Topic 3: Exam Pool C
Which endpoint protection and detection feature performs correlation of telemetry, files, and intrusion events that are flagged as possible active breaches?
A. retrospective detection
B. indication of compromise
C. file trajectory
D. elastic search
Explanation
This question is asking about a specific capability within Cisco Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) for Endpoints that allows security teams to investigate potential security incidents after initial detection.
A. retrospective detection:
This is the correct answer. Retrospective Security is a powerful feature of Cisco AMP that continuously analyzes and correlates all activity on an endpoint—including telemetry, file executions, network connections, and intrusion events—after they have occurred. If a file, IP address, or domain is later determined to be malicious (e.g., through new threat intelligence), AMP can retroactively search through its historical data to find every endpoint that was affected. This allows an analyst to see the full scope of a potential breach, answering the critical questions: "Where did this start?" and "How far did it spread?"
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. indication of compromise (IoC):
This is incorrect. An IoC is a piece of evidence (e.g., a file hash, a malicious IP) that suggests a network intrusion has occurred. It is the data point that you search for, not the feature that performs the correlation and searching itself.
C. file trajectory:
This is incorrect. File Trajectory is a different, though related, feature within Cisco AMP. It shows the complete history of a specific file across the entire organization—which endpoints it has been on, what it did, and where it came from. While incredibly useful, it focuses on a single file's path. Retrospective detection is the broader capability that uses this kind of data, along with other telemetry, to correlate events and identify active breaches.
D. elastic search:
This is incorrect. Elasticsearch is a general-purpose, open-source search and analytics database engine. While Cisco AMP for Endpoints may use a similar technology internally to power its backend, "Elasticsearch" is not the name of a user-facing feature or a marketed capability of the product. The term described in the question is "retrospective detection."
Reference:
This is a core feature highlighted in the Cisco AMP for Endpoints documentation and data sheets.
Cisco AMP for Endpoints Data Sheet: It explicitly describes "Retrospective Security" as the feature that "continuously tracks and analyzes file and threat activity, giving you the power to go back in time to determine the origin and scope of an attack."
In summary, the feature that performs ongoing correlation of telemetry and events to identify possible active breaches, even after the initial activity occurred, is retrospective detection.
How does Cisco AMP for Endpoints provide next-generation protection?
A. It encrypts data on user endpoints to protect against ransomware.
B. It leverages an endpoint protection platform and endpoint detection and response
C. It utilizes Cisco pxGrid, which allows Cisco AMP to pull threat feeds from threat intelligence centers.
D. It integrates with Cisco FTD devices.
Explanation for Each Option:
A. It encrypts data on user endpoints to protect against ransomware (Incorrect):
While data encryption can help mitigate ransomware effects, Cisco AMP for Endpoints does not primarily focus on encrypting data. Its next-generation protection relies on prevention, detection, and response, not encryption as a core feature, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco AMP for Endpoints Ransomware Protection.)
B. It leverages an endpoint protection platform and endpoint detection and response (Correct):
Cisco AMP for Endpoints combines an Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP) for real-time threat prevention (e.g., antivirus, exploit prevention) with Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) for detecting and responding to advanced threats post-infection. This dual approach provides next-generation protection, aligning with this option. (Reference: Cisco AMP for Endpoints Datasheet, EPP/EDR Integration.)
C. It utilizes Cisco pxGrid, which allows Cisco AMP to pull threat feeds from threat intelligence centers (Incorrect):
Cisco pxGrid enables secure data sharing between security products, including threat intelligence, but it is an integration framework, not the primary mechanism for AMP’s next-generation protection. The EPP/EDR combination is the core, making this option secondary and incorrect. (Reference: Cisco pxGrid Overview.)
D. It integrates with Cisco FTD devices (Incorrect):
Integration with Cisco Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) devices enhances network-level security but is not the basis for AMP’s next-generation endpoint protection. AMP’s strength lies in endpoint-specific EPP and EDR capabilities, not network device integration, rendering this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco FTD and AMP Integration Guide.)
Additional Notes:
Understanding AMP’s next-generation protection is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under endpoint security. As of 4:05 PM PKT, October 03, 2025, its EPP/EDR approach is cutting-edge.
Drag and drop the features of Cisco ASA with Firepower from the left onto the benefits on
the right.
