Topic 2: Exam Pool B
A network administrator is configuring SNMPv3 on a new router. The users have already been created; however, an additional configuration is needed to facilitate access to the SNMP views. What must the administrator do to accomplish this?
A. map SNMPv3 users to SNMP views
B. set the password to be used for SNMPv3 authentication
C. define the encryption algorithm to be used by SNMPv3
D. specify the UDP port used by SNMP
Explanation for Each Option:
A. map SNMPv3 users to SNMP views (Correct):
In SNMPv3, after creating users, administrators must map them to specific SNMP views to control access to subsets of the Management Information Base (MIB). This is done using the snmp-server group and snmp-server view commands to associate users with views, ensuring they can only access authorized data, meeting the requirement. (Reference: Cisco IOS SNMPv3 Configuration Guide, View Mapping.)
B. set the password to be used for SNMPv3 authentication (Incorrect):
Setting a password (e.g., via the auth keyword with a hash like SHA) is part of the initial user creation process (e.g., snmp-server user username group auth sha password), which is already completed. The question focuses on facilitating access to views, not reconfiguring authentication, making this option irrelevant. (Reference: Cisco SNMPv3 User Configuration.)
C. define the encryption algorithm to be used by SNMPv3 (Incorrect):
Defining the encryption algorithm (e.g., AES 256 with the priv keyword) is also part of the user creation process and is already configured. The task requires additional configuration for view access, not encryption settings, rendering this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco SNMPv3 Privacy Settings.)
D. specify the UDP port used by SNMP (Incorrect):
SNMP typically uses UDP port 161 for traps and 162 for notifications, and changing the port is not a standard requirement for view access. The default port is sufficient, and the focus is on view mapping, not port configuration, making this option unnecessary. (Reference: Cisco SNMP Port Configuration Guide.)
Additional Notes:
Configuring SNMPv3 views is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under network security. As of 12:10 PM PKT, October 03, 2025, view mapping enhances access control.
How does Cisco Umbrella archive logs to an enterprise owned storage?
A. by using the Application Programming Interface to fetch the logs
B. by sending logs via syslog to an on-premises or cloud-based syslog server
C. by the system administrator downloading the logs from the Cisco Umbrella web portal
D. by being configured to send logs to a self-managed AWS S3 bucket
Explanation
Cisco Umbrella provides several methods for exporting log data for long-term storage, archiving, and integration with on-premises SIEM systems. The key phrase in the question is "archive logs to an enterprise owned storage."
D. by being configured to send logs to a self-managed AWS S3 bucket:
This is the correct and most direct method for archiving to enterprise-owned storage. In the Umbrella dashboard, you can configure a setting called "Log Destinations" where you specify the details of your own (self-managed) Amazon S3 bucket. Once configured, Umbrella will automatically and continuously stream logs directly to your S3 bucket, which you fully control and own. This meets the requirement for enterprise-owned storage, even though it resides in a public cloud.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. by using the Application Programming Interface to fetch the logs:
While Umbrella does have a Reporting API that can be used to query and retrieve data, this is not the primary or recommended method for archiving large volumes of raw logs. The API is better suited for pulling specific, aggregated data for custom dashboards or applications, not for the continuous, bulk transfer required for archiving.
B. by sending logs via syslog to an on-premises or cloud-based syslog server:
This is a valid and common method for sending logs to a SIEM (like Splunk or ArcSight) for real-time analysis and correlation. However, it is generally not considered the best practice for pure archiving. Syslog can be susceptible to network interruptions, and the storage behind the syslog server is managed separately. The question specifically asks for the method to archive to enterprise-owned storage, and while this could be used, the S3 method (Option D) is the more direct, scalable, and recommended solution for this specific purpose.
C. by the system administrator downloading the logs from the Cisco Umbrella web portal:
This is a manual process. The web portal only allows for downloading logs for a limited, recent time window (e.g., the last 7-30 days depending on the license). This is useful for ad-hoc investigations but is completely impractical for automated, continuous archiving of all log data, which is the goal of an archiving solution.
Reference:
This functionality is documented in the Cisco Umbrella administrator guide under log management and configuration.
