Topic 2: Exam Pool B
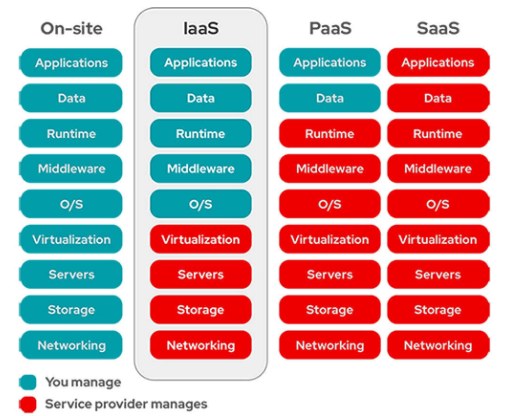
Which two aspects of the cloud PaaS model are managed by the customer but not the
provider? (Choose two)
A.
virtualization
B.
middleware
C.
operating systems
D.
applications
E.
data
applications
data
Customers must manage applications and data in PaaS.
Which type of attack is social engineering?
A.
trojan
B.
phishing
C.
malware
D.
MITM
phishing
Phishing is a form of social engineering. Phishing attacks use
email or malicious web sites to solicit personal,often financial, information. Attackers may send email seemingly from a reputable credit card company orfinancial institution that requests account information, often suggesting that there is a problem.
An organization has a Cisco ESA set up with policies and would like to customize the action assigned for violations. The organization wants a copy of the message to be delivered with a message added to flag it as a DLP violation. Which actions must be performed in order to provide this capability?
A. deliver and send copies to other recipients
B. quarantine and send a DLP violation notification
C. quarantine and alter the subject header with a DLP violation
D. deliver and add disclaimer text
Explanation for Each Option:
A. deliver and send copies to other recipients (Incorrect):
This action allows the original message to be delivered to the intended recipient while sending copies to additional addresses (e.g., for archiving or notification). However, it does not add a message to flag the email as a DLP (Data Loss Prevention) violation, only duplicates the email, making this option insufficient for the requirement. (Reference: Cisco ESA Mail Policies Guide, Copy Actions.)
B. quarantine and send a DLP violation notification (Incorrect):
Quarantining the message holds it for review and can send a notification to an administrator or user, but it does not deliver the message with a flag indicating a DLP violation. The requirement specifies delivering a copy with added text, not just notifying or holding the email, rendering this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco ESA Quarantine Configuration.)
C. quarantine and alter the subject header with a DLP violation (Incorrect):
Altering the subject header with a DLP violation flag is possible, and quarantining holds the message, but this does not meet the requirement to deliver the message with added text. The organization wants the message delivered, not quarantined, making this option misaligned with the desired outcome. (Reference: Cisco ESA Subject Modification Guide.)
D. deliver and add disclaimer text (Correct):
The "deliver and add disclaimer text" action in Cisco ESA allows the original message to be delivered to the recipient while appending custom text (e.g., a DLP violation flag) to the email body. This meets the requirement to deliver a copy with a message added to indicate a DLP violation, providing the desired customization. (Reference: Cisco ESA Disclaimer and Delivery Actions.)
Additional Notes:
Customizing ESA actions for DLP is a key topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under content security. As of 11:25 AM PKT, October 03, 2025, this capability enhances compliance.
In which type of attack does the attacker insert their machine between two hosts that are communicating with each other?
A. LDAP injection
B. man-in-the-middle
C. cross-site scripting
D. insecure API
Detailed Explanation:
This question describes a fundamental network security attack based on interception and potential alteration of communication.
Let's break down each option:
Why Option B is Correct:
A Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack occurs when an attacker secretly positions themself between two communicating parties (e.g., a user and a web server). The attacker can then intercept, relay, and even alter the communication without either victim knowing that the connection has been compromised. From the victims' perspective, they appear to be communicating directly with each other. The attacker's machine acts as an unauthorized, invisible relay or proxy.
