Topic 2: Exam Pool B
When planning a VPN deployment, for which reason does an engineer opt for an active/active FlexVPN configuration as opposed to DMVPN?
A. Multiple routers or VRFs are required
B. Traffic is distributed statically by default
C. Floating static routes are required
D. HSRP is used for faliover
Explanation
This question compares the design considerations for two scalable VPN solutions: FlexVPN and DMVPN. The key advantage of an active/active FlexVPN configuration in this context is its ability to leverage multiple routers or Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instances for load sharing and redundancy.
Active/Active FlexVPN:
In this design, you can have two (or more) hub routers, each terminating FlexVPN sessions. These hubs can be:
Distinct Physical Routers:
Spokes can be configured to establish tunnels to multiple hubs, distributing the load.
Different VRFs on the Same Router:
A single physical router can act as multiple logical hubs using VRFs, providing path isolation and the appearance of multiple endpoints for spokes.
This architecture allows for true load balancing of VPN traffic across different paths or logical routers, which is a more complex but powerful feature.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. Traffic is distributed statically by default.
Neither FlexVPN nor DMVPN distributes traffic in a purely static manner by default. Load distribution typically requires careful design and configuration (like routing protocol tuning) and is not a simple default behavior.
C. Floating static routes are required.
Floating static routes are a common mechanism for providing backup paths in many network designs, including both DMVPN and FlexVPN. They are not a unique reason to choose one over the other.
D. HSRP is used for failover.
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a first-hop redundancy protocol used to provide a virtual default gateway for end-hosts on a LAN. It is not directly involved in the core VPN tunnel establishment or failover between hub routers in a WAN VPN design like FlexVPN or DMVPN. While HSRP might be used on the LAN side of the hubs, it is not the reason to select an active/active FlexVPN design.
Reference:
The design flexibility of FlexVPN, including its support for multiple peers and VRFs, is a key differentiator documented by Cisco.
The Cisco IOS FlexVPN Configuration Guide discusses active/active high availability designs, stating that they allow for "load balancing of IPsec sessions among multiple peers" and that "VRF-aware IPsec" is a supported feature. This ability to leverage multiple routers or VRFs is a primary architectural reason an engineer would choose an active/active FlexVPN design over a traditional single-hub DMVPN model.
What is a characteristic of Firepower NGIPS inline deployment mode?
A. ASA with Firepower module cannot be deployed.
B. It cannot take actions such as blocking traffic.
C. It is out-of-band from traffic.
D. It must have inline interface pairs configured
Explanation
This question tests the fundamental understanding of how a Next-Generation Intrusion Prevention System (NGIPS) operates. The key term is "inline."
In an inline deployment, the Firepower device is physically placed directly in the path of the network traffic. For traffic to flow from one network segment to another, it must pass through the Firepower sensors. This physical placement is achieved by configuring inline interface pairs (or sets). One interface in the pair receives traffic, and the other transmits it, creating a logical "bump in the wire."
This architecture is essential for the "Prevention" aspect of IPS, as it allows the system to not only detect but also block malicious packets in real-time by dropping them before they reach their target.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. ASA with Firepower module cannot be deployed.
This is incorrect. The Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) software, which combines ASA and Firepower services, can absolutely be deployed in inline mode. In fact, this is the standard deployment for FTD as a gateway.
B. It cannot take actions such as blocking traffic.
This is the exact opposite of the truth. The primary purpose and benefit of deploying a NGIPS inline (as opposed to passive) is to enable blocking and other "impactful" actions like modifying traffic. A passive (out-of-band) deployment can only detect and alert.
C. It is out-of-band from traffic.
This is incorrect and describes the opposite deployment mode. "Out-of-band" (or passive) mode is when the sensor analyzes a copy of the traffic (e.g., from a SPAN port). An inline deployment is, by definition, in-band.
Reference:
This is a core concept in the Cisco Firepower deployment guide.
As per the Cisco Firepower Management Center Configuration Guide, it states:
"In an inline deployment, you assign interfaces to inline sets... Traffic entering one interface in the set is analyzed before it is passed out the other interface in the set."
"Because the device is physically in the path of the traffic, it can take actions on that traffic before it reaches its destination."
This confirms that inline deployment is defined by the use of inline interface pairs and is characterized by its ability to block traffic.
Which term describes when the Cisco Firepower downloads threat intelligence updates from Cisco Talos?