Cisco Umbrella Documentation: "Add S3 Bucket as Log Destination": This section provides step-by-step instructions on how to configure Umbrella to send logs to a customer-owned Amazon S3 bucket. This is explicitly the service's built-in mechanism for long-term log archiving to a location controlled by the enterprise.
In summary, while other methods exist for log export or forwarding, the configured, automatic delivery to a self-managed S3 bucket is the standard and recommended way to archive Cisco Umbrella logs to enterprise-owned storage.
Refer to the exhibit.
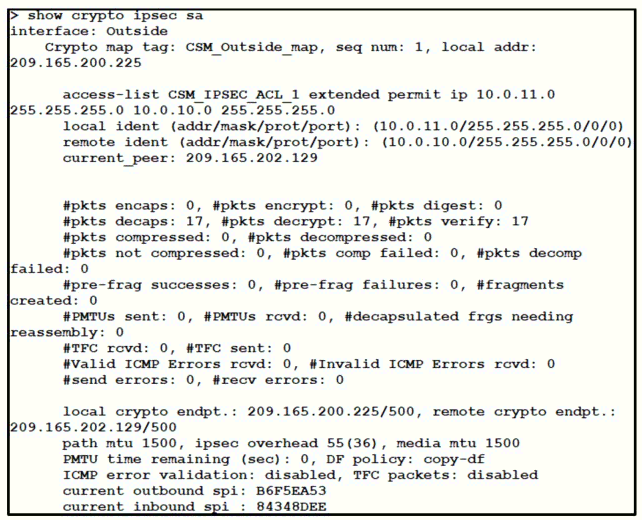
Traffic is not passing through IPsec site-to-site VPN on the Firepower Threat Defense
appliance. What is causing this issue?
A.
No split-tunnel policy is defined on the Firepower Threat Defense appliance
B.
The access control policy is not allowing VPN traffic in.
C.
Site-to-site VPN peers are using different encryption algorithms.
D.
Site-to-site VPN preshared keys are mismatched
No split-tunnel policy is defined on the Firepower Threat Defense appliance
A network administrator configures Dynamic ARP Inspection on a switch. After Dynamic ARP Inspection is applied, all users on that switch are unable to communicate with any destination. The network administrator checks the interface status of all interfaces, and there is no err-disabled interface. What is causing this problem?
A. DHCP snooping has not been enabled on all VLANs
B. The ip arp inspection limit command is applied on all interfaces and is blocking the traffic of all users.
C. Dynamic ARP Inspection has not been enabled on all VLANs
D. The no ip arp inspection trust command is applied on all user host interfaces
Explanation:
Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) is a security feature that validates ARP packets in a network. It relies on the DHCP Snooping binding database to distinguish between legitimate and malicious ARP packets.
The key to this scenario is the trust state of the switch interfaces.
Trusted Interfaces:
DAI forwards all ARP packets received on these interfaces without inspection. These are typically interfaces connected to other switches, routers, or reliable infrastructure.
Untrusted Interfaces:
DAI intercepts and validates all ARP packets received on these interfaces. The validation checks if the ARP packet's IP-to-MAC binding matches an entry in the DHCP Snooping binding database. If there is no match, the ARP packet is dropped.
Let's analyze the options:
Why Option D is Correct:
If the no ip arp inspection trust command is applied to all interfaces connecting to user hosts, it means all user-facing ports are untrusted. When a user's computer sends a gratuitous ARP or an ARP request/reply, DAI will check it against the DHCP Snooping binding table. If the binding isn't found (which is highly likely in this universal failure scenario), the ARP packet is dropped. Without successful ARP, a device cannot resolve an IP address to a MAC address, making all IP communication impossible. The problem is not err-disabled interfaces; it's that the legitimate ARP packets necessary for communication are being silently discarded.
Why Option A is Incorrect:
While DAI does require DHCP Snooping to build its binding table, if DHCP Snooping were not enabled, DAI would not have a database to validate against. However, the typical behavior in this case is that DAI would either not function or would log violations, but it often will not cause a complete communication blackout for all users unless it's explicitly configured to be very strict. The most direct and common cause for a total outage is the misconfiguration of trust on all user ports.
