An analyst received a ticket regarding a degraded processing capability for one of the HR
department's servers. On the same day, an engineer noticed a disabled antivirus software
and was not able to determine when or why it occurred. According to the NIST Incident
Handling Guide, what is the next phase of this investigation?
A.
Recovery
B.
Detection
C.
Eradication
D.
Analysis
Detection
Which event is a vishing attack?
A. obtaining disposed documents from an organization
B. using a vulnerability scanner on a corporate network
C. setting up a rogue access point near a public hotspot
D. impersonating a tech support agent during a phone call
Explanation: Vishing is an attack where fraudsters impersonate legitimate entities via phone calls to deceive individuals into providing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
Refer to the exhibit.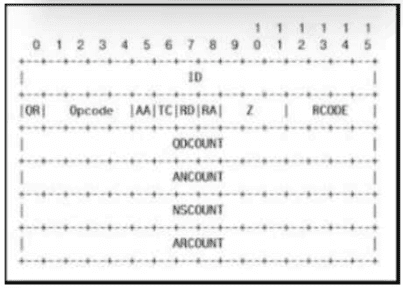
Which field contains DNS header information if the payload is a query or a response?
A. Z
B. ID
C. TC
D. QR
Explanation: The QR field in the DNS header specifies whether the message is a query (QR=0) or a response (QR=1). This bit is set to 0 for query messages and is set to 1 for response messages, allowing the recipient to distinguish between the two.
A security engineer must protect the company from known issues that trigger adware. Recently new incident has been raised that could harm the system. Which security concepts are present in this scenario?
A. exploit and patching
B. risk and evidence
C. analysis and remediation
D. vulnerability and threat
Explanation:
Which items is an end-point application greylist used?
A. Items that have been established as malicious
B. Items that have been established as authorized
C. Items that have been installed with a baseline
D. Items before being established as harmful or malicious
Explanation:
A greylist in endpoint applications refers to a list of items that are not yet classified
as either good (whitelisted) or bad (blacklisted).
The primary function of a greylist is to hold applications, processes, or files that are
under observation due to their unknown status.
These items are neither trusted nor immediately flagged as harmful, allowing
security teams to monitor them closely for any suspicious behavior.
By placing items on a greylist, security operations can prevent potential threats
without disrupting legitimate processes, awaiting further analysis to determine their
true nature.
An employee reports that someone has logged into their system and made unapproved changes, files are out of order, and several documents have been placed in the recycle bin. The security specialist reviewed the system logs, found nothing suspicious, and was not able to determine what occurred. The software is up to date; there are no alerts from antivirus and no failed login attempts. What is causing the lack of data visibility needed to detect the attack?
A. The threat actor used a dictionary-based password attack to obtain credentials.
B. The threat actor gained access to the system by known credentials.
C. The threat actor used the teardrop technique to confuse and crash login services.
D. The threat actor used an unknown vulnerability of the operating system that went undetected.
Explanation: The lack of data visibility needed to detect the attack is caused by the threat actor gaining access to the system by known credentials. This means that the threat actor either obtained the employee’s username and password through phishing, social engineering, or other means, or used a compromised account that had legitimate access to the system. This would explain why there were no suspicious logs, alerts, or failed login attempts, as the threat actor appeared to be a normal user.
What is sliding window anomaly detection?
A. Detect changes in operations and management processes.
B. Identify uncommon patterns that do not fit usual behavior.
C. Define response times for requests for owned applications.
D. Apply lowest privilege/permission level to software
Explanation: Sliding window anomaly detection is a technique used in cybersecurity to identify unusual patterns or behaviors that deviate from the norm. It involves analyzing segments of data over a period of time, referred to as a ‘window,’ and comparing them against typical patterns. Anomalies are detected when observed behaviors significantly differ from expected patterns, indicating potential security incidents or issues that require further investigation.
How does agentless monitoring differ from agent-based monitoring?
A. Agentless can access the data via API. While agent-base uses a less efficient method and accesses log data through WMI.
B. Agent-based monitoring is less intrusive in gathering log data, while agentless requires open ports to fetch the logs
C. Agent-based monitoring has a lower initial cost for deployment, while agentless monitoring requires resource-intensive deployment.
D. Agent-based has a possibility to locally filter and transmit only valuable data, while agentless has much higher network utilization
Explanation:
What describes the impact of false-positive alerts compared to false-negative alerts?
A. A false negative is alerting for an XSS attack. An engineer investigates the alert and discovers that an XSS attack happened A false positive is when an XSS attack happens and no alert is raised
B. A false negative is a legitimate attack triggering a brute-force alert. An engineer investigates the alert and finds out someone intended to break into the system A false positive is when no alert and no attack is occurring
C. A false positive is an event alerting for a brute-force attack An engineer investigates the alert and discovers that a legitimate user entered the wrong credential several times A false negative is when a threat actor tries to brute-force attack a system and no alert is raised.
D. A false positive is an event alerting for an SQL injection attack An engineer investigates the alert and discovers that an attack attempt was blocked by IPS A false negative is when the attack gets detected but succeeds and results in a breach.
Explanation: False positives and false negatives are terms used to describe the accuracy
of security alerts. A false positive occurs when a security system incorrectly identifies
benign activity as malicious, leading to unnecessary investigation and potential disruption
of legitimate activities. Conversely, a false negative happens when a security system fails
to detect actual malicious activity, allowing the attackers to proceed undetected. The
impact of false positives is generally wasted time and resources investigating non-issues,
while the impact of false negatives can be much more severe, potentially leading to
undetected breaches and significant damage.
The CBROPS curriculum covers the concepts of false positives and false negatives in the
context of security monitoring and alerting systems
An analyst see that this security alert "Default-Botnet-Communication-Detection-By- Endpoint" has been raised from the IPS. The analyst checks and finds that an endpoint communicates to the C&C. How must an impact from this event be categorized?
A. true positive
B. true negative
C. false positive
D. false negative
Which type of verification consists of using tools to compute the message digest of the original and copied data, then comparing the similarity of the digests?
A. evidence collection order
B. data integrity
C. data preservation
D. volatile data collection
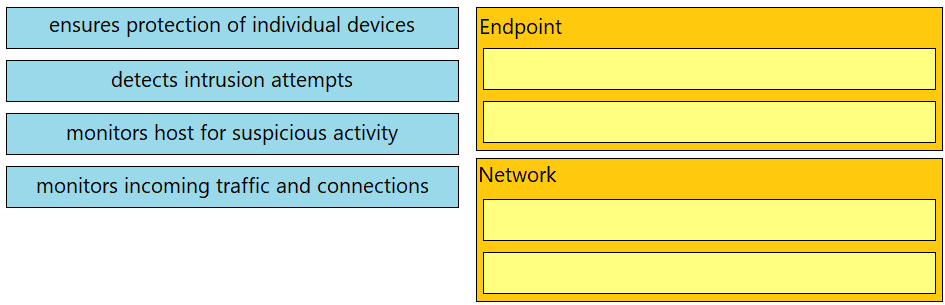
Drag and drop the uses on the left onto the type of security system on the right.
| Page 14 out of 34 Pages |
| 910111213141516171819 |
| 200-201 Practice Test Home |
Real-World Scenario Mastery: Our 200-201 practice exam don't just test definitions. They present you with the same complex, scenario-based problems you'll encounter on the actual exam.
Strategic Weakness Identification: Each practice session reveals exactly where you stand. Discover which domains need more attention, before Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS) exam day arrives.
Confidence Through Familiarity: There's no substitute for knowing what to expect. When you've worked through our comprehensive 200-201 practice exam questions pool covering all topics, the real exam feels like just another practice session.