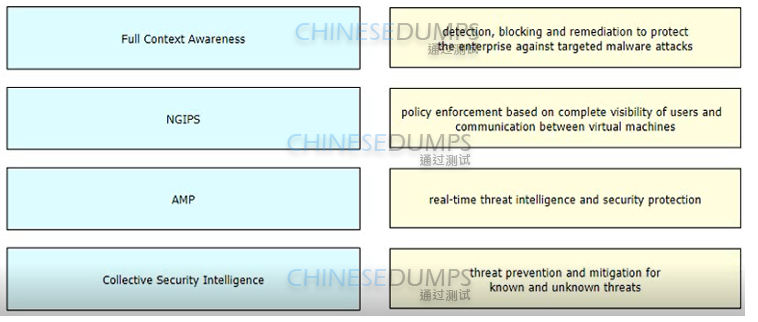
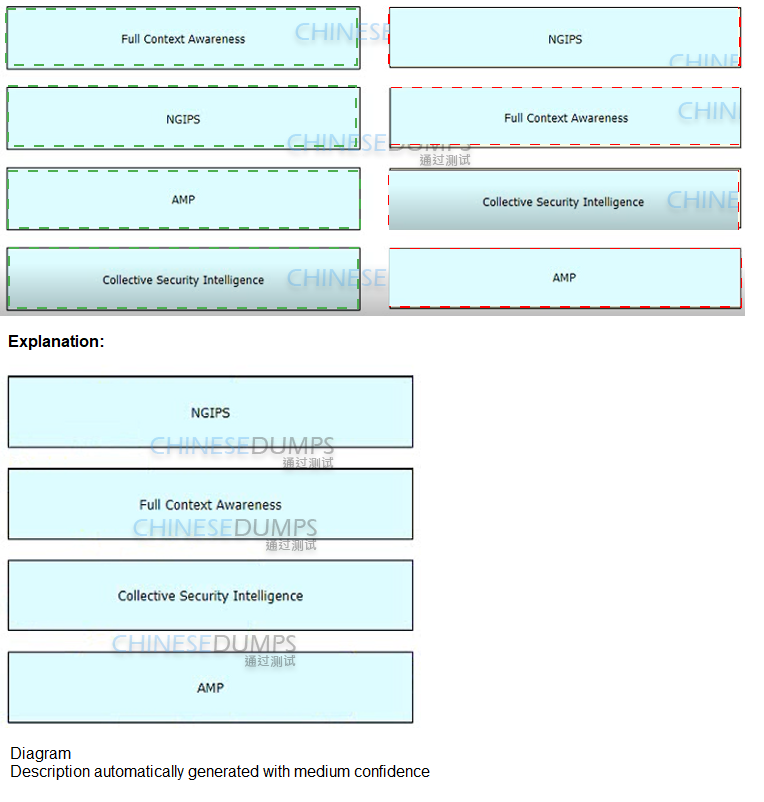
Which technology provides a combination of endpoint protection endpoint detection, and response?
A. Cisco AMP
B. Cisco Talos
C. Cisco Threat Grid
D. Cisco Umbrella
Explanation:
This question is about identifying the Cisco product that integrates the core functionalities of modern endpoint security.
Let's analyze each option:
Why Option A is Correct:
Cisco AMP (Advanced Malware Protection) for Endpoints is the product that directly provides this combination. It has evolved from a traditional antivirus into a full Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solution, which is now marketed as Cisco Secure Endpoint.
Endpoint Protection: It provides prevention capabilities like signature-based antivirus and behavioral monitoring to stop known and unknown threats.
Endpoint Detection: It continuously monitors all file and process activity on the endpoint, recording this information in a cloud timeline.
Response: If a threat is detected, it allows security analysts to investigate the entire attack scope using the timeline, contain the endpoint, and remediate the threat.
Why the Other Options are Incorrect:
Why Option B is Incorrect:
Cisco Talos is Cisco's threat intelligence and research group. It is the "brains" behind many Cisco security products. Talos analyzes global threat data to create the signatures, rules, and intelligence that power products like Cisco AMP, Firepower, and Umbrella. Talos is not a standalone product you deploy to endpoints; it is the intelligence service that feeds them.