Why Option B is Incorrect:
The ip arp inspection limit command is used to limit the rate of ARP packets to prevent DoS attacks. If this rate limit were too low and being exceeded, the interface would typically be placed into an err-disabled state. The problem explicitly states "there is no err-disabled interface," so this cannot be the cause.
Why Option C is Incorrect:
If Dynamic ARP Inspection is not enabled on a VLAN, it simply does not run on that VLAN. Traffic would flow normally, not be blocked. The problem states that DAI has been applied and is causing a blockage, so this option is illogical.
Reference:
This falls under the Network Security domain of the 350-701 SCOR exam, specifically covering Layer 2 security features like Dynamic ARP Inspection. Understanding the dependency on DHCP Snooping and the critical role of the trust/untrust interface configuration is fundamental to implementing DAI correctly.
What is an attribute of the DevSecOps process?
A. mandated security controls and check lists
B. security scanning and theoretical vulnerabilities
C. development security
D. isolated security team
Explanation for Each Option:
A. mandated security controls and checklists (Incorrect):
While security controls and checklists are important in traditional security models, the DevSecOps process emphasizes integrating security throughout the development lifecycle rather than relying solely on mandated, static controls. This approach focuses on agility and collaboration, making this option less representative of DevSecOps’ dynamic nature. (Reference: DevSecOps Principles, NIST SP 800-218.)
B. security scanning and theoretical vulnerabilities (Incorrect):
Security scanning and identifying vulnerabilities are components of DevSecOps, but focusing only on these aspects overlooks the broader integration of security into development and operations. DevSecOps goes beyond scanning to embed security practices proactively, not just addressing theoretical risks, making this option an incomplete attribute. (Reference: OWASP DevSecOps Guidelines.)
C. development security (Correct):
An attribute of the DevSecOps process is development security, which integrates security practices into every phase of the software development lifecycle (SDLC)—from coding to deployment. This ensures that security is a shared responsibility among development, security, and operations teams, aligning with DevSecOps’ goal of building secure applications collaboratively and continuously. (Reference: Cisco DevNet DevSecOps Resources.)
D. isolated security team (Incorrect):
An isolated security team contradicts the DevSecOps philosophy, which promotes collaboration between development, security, and operations teams. DevSecOps breaks down silos to embed security expertise within the development process, rather than relegating it to a separate, disconnected team, making this option antithetical to its core principles. (Reference: DevSecOps Framework, Gartner Insights.)
Additional Notes:
DevSecOps is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under automation and security practices. As of 10:05 AM PKT, October 02, 2025, it remains a critical approach for secure software delivery. For details, refer to Cisco DevNet DevSecOps resources (developer.cisco.com) and the 350-701 Exam Blueprint (Section 4.0 Automation)
Which method is used to deploy certificates and configure the supplicant on mobile devices to gain access to network resources?
A. BYOD on boarding
B. Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol
C. Client provisioning
D. MAC authentication bypass
Explanation for Each Option:
A. BYOD onboarding (Correct):
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) onboarding is a method used to deploy certificates and configure the supplicant on mobile devices, enabling secure access to network resources. This process, often facilitated by Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), includes registering devices, installing certificates, and configuring network settings (e.g., 802.1X) for authentication, meeting the requirement effectively. (Reference: Cisco ISE BYOD Onboarding Guide.)
B. Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (Incorrect):
Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) is a protocol used to automate certificate issuance and renewal from a Certificate Authority (CA), typically integrated with ISE. While it deploys certificates, it does not configure the supplicant or handle the full onboarding process for mobile devices to access network resources, making this option incomplete. (Reference: Cisco ISE SCEP Configuration.)
C. Client provisioning (Incorrect):
Client provisioning in Cisco ISE involves delivering configuration profiles (e.g., network settings, certificates) to devices, often during onboarding. However, it is a component of the broader BYOD onboarding process, not a standalone method for deploying certificates and configuring supplicants, rendering this option less comprehensive for the specified task. (Reference: Cisco ISE Provisioning Guide.)