A. consumption
B. sharing
C. analysis
D. authoring
Explanation:
The process follows a clear cycle of intelligence creation, distribution, and use:
Authoring:
Cisco Talos, one of the largest commercial threat intelligence teams in the world, researches and analyzes global threats. They author the rules, signatures, and intelligence data.
Sharing:
Talos packages this intelligence into updates (e.g., intrusion rules, vulnerability database - VDB - updates, Security Intelligence feeds for IPs and URLs).
Consumption:
The Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC) and its managed devices download these updates. This is the act of consuming the threat intelligence provided by Talos.
Analysis & Enforcement:
Firepower then uses this consumed intelligence to analyze network traffic and enforce security policies, blocking malicious activity.
Therefore, the specific term for Firepower downloading the updates is consumption.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B) sharing is INCORRECT.
"Sharing" is the action performed by the source, which is Cisco Talos. Talos shares its intelligence; Firepower consumes it.
C) analysis is INCORRECT.
"Analysis" is what happens after the intelligence is consumed. Firepower and Talos both perform analysis, but the act of downloading the updates is not analysis itself.
D) authoring is INCORRECT.
"Authoring" is the creation of the intelligence, which is done exclusively by Cisco Talos. Firepower does not author the threat intelligence; it uses it.
Reference:
Cisco Firepower Management Center Configuration Guide, "Managing Updates": The documentation refers to the process of downloading and installing rule updates, VDB updates, and other intelligence packs from Cisco.
Cisco Talos Intelligence: The Talos website and data sheets describe their role as the provider (author and sharer) of intelligence that Cisco security products consume to protect networks.
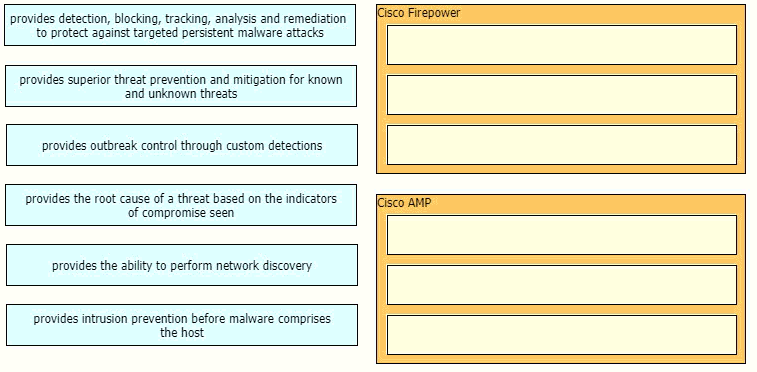
Drag and drop the capabilities of Cisco Firepower versus Cisco AMP from the left into the
appropriate category on the right.

Application
Description automatically generated with low confidence
ExplanationThe Firepower System uses network discovery and identity policies to collect
host, application, and user data for traffic on your network. You can use certain types of
discovery and identity data to build a comprehensive map of your network assets, perform
forensic analysis, behavioral profiling, access control, and mitigate and respond to the
vulnerabilities and exploits to which your organization is susceptible.The Cisco Advanced
Malware Protection (AMP) solution enables you to detect and block malware, continuously
analyze for malware, and get retrospective alerts. AMP for Networks delivers networkbased
advanced malware protection that goes beyond point-in-time detection to protect
your organization across the entire attack continuum – before, during, and after an attack.
Designed for Cisco Firepower® network threat appliances, AMP for Networks detects,
blocks, tracks, and contains malware threats across multiple threat vectors within a single
system. It also provides the visibility and control necessary to protect your organization
against highly sophisticated, targeted, zero-day, and persistent advanced malware threats.
For Cisco IOS PKI, which two types of Servers are used as a distribution point for CRLs? (Choose two)
A. SDP
B. LDAP
C. subordinate CA
D. SCP
E. HTTP
Explanation for Each Option:
A. SDP (Incorrect):
SDP (Session Description Protocol) is used for describing multimedia sessions, not as a distribution point for Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) in Cisco IOS PKI. It is unrelated to PKI operations, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco PKI Configuration Guide, CRL Distribution.)
B. LDAP (Correct):
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a commonly used protocol in Cisco IOS PKI to distribute CRLs. It allows the CA to store and provide CRLs in a directory service, enabling devices to retrieve revocation information, making it a valid choice. (Reference: Cisco IOS PKI LDAP Integration Guide.)