Why Option C is Incorrect:
Cisco Threat Grid is a powerful malware analysis sandboxing technology. It executes suspicious files in a safe, virtual environment to analyze their behavior and produce a detailed report. While it integrates closely with Cisco AMP (AMP can automatically submit samples to Threat Grid), Threat Grid itself is not the endpoint agent. It is a supporting service for deep malware analysis.
Why Option D is Incorrect:
Cisco Umbrella is a cloud-delivered security service that acts as a secure internet gateway. It provides protection by blocking requests to malicious domains, IPs, and URLs before a connection is even established. This is a form of network-level security, not endpoint-based security. While it offers a roaming client for off-network endpoints, its primary function is DNS-layer security, not the deep endpoint detection and response provided by AMP.
Reference:
This is a fundamental product knowledge question within the Endpoint Protection and Detection domain. Understanding the distinct roles of Cisco's core security technologies—where AMP (Secure Endpoint) is the dedicated EDR platform—is essential for the 350-701 exam.
Which solution is made from a collection of secure development practices and guidelines that developers must follow to build secure applications?
A. AFL
B. Fuzzing Framework
C. Radamsa
D. OWASP
Explanation for Each Option:
A. AFL (Incorrect):
AFL (American Fuzzy Lop) is a security testing tool that uses fuzzing to identify vulnerabilities in software by providing invalid or unexpected inputs. While useful for secure development, it is a specific tool, not a collection of practices or guidelines that developers must follow to build secure applications, making this option incorrect. (Reference: AFL Fuzzing Documentation.)
B. Fuzzing Framework (Incorrect):
A fuzzing framework is a set of tools or libraries (e.g., Peach or Sulley) used to perform fuzz testing to uncover software vulnerabilities. It is a testing methodology, not a comprehensive set of development practices or guidelines for building secure applications, rendering this option unsuitable for the described solution. (Reference: Fuzzing Frameworks Overview.)
C. Radamsa (Incorrect):
Radamsa is an open-source fuzzing tool designed to generate test cases and detect software bugs or vulnerabilities. Like other fuzzing tools, it is a specific testing instrument, not a collection of secure development practices or guidelines that developers follow, making this option incorrect for the requirement. (Reference: Radamsa Project Documentation.)
D. OWASP (Correct):
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) provides a collection of secure development practices, guidelines, and tools (e.g., OWASP Top Ten, Secure Coding Practices) that developers must follow to build secure applications. It offers a framework for identifying, preventing, and mitigating security risks throughout the development lifecycle, aligning with the described solution. (Reference: OWASP Secure Coding Practices.)
Additional Notes:
OWASP’s guidelines are a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under secure development. As of 10:32 AM PKT, October 02, 2025, it remains a leading resource for application security. For details, refer to the OWASP website (owasp.org) and the 350-701 Exam Blueprint (Section 4.0 Automation and Development Security)
An engineer is configuring IPsec VPN and needs an authentication protocol that is reliable
and supports ACK
and sequence. Which protocol accomplishes this goal?
A.
AES-192
B.
IKEv1
C.
AES-256
D.
ESP
ESP
An organization is selecting a cloud architecture and does not want to be responsible for
patch management of the operating systems. Why should the organization select either
Platform as a Service or Infrastructure as a Service for this environment?
A.
Platform as a Service because the customer manages the operating system
B.
Infrastructure as a Service because the customer manages the operating system
C.
Platform as a Service because the service provider manages the operating system
D.
Infrastructure as a Service because the service provider manages the operating system
Platform as a Service because the service provider manages the operating system
What is a benefit of using GET VPN over FlexVPN within a VPN deployment?
A. GET VPN supports Remote Access VPNs
B. GET VPN natively supports MPLS and private IP networks
C. GET VPN uses multiple security associations for connections
D. GET VPN interoperates with non-Cisco devices
Explanation:
Group Encrypted Transport VPN (GET VPN) is designed for a specific use case: securing multicast and unicast traffic over a trusted, private WAN core, such as MPLS or private IP networks.
B) GET VPN natively supports MPLS and private IP networks is CORRECT.
This is the core benefit and design goal of GET VPN. In a traditional IPsec VPN, tunnels are built between the edges of the network, which can break the native routing and multicast capabilities of the underlying WAN. GET VPN operates differently:
It encrypts the payload but leaves the original IP headers intact.