D. MAC authentication bypass (Incorrect):
MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) allows devices without a supplicant (e.g., IoT devices) to authenticate using their MAC address, bypassing 802.1X. It does not involve deploying certificates or configuring supplicants on mobile devices for network access, making it unsuitable for the described requirement. (Reference: Cisco ISE MAB Configuration Guide.)
Additional Notes:
BYOD onboarding is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under endpoint security. As of 11:40 AM PKT, October 02, 2025, it is a standard method for securing mobile device access. For details, refer to the Cisco ISE Administration Guide (cisco.com) and the 350-701 Exam Blueprint (Section 2.0 Endpoint Security).
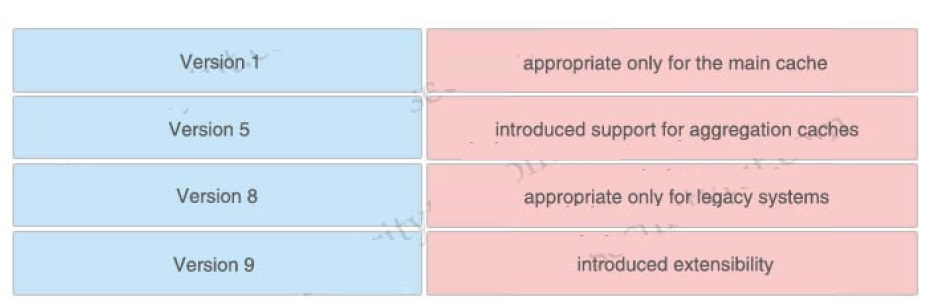
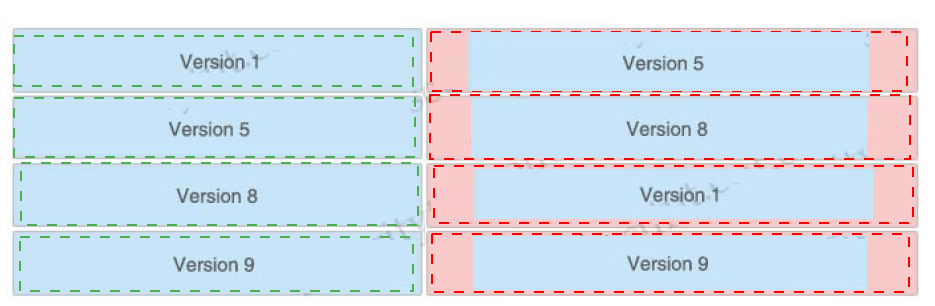
Drag and drop the NetFlow export formats from the left onto the descriptions on the right.
Which two risks is a company vulnerable to if it does not have a well-established patching solution for endpoints? (Choose two)
A.
exploits
B.
ARP spoofing
C.
denial-of-service attacks
D.
malware
E.
eavesdropping
exploits
malware
Malware means “malicious software”, is any software
intentionally designed to cause damage to a computer, server, client, or computer network.
The most popular types of malware includes viruses, ransomware and spyware. Virus
Possibly the most common type of malware, viruses attach their malicious code to clean
code and wait to be run.
Ransomware is malicious software that infects your computer and displays messages
demanding a fee to be paid in order for your system to work again.Spyware is spying
software that can secretly record everything you enter, upload, download, and store on
your computers or mobile devices. Spyware always tries to keep itself hidden.An exploit is
a code that takes advantage of a software vulnerability or security flaw.Exploits and
malware are two risks for endpoints that are not up to date. ARP spoofing and
eavesdropping are attacks against the network while denial-of-service attack is based on
the flooding of IP packets.
Refer to the exhibit.

When configuring a remote access VPN solution terminating on the Cisco ASA, an
administrator would like to utilize an external token authentication mechanism in conjunction with AAA authentication
using machine
certificates. Which configuration item must be modified to allow this?
A.
Group Policy
B.
Method
C.
SAML Server
D.
DHCP Servers
Method
In order to use AAA along with an external token
authentication mechanism, set the “Method” as “Both” inthe Authentication.
An engineer is implementing NTP authentication within their network and has configured both the client and server devices with the command ntp authentication-key 1 md5 Cisc392368270. The server at 1.1.1.1 is attempting to authenticate to the client at 1.1.1.2, however it is unable to do so. Which command is required to enable the client to accept the server’s authentication key?