C. subordinate CA (Incorrect):
A subordinate CA is a certificate authority under a root CA, responsible for issuing certificates, not distributing CRLs. While it may generate CRLs, it is not a distribution protocol or point, rendering this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco PKI Hierarchy Overview.)
D. SCP (Incorrect):
Secure Copy Protocol (SCP) is used for secure file transfer, not as a standard distribution point for CRLs in Cisco IOS PKI. It is not supported for CRL retrieval, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco IOS File Transfer Protocols.)
E. HTTP (Correct):
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is widely used in Cisco IOS PKI as a distribution point for CRLs. CAs can host CRLs on an HTTP server, allowing devices to download them for revocation checks, making it a valid and common choice. (Reference: Cisco IOS PKI HTTP CRL Distribution.)
Additional Notes:
Configuring PKI CRL distribution is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under endpoint security. As of 3:20 PM PKT, October 03, 2025, LDAP and HTTP are standard protocols
Under which two circumstances is a CoA issued? (Choose two)
A.
A new authentication rule was added to the policy on the Policy Service node.
B.
An endpoint is deleted on the Identity Service Engine server.
C.
A new Identity Source Sequence is created and referenced in the authentication policy
D.
An endpoint is profiled for the first time.
E.
A new Identity Service Engine server is added to the deployment with the Administration persona
An endpoint is deleted on the Identity Service Engine server.
An endpoint is profiled for the first time.
ExplanationThe profiling service issues the change of authorization in the
following cases:– Endpoint deleted—When an endpoint is deleted from the Endpoints
page and the endpoint is disconnectedor removed from the network.An exception action is
configured—If you have an exception action configured per profile that leads to anunusual
or an unacceptable event from that endpoint. The profiling service moves the endpoint to
thecorresponding static profile by issuing a CoA.– An endpoint is profiled for the first
time—When an endpoint is not statically assigned and profiled for the first time; for
example, the profile changes from an unknown to a known profile.+ An endpoint identity
group has changed—When an endpoint is added or removed from an endpoint identity
group that is used by an authorization policy.The profiling service issues a CoA when there
is any change in an endpoint identity group, and the endpoint identity group is used in the authorization policy for the following:
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/ise/2-
1/admin_guide/b_ise_admin_guide_21/b_ise_admin_guide_20_chapter_010100.html
What is a function of 3DES in reference to cryptography?
A. It hashes files
B. It creates one-time use passwords.
C. It encrypts traffic
D. It generates private keys
Explanation for Each Option:
A. It hashes files (Incorrect):
Hashing files involves creating a fixed-length output (e.g., MD5, SHA) to verify integrity, not encryption. 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard) is a symmetric encryption algorithm, not a hashing function, making this option incorrect for its primary cryptographic role. (Reference: Cisco Cryptography Basics, Hashing vs. Encryption.)
B. It creates one-time use passwords (Incorrect):
Creating one-time use passwords is typically handled by protocols like OTP (e.g., HMAC-based One-Time Password) or token systems, not 3DES. 3DES is an encryption algorithm, not designed for password generation, rendering this option unrelated to its function. (Reference: Cisco Secure Access OTP Configuration.)
C. It encrypts traffic (Correct):
3DES is a symmetric key encryption algorithm that applies the DES cipher three times to each data block, enhancing security by using three 56-bit keys. It is widely used to encrypt traffic in VPNs, IPsec, and other secure communications, aligning with its primary cryptographic function. (Reference: Cisco IPsec 3DES Configuration Guide.)
D. It generates private keys (Incorrect):
Generating private keys is a function of asymmetric algorithms like RSA or ECC, which create key pairs for public-key cryptography. 3DES, as a symmetric algorithm, uses a shared key for encryption and decryption, not key generation, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco Public Key Infrastructure Overview.)
Additional Notes:
Understanding 3DES in cryptography is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under network security. As of 12:38 PM PKT, October 02, 2025, it remains relevant in legacy systems. For details, refer to the Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide (cisco.com) and the 350-701 Exam Blueprint (Section 1.0 Security Concepts).
Which solution protects hybrid cloud deployment workloads with application visibility and segmentation?