This allows the traffic to be routed natively across the MPLS or private IP cloud.
It preserves multicast functionality because the original multicast group addresses are still visible to the network core.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A) GET VPN supports Remote Access VPNs is INCORRECT.
GET VPN is strictly a site-to-site technology. FlexVPN, on the other hand, is a unified VPN solution that supports both site-to-site and remote access (client-based) VPNs.
C) GET VPN uses multiple security associations for connections is INCORRECT.
This is a characteristic of many VPNs and is not a unique benefit of GET VPN. In fact, a key feature of GET VPN is its use of a Group Security Association (GSA), which is a single, shared security association for the entire group, simplifying key management.
D) GET VPN interoperates with non-Cisco devices is INCORRECT.
GET VPN is a Cisco-proprietary technology. FlexVPN, which is based on IKEv2, has much better interoperability with non-Cisco devices that support standard IKEv2.
Reference:
Cisco GET VPN Design and Implementation Guides: These guides consistently highlight the technology's purpose of providing "end-to-end data confidentiality in a native mode" for "enterprise WANs built on a private IP or MPLS infrastructure."
Refer to the exhibit.

What does this Python script accomplish?
A.
It allows authentication with TLSv1 SSL protocol
B.
It authenticates to a Cisco ISE with an SSH connection
C.
lt authenticates to a Cisco ISE server using the username of ersad
D.
It lists the LDAP users from the external identity store configured on Cisco ISE
lt authenticates to a Cisco ISE server using the username of ersad
What is the process of performing automated static and dynamic analysis of files against
preloaded
behavioral indicators for threat analysis?
A.
deep visibility scan
B.
point-in-time checks
C.
advanced sandboxing
D.
advanced scanning
advanced sandboxing
An organization is implementing AAA for their users. They need to ensure that
authorization is verified for every command that is being entered by the network
administrator. Which protocol must be configured in order to provide this capability?
A.
EAPOL
B.
SSH
C.
RADIUS
D.
TACACS+
RADIUS
Cisco SensorBase gaihers threat information from a variety of Cisco products and services
and performs analytics to find patterns on threats Which term describes this process?
A.
deployment
B.
consumption
C.
authoring
D.
sharing
consumption
Explanation for Each Option:
A. deployment (Incorrect):
Deployment refers to the process of installing, configuring, or rolling out Cisco products and services, such as sensors or security appliances, across a network. While Cisco SensorBase relies on data from deployed devices, the term does not describe the analytical process of gathering threat information and identifying patterns, making this option incorrect for the described scenario. (Reference: Cisco Security Solutions Overview, Deployment Strategies.)
B. consumption (Correct):
Consumption in this context refers to the process by which Cisco SensorBase collects and analyzes threat data from various Cisco products and services, such as firewalls, IPS, and web gateways. It processes this data to detect patterns and generate actionable threat intelligence, which is then used to enhance security. This aligns with the analytics and pattern-finding described. (Reference: Cisco SensorBase Data Sheet, Threat Intelligence.)
C. authoring (Incorrect):
Authoring typically involves creating or writing content, such as security policies, signatures, or documentation. Cisco SensorBase does not focus on creating threat data from scratch but rather aggregates and analyzes existing data from Cisco devices. This term is unrelated to the analytics and pattern recognition process, making it an incorrect choice. (Reference: Cisco SecureX Overview, Policy Authoring.)
D. sharing (Incorrect):
Sharing implies distributing or exchanging threat intelligence with other systems, partners, or users, which Cisco SensorBase may do after analysis. However, the question focuses on the internal process of gathering data and performing analytics to find patterns, not the subsequent distribution. Thus, sharing describes an outcome, not the core process, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco Threat Intelligence Sharing, Collaboration.)
Additional Notes:
Cisco SensorBase is a cloud-based threat intelligence system covered in the 350-701 SCOR exam under network security and threat intelligence. As of 04:18 PM PKT, October 01, 2025, it remains a key component of Cisco’s security ecosystem. For more details, refer to the Cisco SensorBase Data Sheet (cisco.com) and the 350-701 Exam Blueprint (Section 1.0 Security Concepts). More questions?
| Page 27 out of 61 Pages |
| 18192021222324252627282930313233343536 |
| 350-701 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our 350-701 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies (SCOR 350-701) exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive 350-701 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.