Topic 1: Exam Pool A
Which information is required when adding a device to Firepower Management Center?
A. username and password
B. encryption method
C. device serial number
D. registration key
Explanation
Cisco Container Platform (CCP) was a Kubernetes-based platform designed to simplify the deployment and management of containerized applications. Its value proposition for customers using cloud service providers was centered around consistency and management.
A. Allows developers to create code once and deploy to multiple clouds:
This describes the concept of hybrid cloud portability. CCP provided a consistent Kubernetes layer on top of different infrastructures, including various cloud service providers (like AWS, Azure) and on-premises environments. This meant developers could package their application into containers and deploy it to any environment supported by CCP without rewriting the underlying deployment logic, avoiding "cloud vendor lock-in."
D. manages Kubernetes clusters:
This was the core function of CCP. It automated the complex process of provisioning, scaling, upgrading, and maintaining the entire Kubernetes cluster lifecycle (including the master and worker nodes). This relieved operational teams from the heavy lifting of manually managing Kubernetes, allowing them to focus on the applications running on the clusters.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. helps maintain source code for cloud deployments:
CCP operated at the application deployment and orchestration layer (containers and Kubernetes). It did not interact with or manage the application's source code, which is the domain of source code repositories (like GitLab, GitHub) and CI/CD pipelines.
C. manages Docker containers:
This is misleading. While CCP uses Docker containers (or other container runtimes), it does not manage individual containers. It manages them at a higher level of abstraction by orchestrating them with Kubernetes. Kubernetes is the system that manages the containers; CCP manages the Kubernetes clusters themselves.
E. Creates complex tasks for managing code:
This is the direct opposite of CCP's purpose. The platform was designed to reduce complexity and automate tasks, not create them.
Important Note:
*As mentioned previously, Cisco announced the End-of-Life (EOL) for the Cisco Container Platform (CCP) in 2021. However, for the purpose of the 350-701 SCOR exam, which may reference this product, A and D remain the historically correct answers.*
In which scenario is endpoint-based security the solution?
A. inspecting encrypted traffic
B. device profiling and authorization
C. performing signature-based application control
D. inspecting a password-protected archive
Explanation:
Endpoint-based security refers to security software installed directly on a device (like a laptop, server, or mobile phone), such as Cisco Secure Endpoint (formerly AMP for Endpoints). This software has deep visibility into the activities on that specific host.
Let's analyze why this is the correct scenario and why the others are better handled by other security tools:
Why Option C is Correct:
Signature-based application control is a classic function of endpoint protection. The security agent on the endpoint can monitor all processes and applications running on the system. It can compare these applications against a database of known malicious software signatures (or hashes) and block them from executing. Because the agent resides directly on the system where the applications run, it has the perfect vantage point to perform this control effectively.
Why the Other Options are Incorrect:
Why Option A is Incorrect:
Inspecting encrypted traffic (like HTTPS) is primarily the role of a network-based security appliance, not an endpoint agent. While an endpoint agent can see the decrypted traffic after it has been processed by the web browser on the machine, the heavy lifting of decrypting, inspecting, and re-encrypting traffic in transit is typically done by a firewall, IPS, or secure web gateway. Some endpoint agents can perform limited inspection, but it is not their primary strength.
Why Option B is Incorrect:
Device profiling and authorization is a function of network access control (NAC) systems like Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE). ISE uses information from network infrastructure (switches, wireless controllers) and may collect data from an endpoint agent, but the final decision on profiling (identifying the device type) and granting network access (authorization) is made by the central ISE policy engine, not the endpoint security software itself.
Why Option D is Incorrect:
Inspecting a password-protected archive (like a .zip or .rar file) is extremely difficult for any security solution. A network appliance cannot inspect the contents without the password. An endpoint-based solution has a significant advantage here. It can wait for the file to reach the endpoint, and if the user enters the password to open it, the endpoint agent can then scan the now-unpacked contents for malware. However, the question asks for the scenario where endpoint security is the solution. While it's the best available solution for this problem, it's not foolproof, as it relies on the user providing the password. The most clear-cut and definitive "solution" among the options is using the endpoint for signature-based application control.