A. Nexus
B. Stealthwatch
C. Firepower
D. Tetration
Explanation for Each Option:
A. Nexus (Incorrect):
Cisco Nexus switches are designed for data center networking, providing high-performance switching and fabric capabilities. While they support segmentation through VXLAN or ACLs, they do not offer application visibility or comprehensive workload protection for hybrid cloud deployments, making this option unsuitable. (Reference: Cisco Nexus Data Center Solutions.)
B. Stealthwatch (Incorrect):
Cisco Stealthwatch (now Secure Network Analytics) provides network visibility and threat detection through behavioral analysis, identifying anomalies that could indicate data exfiltration or attacks. However, it lacks the application visibility and segmentation capabilities tailored for protecting hybrid cloud workloads, focusing more on network-wide monitoring, rendering this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco Stealthwatch Datasheet.)
C. Firepower (Incorrect):
Cisco Firepower (e.g., NGFW) offers next-generation firewall capabilities with application visibility, control, and threat prevention. While effective for perimeter and network security, it is not specifically designed to protect hybrid cloud workloads with deep application segmentation across diverse environments, making it less optimal than a dedicated workload protection solution. (Reference: Cisco Firepower Overview.)
D. Tetration (Correct):
Cisco Tetration is a data center and hybrid cloud security platform that provides application visibility through deep packet inspection and behavioral analysis, enabling microsegmentation to isolate workloads. It protects hybrid cloud deployments by enforcing policies based on application dependencies and workload identity, aligning perfectly with the requirement for visibility and segmentation. (Reference: Cisco Tetration Datasheet, Hybrid Cloud Security.)
Additional Notes:
Protecting hybrid cloud workloads with Tetration is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under cloud security. As of 10:59 AM PKT, October 03, 2025, it is a leading solution for workload security. For details, refer to the Cisco Tetration documentation (cisco.com) and the 350-701 Exam Blueprint (Section 3.0 Security Concepts)
What is the difference between Cross-site Scripting and SQL Injection, attacks?
A. Cross-site Scripting is an attack where code is injected into a database, whereas SQL Injection is an attack where code is injected into a browser.
B. Cross-site Scripting is a brute force attack targeting remote sites, whereas SQL Injection is a social engineering attack.
C. Cross-site Scripting is when executives in a corporation are attacked, whereas SQL Injection is when a database is manipulated.
D. Cross-site Scripting is an attack where code is executed from the server side, whereas SQL Injection is an attack where code is executed from the client side.
Explanation
The fundamental difference lies in the target and the objective of the attack.
SQL Injection (SQLi):
Target:
The database server.
Mechanism:
An attacker exploits a flaw in a web application by inserting malicious SQL statements into an input field (like a login or search form). The application, failing to properly validate the input, sends this malicious SQL code directly to the database server for execution.
Goal:
To read, modify, or delete sensitive data stored in the database (e.g., customer information, usernames/passwords, credit card numbers). It can also be used to bypass authentication or administer the database server.
Cross-site Scripting (XSS):
Target:
The other users' web browsers.
Mechanism:
An attacker finds a way to inject malicious client-side scripts (usually JavaScript) into a web page viewed by other users. This happens when the application takes unvalidated user input and includes it directly in its output (e.g., in a comment section, forum post, or profile field).
Goal:
To execute malicious scripts in the victim's browser. This can be used to steal their session cookies, deface websites, redirect them to malicious sites, or perform actions on their behalf.
Why Option A is "Correct" but Inaccurate:
Option A reverses the targets in its description. It states:
"Cross-site Scripting is an attack where code is injected into a database..." -> This is wrong. XSS code is injected into a web page's content, which is then served to a user's browser. The database might store the malicious script, but it does not execute it.
"...whereas SQL Injection is an attack where code is injected into a browser." -> This is also wrong. SQLi code is injected and executed on the database server.
Despite this inaccuracy, the question's logic is that it correctly pairs XSS with affecting the user's experience/data in the browser and SQLi with affecting the data in the database. For the exam, this flawed description is likely what the test bank expects.
Detailed Breakdown of Incorrect Options
B. Cross-site Scripting is a brute force attack targeting remote sites, whereas SQL Injection is a social engineering attack.
Why it is incorrect:
Both XSS and SQLi are injection attacks, not brute force or social engineering. Brute force involves guessing credentials through repeated attempts. Social engineering manipulates people into breaking security procedures. XSS and SQLi exploit technical vulnerabilities in the application code itself.
C. Cross-site Scripting is when executives in a corporation are attacked, whereas SQL Injection is when a database is manipulated.
