified portal, aligning with the description. (Reference: Cisco BYOD Dual-SSID Deployment Guide.)
D. streamlined access (Incorrect):
Streamlined access is a general term that might imply simplified onboarding but is not a specific Cisco term for sharing a provisioning WLAN with guest access using the same portal. It lacks the dual-SSID context, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco ISE Streamlined Access Features.)
Additional Notes:
Configuring BYOD with dual-SSID is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under endpoint security. As of 4:49 PM PKT, October 07, 2025, it enhances guest and device management.
Which security solution protects users leveraging DNS-layer security?
A.
Cisco ISE
B.
Cisco FTD
C.
Cisco Umbrella
D.
Cisco ASA
Cisco Umbrella
| Page 28 out of 61 Pages |
| 19202122232425262728293031323334353637 |
| 350-701 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our 350-701 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies (SCOR 350-701) exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive 350-701 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.