Reference:
This falls under the Endpoint Protection and Detection domain. A core capability of any Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) or antivirus product is to control which applications can run on a host, which is fundamentally a task for software residing on that host.
Which category includes DoS Attacks?
A.
Virus attacks
B.
Trojan attacks
C.
Flood attacks
D.
Phishing attacks
Flood attacks
Which two mechanisms are used to control phishing attacks? (Choose two)
A. Enable browser alerts for fraudulent websites
B. Define security group memberships.
C. Revoke expired CRL of the websites.
D. Use antispyware software.
E. Implement email filtering techniques.
Explanation
Phishing attacks are social engineering attacks that trick users into revealing sensitive information, most commonly via deceptive emails that lead to fraudulent websites.
A. Enable browser alerts for fraudulent websites:
Modern web browsers integrate with services like Google Safe Browsing or Microsoft SmartScreen. These services maintain databases of known phishing websites. When this feature is enabled, the browser will display a prominent warning alert to the user before they access a site identified as fraudulent, giving them a chance to turn back. This is a direct control against the "landing" part of a phishing attack.
E. Implement email filtering techniques:
This is a primary defense against the "delivery" mechanism of phishing. Email security gateways (like Cisco Secure Email) use sophisticated techniques to filter incoming emails. They analyze sender reputation, check links against URL databases, inspect email content for phishing language, and use machine learning to identify and quarantine phishing emails before they ever reach the user's inbox.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. Define security group memberships:
This is related to network access control and authorization (e.g., using Cisco ISE). It determines what resources a user can access after they are authenticated. It does not prevent a user from being tricked by a phishing email into giving away their credentials in the first place.
C. Revoke expired CRL of the websites:
A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) is used to check if a website's SSL certificate has been revoked. This is a control for verifying the authenticity of a legitimate website that uses a certificate. It does not specifically protect against phishing, as phishing sites often use valid certificates for their own domains or use HTTP instead of HTTPS.
D. Use antispyware software:
Antispyware is designed to detect and remove spyware and other malicious software that may already be on a system. It is a reactive measure for malware that has been installed, often after a separate initial compromise. It is not a primary mechanism for preventing the social engineering and email delivery that defines a phishing attack.
Reference:
These controls are standard recommendations in cybersecurity frameworks for mitigating phishing. The CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency) and NIST guidelines for phishing prevention highlight email filtering and web browser security controls as essential first lines of defense.
What are two features of NetFlow flow monitoring? (Choose two)
A. Can track ingress and egress information
B. Include the flow record and the flow importer
C. Copies all ingress flow information to an interface
D. Does not required packet sampling on interfaces
E. Can be used to track multicast, MPLS, or bridged traffic
Explanation for Each Option:
A. Can track ingress and egress information (Correct):
NetFlow flow monitoring tracks both ingress (incoming) and egress (outgoing) traffic on an interface, providing detailed visibility into the direction of data flows. This is a key feature for understanding network traffic patterns, making it a correct choice. (Reference: Cisco NetFlow Configuration Guide, Ingress/Egress Tracking.)
B. Include the flow record and the flow importer (Incorrect):
While NetFlow involves flow records (data collected about flows) and a flow exporter (which sends data to a collector), the "flow importer" is not a standard term. The correct component is the flow collector, and this option misrepresents the feature, rendering it incorrect. (Reference: Cisco NetFlow Components Overview.)
C. Copies all ingress flow information to an interface (Incorrect):
NetFlow does not copy all ingress flow information to an interface; it samples and aggregates flow data based on configured parameters. This option suggests a full copy, which is inaccurate and not a feature of NetFlow, making it incorrect. (Reference: Cisco NetFlow Sampling Guide.)
D. Does not required packet sampling on interfaces (Incorrect):
NetFlow often requires packet sampling (e.g., using NetFlow sampling or sFlow) to manage high traffic volumes, especially on busy interfaces. The statement is false, as sampling is a common requirement, rendering this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco NetFlow Sampling Configuration.)