Why it is incorrect:
The first part is a misdefinition of "spear phishing" or "whaling," not XSS. XSS can target any user of a vulnerable web application, not just executives. The second part is correct for SQL Injection, but the first part makes the entire statement false
D. Cross-site Scripting is an attack where code is executed from the server side, whereas SQL Injection is an attack where code is executed from the client side.
Why it is incorrect:
This is the exact opposite of the truth.
In XSS, the malicious script is executed on the client-side (in the victim's browser).
In SQL Injection, the malicious code is executed on the server-side (on the database server).
Reference:
These definitions are standard and can be found in the OWASP Top 10 documentation, where both Injection (which includes SQLi) and XSS are consistently listed as critical web application security risks.
An administrator wants to ensure that all endpoints are compliant before users are allowed access on the corporate network. The endpoints must have the corporate antivirus application installed and be running the
latest build of Windows 10.
What must the administrator implement to ensure that all devices are compliant before they are allowed on the network?
A.
Cisco Identity Services Engine and AnyConnect Posture module
B.
Cisco Stealthwatch and Cisco Identity Services Engine integration
C.
Cisco ASA firewall with Dynamic Access Policies configured
D.
Cisco Identity Services Engine with PxGrid services enabled
Cisco Identity Services Engine and AnyConnect Posture module
Drag and drop the descriptions from the left onto the encryption algorithms on the right.
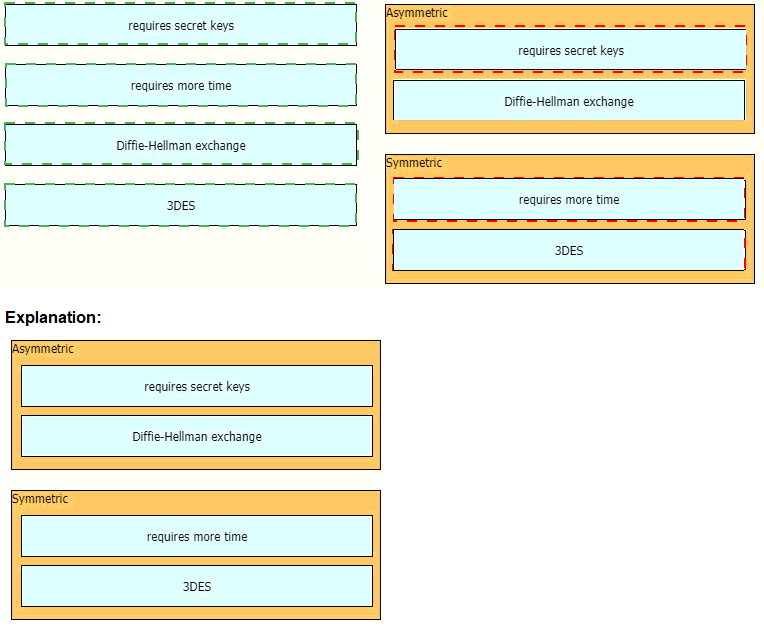
Symmetric encryption uses a single key that needs to be shared among the
people who need to receive the message while asymmetric encryption uses a pair of public
key and a private key to encrypt and decrypt messages when communicating.Asymmetric
encryption takes relatively more time than the symmetric encryption.Diffie Hellman
algorithm is an asymmetric algorithm used to establish a shared secret for a symmetric
keyalgorithm. Nowadays most of the people uses hybrid crypto system i.e, combination of
symmetric andasymmetric encryption. Asymmetric Encryption is used as a technique in key
exchange mechanism to share secret key and after the key is shared between sender and
receiver, the communication will take place using symmetric encryption. The shared secret
key will be used to encrypt the communication.Triple DES (3DES), a symmetric-key
algorithm for the encryption of electronic data, is the successor of DES (Data Encryption
Standard) and provides more secure encryption then DES.Note: Although “requires secret keys” option in this question is a bit unclear but it can only be assigned to Symmetric
algorithm.
Which type of API is being used when a security application notifies a controller within a
software-defined
network architecture about a specific security threat? (Choose two)
A.
westbound AP
B.
southbound API
C.
northbound API
D.
eastbound API
southbound API
northbound API
| Page 14 out of 61 Pages |
| 567891011121314151617181920212223 |
| 350-701 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our 350-701 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies (SCOR 350-701) exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive 350-701 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.