Why Option A is Incorrect:
An LDAP Injection attack is a type of code injection that targets web applications. An attacker exploits vulnerabilities in an application that constructs LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) statements from user input. By sending manipulated input, the attacker can modify LDAP statements to bypass security, alter directory content, or execute unauthorized queries. This does not involve inserting a machine between two communicating hosts; it exploits an application's backend logic.
Why Option C is Incorrect:
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is an application-layer attack that targets the users of a web application, not the network path between hosts. In an XSS attack, an attacker injects malicious client-side scripts (usually JavaScript) into a trusted website. When other users view the infected web page, the malicious script executes in their browser, allowing the attacker to steal cookies, session tokens, or deface the website. The communication channel itself is not intercepted.
Why Option D is Incorrect:
An Insecure API refers to a vulnerability in the design or implementation of an Application Programming Interface (API). Attackers can exploit these weaknesses (e.g., broken authentication, excessive data exposure, lack of rate limiting) to gain unauthorized access to data or functionality. While an attacker might communicate directly with an insecure API, this is not the same as secretly interposing themselves between two other communicating hosts on the network.
Reference:
This question falls under the Security Concepts domain of the 350-701 SCOR exam, specifically covering common threats and vulnerabilities. Understanding the mechanics of a Man-in-the-Middle attack is crucial, as it is a foundational technique used in many other complex attacks. Common examples include ARP spoofing on a LAN and DNS spoofing on the internet.
The main function of northbound APIs in the SDN architecture is to enable communication between which two areas of a network?
A.
SDN controller and the cloud
B.
management console and the SDN controller
C.
management console and the cloud
D.
SDN controller and the management solution
SDN controller and the management solution
How does Cisco Advanced Phishing Protection protect users?
A.
It validates the sender by using DKIM
B.
It determines which identities are perceived by the sender
C.
It utilizes sensors that send messages securely
D.
It uses machine learning and real-time behavior analytics.
It uses machine learning and real-time behavior analytics.
An organization received a large amount of SPAM messages over a short time period. In order to take action on the messages, it must be determined how harmful the messages are and this needs to happen dynamically. What must be configured to accomplish this?
A. Configure the Cisco WSA to modify policies based on the traffic seen
B. Configure the Cisco ESA to receive real-time updates from Talos
C. Configure the Cisco WSA to receive real-time updates from Talos
D. Configure the Cisco ESA to modify policies based on the traffic seen
Explanation:
A phishing attack is a type of social engineering attack where the attacker's goal is to trick a person into performing an action or revealing sensitive information.
D. endpoint:
In the context of a phishing attack, the "endpoint" is the user and their device (laptop, desktop, phone). The attacker sends a deceptive email or message designed to manipulate the human target into:
Clicking a malicious link.
Opening a malicious attachment.
Entering credentials into a fake login page.
The ultimate target is the human element behind the endpoint, and the compromise happens on the endpoint device itself (e.g., malware execution, credential theft).
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. perimeter firewall:
While attackers may try to evade the firewall to deliver the phishing email, the firewall itself is not the target of manipulation in a phishing attack. The attacker's goal is to get past it, not to compromise it.
B. IPS (Intrusion Prevention System):
Similar to the firewall, the IPS is a defensive control that the attacker hopes to bypass. The phishing payload is not designed to attack the IPS directly.
C. web server:
In a phishing campaign, an attacker may compromise a web server to host a fake login page, making that server a tool in the attack. However, the primary target of the phishing attack is still the end-user who is tricked into visiting that server. The server is a means to an end, not the end itself.
Reference:
The definition of phishing consistently identifies the human user as the target.
As defined by security organizations like CISA, "Phishing is an attempt by an individual or group to solicit personal information from unsuspecting users by employing social engineering techniques." This clearly identifies the "users"—who operate endpoints—as the target.
Which policy is used to capture host information on the Cisco Firepower Next Generation Intrusion Prevention System?