E. Can be used to track multicast, MPLS, or bridged traffic (Correct):
NetFlow supports monitoring of multicast, MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), and bridged traffic, providing visibility into these specialized traffic types. This flexibility is a valuable feature, making it a correct choice. (Reference: Cisco NetFlow Advanced Features Guide, Multicast/MPLS Support.)
Additional Notes:
Understanding NetFlow features is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under network security. As of 3:50 PM PKT, October 03, 2025, its tracking capabilities are critical for monitoring.
Drag and drop the concepts from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right:
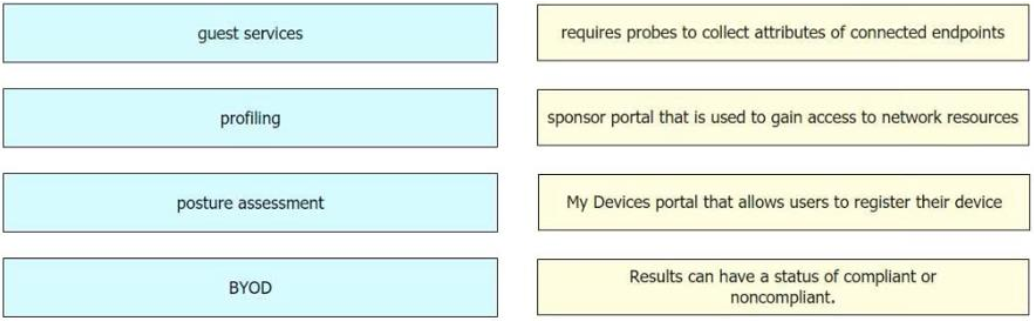
What is a characteristic of a bridge group in ASA Firewall transparent mode?
A.
It includes multiple interfaces and access rules between interfaces are customizable
B.
It is a Layer 3 segment and includes one port and customizable access rules
C.
It allows ARP traffic with a single access rule
D.
It has an IP address on its BVI interface and is used for management traffic
It includes multiple interfaces and access rules between interfaces are customizable
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/asa/asa95/configuration/general/asa-95- generalconfig/intro-fw.htmlNote: BVI interface is not used for management purpose. But we can add a separate Management slot/port interface that is not part of any bridge group, and that allows only management traffic to the ASA.
Which two criteria must a certificate meet before the WSA uses it to decrypt application traffic? (Choose two.)
A. It must include the current date.
B. It must reside in the trusted store of the WSA.
C. It must reside in the trusted store of the endpoint.
D. It must have been signed by an internal CA.
E. it must contain a SAN.
Explanation:
For the WSA to perform SSL decryption (acting as a man-in-the-middle), it must dynamically generate a certificate for the website the user is visiting. For this to work without causing security errors in the user's browser, the certificate used to sign these dynamic certificates must meet specific criteria.
Let's break down why B and E are correct:
B) It must reside in the trusted store of the WSA.
This is CORRECT. The WSA needs the root Certificate Authority (CA) certificate or the intermediate CA certificate to sign the dynamically generated certificates it presents to users. This signing certificate must be installed in the WSA's local trusted certificate store so it can be used for this purpose.
E) It must contain a SAN. This is CORRECT.
A Subject Alternative Name (SAN) is a critical extension in an X.509 certificate that allows a single certificate to secure multiple domain names. Modern browsers require the SAN field to match the domain name being accessed. If the WSA's signing certificate does not have a SAN, the dynamically generated certificates it creates will be missing this field, causing browsers to display certificate warnings and block the connection.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A) It must include the current date. This is INCORRECT.
While it is a fundamental requirement for any valid certificate to be within its validity period (not before/not after dates), this is a generic requirement for all certificates, not a specific criterion for the WSA's decryption certificate.
C) It must reside in the trusted store of the endpoint.