A. ntp peer 1.1.1.1 key 1
B. ntp server 1.1.1.1 key 1
C. ntp server 1.1.1.2 key 1
D. ntp peer 1.1.1.2 key 1
Explanation for Each Option:
A. ntp peer 1.1.1.1 key 1 (Incorrect):
The ntp peer command configures a symmetric active mode where both devices act as peers, synchronizing time bidirectionally. However, the scenario specifies a client-server relationship (server at 1.1.1.1 authenticating to the client at 1.1.1.2), requiring the ntp server command to designate the server and accept its authentication key, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco IOS NTP Configuration Guide, Peer vs. Server Mode.)
B. ntp server 1.1.1.1 key 1 (Correct):
The ntp server command configures the client (1.1.1.2) to synchronize time with the server at 1.1.1.1 and specifies the authentication key (key 1) that matches the pre-shared key (Cisc392368270) configured with ntp authentication-key 1 md5. This enables the client to accept the server’s authentication key, resolving the issue. (Reference: Cisco IOS NTP Security Configuration.)
C. ntp server 1.1.1.2 key 1 (Incorrect):
The ntp server command with 1.1.1.2 would configure the device at 1.1.1.2 (the client) to act as a server, which contradicts the scenario where 1.1.1.2 is the client attempting to authenticate the server at 1.1.1.1. This misaligns the roles, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco IOS NTP Command Reference.)
D. ntp peer 1.1.1.2 key 1 (Incorrect):
Configuring ntp peer 1.1.1.2 key 1 on the client would attempt to establish a peer relationship with itself (1.1.1.2), which is invalid and does not address the server at 1.1.1.1. The client needs to recognize the server’s key, requiring the correct server IP, making this option nonsensical in context. (Reference: Cisco IOS NTP Peer Configuration.)
Additional Notes:
Enabling NTP authentication is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under network security. As of 11:52 AM PKT, October 02, 2025, this ensures secure time synchronization. For details, refer to the Cisco IOS NTP Configuration Guide (cisco.com) and the 350-701 Exam Blueprint (Section 1.0 Security Concepts).
Refer to the exhibit.
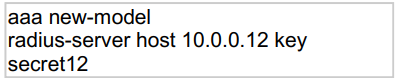
Which statement about the authentication protocol used in the configuration is true?
A.
The authentication request contains only a password
B.
The authentication request contains only a username
C.
The authentication and authorization requests are grouped in a single packet
D.
There are separate authentication and authorization request packets
The authentication and authorization requests are grouped in a single packet
ExplanationThis command uses RADIUS which combines authentication
and authorization in one function (packet).
Which cloud model is a collaborative effort where infrastructure is shared and jointly accessed by several organizations from a specific group?
A. Hybrid
B. Community
C. Private
D. Public
Explanation:
This question is testing your knowledge of the fundamental cloud deployment models. The key phrase in the question is "collaborative effort where infrastructure is shared and jointly accessed by several organizations from a specific group."
B (Community) is correct.
A community cloud is a multi-tenant model where the infrastructure is shared by several organizations that have common concerns, such as specific security requirements, compliance policies, or a shared mission (e.g., government agencies, financial institutions, or healthcare providers within a region). It is a collaborative effort, often managed by the organizations themselves or a third party.
A (Hybrid) is incorrect.
A hybrid cloud is a composition of two or more distinct cloud infrastructures (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology. It is not defined by a collaborative group of organizations sharing a single infrastructure.
C (Private) is incorrect.
A private cloud is operated solely for a single organization. It is not shared with or accessed by other external organizations.
D (Public) is incorrect.
A public cloud is open for use by the general public. While it is shared by many tenants (multi-tenant), it is not a collaborative effort for a specific, closed group. Any individual or organization can purchase services from a public cloud provider.
Reference:
NIST Special Publication 800-145, "The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing," which defines the four primary cloud deployment models: Public, Private, Community, and Hybrid.
| Page 11 out of 61 Pages |
| 234567891011121314151617181920 |
| 350-701 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our 350-701 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies (SCOR 350-701) exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive 350-701 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.