A. Correlation
B. Intrusion
C. Access Control
D. Network Discovery
Explanation:
The Cisco Firepower NGIPS does more than just block threats; it is also a powerful network visibility and discovery tool. The policy specifically designed to gather and catalog information about hosts on the network is the Network Discovery policy.
Let's break down the role of each policy:
D) Network Discovery is CORRECT.
The Network Discovery policy is used to passively and actively discover hosts, operating systems, applications, and open services on your network. It uses various methods to capture host information, including:
Analyzing NetFlow data.
Performing passive OS fingerprinting.
Sending out active probes (if configured).
Listening to network traffic to identify hosts and the services they are running.
This collected host data populates the Hosts table in the FMC and is used for creating more targeted and effective intrusion and access control policies.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A) Correlation is INCORRECT.
Correlation policies are used to define automated responses to specific event patterns. For example, you can create a correlation rule that triggers an alert if a single host triggers ten different critical intrusions within one minute. It is an event-based analysis and response tool, not a host information gathering tool.
B) Intrusion is INCORRECT.
The Intrusion Policy is the core of the NGIPS. It is where you manage Snort rules to detect and prevent known vulnerability exploits, malware activity, and other malicious traffic. It uses the information gathered by the Network Discovery policy to be more effective, but its primary function is threat detection/prevention, not host discovery.
C) Access Control is INCORRECT.
The Access Control Policy is the main policy applied to traffic. It contains the ordered list of rules that determine whether to allow, block, or inspect traffic. It is the master policy that can invoke Intrusion, Network Discovery, and other policies, but it does not itself capture the host information.
Reference:
Cisco Firepower Management Center Configuration Guide, "Network Discovery Policies": The official documentation states, "Use network discovery policies to discover the hosts, operating systems, applications, and open services on your network."
Firepower System Overview: The architecture clearly separates the functions: Network Discovery handles host and application visibility, which then informs the enforcement actions taken by the Access Control and Intrusion policies.
What are two benefits of Flexible NetFlow records? (Choose two)
A. They allow the user to configure flow information to perform customized traffic
identification
B. They provide attack prevention by dropping the traffic
C. They provide accounting and billing enhancements
D. They converge multiple accounting technologies into one accounting mechanism
E. They provide monitoring of a wider range of IP packet information from Layer 2 to 4
Explanation for Each Option:
A. They allow the user to configure flow information to perform customized traffic identification (Correct):
Flexible NetFlow enables users to define custom flow records by selecting specific fields (e.g., IP addresses, ports, protocols) to monitor and analyze traffic. This customization supports tailored traffic identification for specific needs, such as detecting anomalies or optimizing network performance, making it a key benefit of the technology. (Reference: Cisco NetFlow Configuration Guide, Flexible NetFlow.)
B. They provide attack prevention by dropping the traffic (Incorrect):
Flexible NetFlow is designed for traffic monitoring, analysis, and accounting, not for active attack prevention or traffic dropping. Security features like packet dropping are handled by firewalls or intrusion prevention systems, not NetFlow, which focuses on collecting and reporting data, making this option incorrect. (Reference: Cisco Secure Firewall Overview.)
C. They provide accounting and billing enhancements (Incorrect):
While Flexible NetFlow can support accounting by tracking traffic usage, this is a secondary benefit derived from its data collection capabilities. It does not inherently enhance billing processes; that requires integration with billing systems. This option overstates its primary purpose, making it less accurate than the correct choices. (Reference: Cisco NetFlow Accounting Applications.) (61 words)
D. They converge multiple accounting technologies into one accounting mechanism (Correct):
Flexible NetFlow consolidates various legacy accounting methods (e.g., NetFlow v5, v9) into a single, flexible framework. This unification allows organizations to streamline traffic accounting across different network devices and protocols, reducing complexity and improving efficiency, which is a significant advantage of its design. (Reference: Cisco Flexible NetFlow White Paper.)