This is a tricky one but is INCORRECT in the context of what the question is asking. The certificate that must be in the endpoint's trusted store is the Root CA certificate that issued the WSA's signing certificate. The question asks about the certificate the WSA uses, which is the signing certificate (often an intermediate CA). The trust chain must ultimately lead to a root CA trusted by the endpoint, but the specific certificate the WSA uses does not itself need to be in the endpoint's store.
D) It must have been signed by an internal CA.
This is INCORRECT. While it is a very common and recommended practice to use an internally managed CA for this purpose (for security and control), it is not a strict technical requirement. The WSA can use a certificate from a public CA. However, this is highly discouraged for security and practical reasons (a public CA would not issue a certificate for another entity's domain).
Reference:
Cisco WSA AsyncOS Administration Guide for Web Security (SSL Decryption Chapter): The configuration guide for enabling SSL decryption explicitly states the requirement to upload a CA certificate and private key to the WSA and emphasizes that the certificate must contain X.509 v3 extensions, specifically the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field, to be compatible with modern browsers.
An engineer is trying to decide between using L2TP or GRE over IPsec for their site-to-site
VPN implementation. What must be un solution?
A.
L2TP is an IP packet encapsulation protocol, and GRE over IPsec is a tunneling protocol.
B.
L2TP uses TCP port 47 and GRE over IPsec uses UDP port 1701.
C.
GRE over IPsec adds its own header, and L2TP does not.
D.
GRE over IPsec cannot be used as a standalone protocol, and L2TP can.
GRE over IPsec cannot be used as a standalone protocol, and L2TP can.
What two mechanisms are used to redirect users to a web portal to authenticate to ISE for guest services?
(Choose two)
A.
multiple factor auth
B.
local web auth
C.
single sign-on
D.
central web auth
E.
TACACS+
local web auth
central web auth
What is the process In DevSecOps where all changes In the central code repository are
merged and synchronized?
A.
CD
B.
EP
C.
CI
D.
QA
CI
Which two parameters are used to prevent a data breach in the cloud? (Choose two.)
A. DLP solutions
B. strong user authentication
C. encryption
D. complex cloud-based web proxies
E. antispoofing programs
Explanation for Each Option:
A. DLP solutions (Correct):
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions monitor, detect, and prevent unauthorized data exfiltration from the cloud by enforcing policies on sensitive data (e.g., PII, financial records). This directly mitigates data breaches by controlling data movement, making it a key parameter. (Reference: Cisco Secure Cloud DLP Features.)
B. strong user authentication (Correct):
Strong user authentication, such as multifactor authentication (MFA), ensures only authorized users access cloud resources. By reducing the risk of credential-based attacks (e.g., phishing), it prevents unauthorized access that could lead to data breaches, making it an essential parameter. (Reference: Cisco Cloud Security Best Practices, MFA.)
C. encryption (Incorrect):
Encryption protects data at rest and in transit, enhancing security, but it is a protective measure rather than a preventive parameter against breaches. If access is already compromised, encryption alone cannot stop data exfiltration, making it a supporting rather than primary factor. (Reference: Cisco Cloud Encryption Guide.)
D. complex cloud-based web proxies (Incorrect):
Complex cloud-based web proxies (e.g., for filtering or caching) improve performance and security but are not specifically designed to prevent data breaches. They address web traffic management, not direct data loss prevention or access control, rendering this option less relevant. (Reference: Cisco Umbrella Proxy Features.)
E. antispoofing programs (Incorrect):
Antispoofing programs prevent IP spoofing in network attacks (e.g., DDoS), which is valuable for network security but not a primary measure against cloud data breaches. They do not address insider threats or data exfiltration, making this option incorrect for the context. (Reference: Cisco Secure Firewall Antispoofing.)
Additional Notes:
Preventing cloud data breaches is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under cloud security. As of 12:30 PM PKT, October 03, 2025, DLP and authentication are critical defenses.
| Page 24 out of 61 Pages |
| 15161718192021222324252627282930313233 |
| 350-701 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our 350-701 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies (SCOR 350-701) exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive 350-701 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.