E. They provide monitoring of a wider range of IP packet information from Layer 2 to 4 (Incorrect):
Although Flexible NetFlow can monitor a broad range of packet data (e.g., Layer 3 and 4 fields like IP and TCP/UDP headers), it is not designed to extend to Layer 2 details (e.g., MAC addresses) in a comprehensive way. Its focus is on customizable flow data, not wide-layer monitoring, making this option overstated. (Reference: Cisco NetFlow Feature Overview.)
Additional Notes:
Flexible NetFlow, a topic in the 350-701 SCOR exam under network monitoring, enhances visibility and accounting. As of 05:03 PM PKT, October 01, 2025, it remains a vital tool for network management. For details, refer to the Cisco NetFlow Configuration Guide (cisco.com) and the 350-701 Exam Blueprint (Section 1.0 Security Concepts).
Which component of Cisco umbrella architecture increases reliability of the service?
A.
Anycast IP
B.
AMP Threat grid
C.
Cisco Talos
D.
BGP route reflector
Cisco Talos
Which CLI command is used to register a Cisco FirePower sensor to Firepower Management Center?
A. configure system add
B. configure manager
C. configure manager delete
D. configure manager add
Explanation
This command is the exact syntax used on a Cisco Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) sensor, or any Firepower module, to initiate the registration process with a Firepower Management Center (FMC).
configure manager:
This is the base command that enters the configuration mode for managing the connection to the FMC.
add:
This sub-command specifies that you are adding a new manager.
This is a placeholder for the IP address or hostname of the FMC to which you want to register the sensor.
This is a placeholder for the unique registration key that must be pre-configured on the FMC. This key acts as a shared secret to authenticate the sensor during the registration process. It ensures that only authorized devices can register to the management center.
The Process Flow:
An administrator generates a unique registration key on the FMC for a specific sensor.
The administrator logs into the CLI of the Firepower sensor (FTD device).
The command configure manager add
The sensor uses this information to contact the FMC, authenticate itself using the key, and establish a secure communication channel.
The sensor then appears in the FMC web interface as a pending device, ready to be deployed with policies.
Detailed Breakdown of Incorrect Options:
A. configure system add
Why it is incorrect:
This command uses an invalid syntax and context. The configure system command family is typically used for basic system configurations like setting the hostname, timezone, or DNS servers, not for manager registration. The keyword manager is crucial and missing here. The Firepower OS does not recognize configure system add as a valid command for this purpose.
B. configure manager
Why it is incorrect:
This command has the correct verb (configure manager) but the order of the parameters is wrong. The syntax is very specific: the add keyword must come immediately after configure manager, followed by the host, and then the key. Placing the
C. configure manager delete
Why it is incorrect:
This command is a valid command, but it performs the exact opposite action. It is used to unregister the sensor from its current FMC, not to register it. If you run this command on a managed sensor, it will sever its connection with the management center. While it is a real command, its function is the reverse of what the question asks.
Reference:
Cisco Official Documentation:
The command is documented in the Cisco Firepower Threat Defense Command Reference guide. Searching for "configure manager add" will lead you to the exact syntax and usage.
Cisco FMC Configuration Guide:
The process of registering devices using the CLI is a standard procedure outlined in the "Add Devices" section of the Firepower Management Center configuration guide.
Key Takeaway:
The correct command is a logical sequence: configure the manager, add it, specify where (
What is the purpose of the certificate signing request when adding a new certificate for a
server?
A.
It is the password for the certificate that is needed to install it with
B.
It provides the server information so a certificate can be created and signed
C.
It provides the certificate client information so the server can authenticate against it
when installing
D.
It is the certificate that will be loaded onto the server
It provides the server information so a certificate can be created and signed
A certificate signing request (CSR) is one of the
first steps towards getting your own SSL Certificate. Generated on the same server you
plan to install the certificate on, the CSR contains information (e.g. common name,
organization, country) that the Certificate Authority (CA) will use to create your certificate. It
also contains the public key that will be included in your certificate and is signed with the
corresponding private key.
| Page 10 out of 61 Pages |
| 12345678910111213141516171819 |
| 350-701 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our 350-701 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies (SCOR 350-701) exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive 350-701 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.